Mind Mapping Techniques for Accelerated Learning
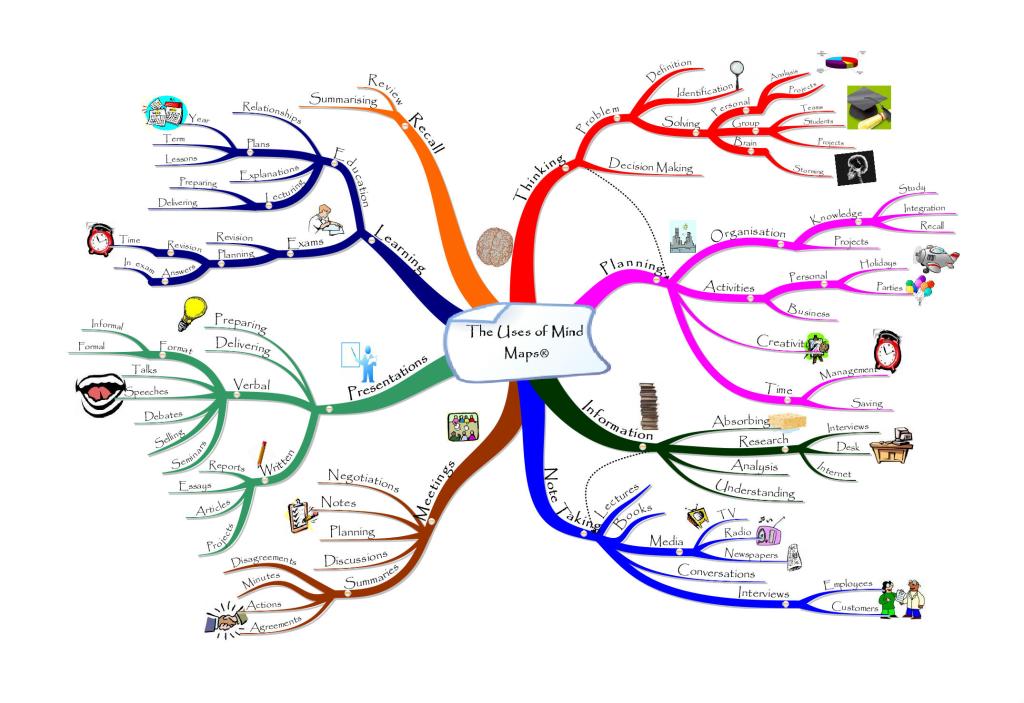
Alternative education approaches often focus on creating an engaging and interactive learning environment that caters to the unique needs and interests of students. One technique that has gained popularity in recent years is mind mapping. Mind maps are visual representations of information, allowing learners to organize their thoughts, make connections between ideas, and improve comprehension.
To create a mind map, start by placing a central idea or topic at the center of a blank page or digital canvas. From there, branch out into subtopics or related concepts using lines or branches. Each subtopic can then be further expanded upon with additional branches, creating a hierarchical structure that visually represents the relationships between different ideas.
One of the key benefits of mind mapping is its ability to stimulate both hemispheres of the brain. The left hemisphere is responsible for logical thinking and analysis, while the right hemisphere is associated with creativity and visual processing. By incorporating words, images, colors, and symbols into their mind maps, alternative learners can engage both sides of their brain simultaneously.
In addition to enhancing creativity and critical thinking skills, mind mapping also helps with memory retention. Research has shown that when information is presented in a visual format like a mind map, it becomes easier for the brain to encode and retrieve later on. This makes mind maps particularly effective for studying complex subjects or preparing for exams.
Gamification in Alternative Education
Gamification refers to incorporating elements from games into educational activities to enhance engagement and motivation among students. In alternative education settings where traditional teaching methods may not resonate with all learners, gamification offers an exciting approach to foster active participation.
One way gamification can be applied is through the use of educational apps or online platforms designed specifically for alternative schooling environments. These platforms often feature interactive quizzes, challenges with rewards systems (such as badges or points), and progress tracking tools which allow students to see their improvement over time.
The use of game-based learning also encourages collaboration and healthy competition. Students can work together to solve problems or engage in friendly competitions, fostering a sense of teamwork and camaraderie. This not only enhances social skills but also motivates students to actively participate in their own learning process.
Furthermore, gamification can help alternative learners develop important life skills such as problem-solving, decision-making, and perseverance. Through immersive game experiences, students are presented with challenges that require them to think critically and strategize effectively. They learn the value of persistence when faced with setbacks or obstacles within the game environment.
Neuroplasticity and Its Role in Accelerated Learning
Neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. This concept has significant implications for accelerated learning in alternative education settings.
Traditionally, it was believed that the brain’s capacity for learning diminished after childhood. However, research on neuroplasticity has shown that this is not the case. The human brain remains adaptable throughout life, allowing individuals to acquire new knowledge and skills at any age.
In alternative schooling environments where personalized instruction is emphasized, understanding neuroplasticity becomes even more crucial. By recognizing that every student’s brain has the potential for growth and change, educators can tailor their teaching methods accordingly.
One way to harness neuroplasticity for accelerated learning is through deliberate practice. Deliberate practice refers to focused and intentional practice aimed at improving specific skills or areas of knowledge. By engaging in targeted activities that challenge students’ abilities within their zone of proximal development (the range between what they already know and what they are capable of), alternative learners can strengthen neural connections associated with those skills or knowledge areas.
Additionally, providing feedback is essential when leveraging neuroplasticity for accelerated learning. Constructive feedback helps students identify areas where improvement is needed while reinforcing existing neural pathways associated with correct responses or actions.
The Impact of Music on Memory and Learning
The power of music to enhance memory and learning has been recognized for centuries. In alternative education, where creativity and individualized approaches are valued, incorporating music into the curriculum can have numerous benefits.
Research suggests that listening to certain types of music, particularly classical or instrumental pieces, can improve cognitive functions such as memory retention and information processing. The Mozart Effect is a popular theory that proposes listening to Mozart’s compositions enhances spatial-temporal reasoning skills. While the direct impact on intelligence remains debated among experts, there is evidence supporting the positive influence of music on learning abilities.
Music also has a unique ability to evoke emotions and create associations in our minds. When students associate specific information with particular melodies or rhythms, it becomes easier for them to recall that information later on. This technique is known as mnemonic association.
Furthermore, actively engaging with music through playing an instrument or singing can help develop coordination skills, concentration abilities, and discipline – all of which are valuable attributes for accelerated learning.
Visualization Techniques for Enhanced Comprehension
In alternative schooling settings where diverse learners may have varying strengths and preferences in their approach to learning, visualization techniques offer an effective way to enhance comprehension.
Visualization involves creating mental images or representations of information being learned. By visualizing concepts or ideas in their mind’s eye, students can deepen their understanding by connecting abstract concepts with concrete images.
One popular visualization technique is “mental movies.” Students imagine themselves watching a movie where they play the main character interacting with different elements related to the topic at hand. This technique helps activate multiple senses (visualizing scenes while mentally hearing sounds or feeling sensations) which aids in encoding information more effectively.
Another visualization strategy is concept mapping. Similar to mind mapping but focused on visual representation rather than hierarchical organization, concept maps allow learners to visually connect ideas using shapes and lines instead of words alone. This method encourages students to make connections between various concepts visually represented within the map.
Both mental movies and concept mapping can be particularly useful for alternative learners who may struggle with traditional text-based approaches. By engaging their visual and creative faculties, students can enhance comprehension and retain information more effectively.
Speed Reading Strategies for Alternative Learners
Speed reading is a technique that involves increasing reading speed while maintaining or improving comprehension. In alternative education settings where personalized learning is emphasized, speed reading strategies can help students process information more efficiently.
One of the fundamental principles of speed reading is reducing subvocalization – the habit of silently pronouncing each word while reading. Subvocalization slows down reading speed significantly as it limits the rate at which information is taken in by the brain.
Alternative learners can practice minimizing subvocalization through exercises such as “chunking.” Chunking involves grouping words together instead of processing them individually. This allows readers to take in larger chunks of text at once, leading to faster overall reading pace.
Another strategy for accelerated reading is using a pacer tool, such as a pen or finger, to guide eye movement across lines of text. The pacer helps maintain focus and prevents regression (re-reading previously read words) by keeping the eyes moving steadily forward.
In addition to these techniques, skimming and scanning are valuable skills for alternative learners aiming to quickly locate specific information within texts. Skimming involves rapidly glancing over a passage to get a general sense of its content, while scanning involves looking for specific keywords or phrases without thoroughly reading every word.
By practicing these speed-reading strategies regularly, alternative learners can not only save time but also improve their overall comprehension abilities by training their brains to process information more quickly and efficiently.
Multisensory Approaches to Accelerate Learning
Incorporating multiple senses into the learning process has been shown to enhance memory retention and engagement among students in alternative education settings. Multisensory approaches allow individuals with different learning styles or preferences (visual, auditory, kinesthetic) to access and process information effectively.
One multisensory technique commonly used is kinesthetic learning, which involves engaging the body’s sense of movement and physical touch. This approach can be particularly effective for alternative learners who may struggle with traditional sit-and-listen teaching methods.
Kinesthetic activities can include hands-on experiments, role-playing, or using manipulatives such as building blocks or models. By physically interacting with objects or performing actions related to a concept being learned, students solidify their understanding through direct experience.
Another multisensory approach is incorporating visual aids into lessons. Visual materials such as diagrams, charts, or infographics help reinforce key concepts by providing additional context and visual representation. Combining visuals with verbal explanations allows alternative learners to make connections between abstract ideas and concrete images.
Additionally, auditory learning can be enhanced by incorporating audio recordings or lectures into the curriculum. Alternative learners can also benefit from discussions or debates that encourage active listening and participation in group settings. By engaging both their auditory and verbal faculties simultaneously, students deepen their comprehension and retention of information.
By embracing multisensory approaches in alternative education settings, educators cater to diverse learning styles while fostering an inclusive environment where all students have opportunities for accelerated learning.
Mindfulness Practices for Improved Focus and Retention
Mindfulness practices involve intentionally focusing one’s attention on the present moment without judgment. In alternative education settings where individualized approaches are prioritized, mindfulness techniques offer valuable tools to enhance focus and retention among students.
Regular mindfulness practice has been shown to improve concentration abilities by training the brain to tune out distractions more effectively. Mindfulness meditation exercises typically involve focusing on the breath or bodily sensations while observing any thoughts that arise without getting caught up in them.
Alternative learners can incorporate mindfulness breaks throughout their day to reset their focus during study sessions or classroom activities. These breaks may involve short guided meditation sessions led by teachers or self-guided practices using apps designed specifically for mindfulness exercises.
Furthermore, mindfulness practices can improve memory retention by cultivating a state of relaxed awareness. When students are fully present and engaged with the material they are learning, their brains have an easier time encoding information into long-term memory.
Mindfulness techniques can also support emotional regulation and stress management in alternative education settings. By developing self-awareness and the ability to observe thoughts and emotions without judgment, students gain valuable tools for managing their own well-being, which ultimately enhances their ability to learn effectively.
The Role of Physical Activity in Accelerating Learning
Physical activity has numerous benefits for overall health and well-being. In alternative education settings, incorporating physical activity into the curriculum can significantly enhance learning outcomes.
Research has shown that exercise stimulates the release of neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, which play essential roles in mood regulation and cognitive function. Regular physical activity has been linked to improved attention span, memory retention, and problem-solving abilities – all crucial components of accelerated learning.
One way to integrate physical activity into alternative schooling is through movement breaks or active learning activities. These breaks allow students to engage in short bursts of exercise between study sessions or classroom activities. Simple exercises like stretching or jumping jacks can help increase blood flow to the brain and improve alertness.
In addition to brief movement breaks, some alternative schools have embraced more extensive physical education programs that incorporate sports or outdoor activities into the daily schedule. These programs not only provide opportunities for cardiovascular fitness but also foster teamwork skills, resilience, and goal-setting – all attributes that contribute to accelerated learning.
Alternative learners who struggle with traditional sedentary classroom environments may particularly benefit from physically active approaches to education. By giving students outlets for releasing excess energy while promoting healthy habits at a young age, educators create an environment conducive to optimal academic performance.
Memory Palaces and Memory Techniques in Alternative Education
Memory palaces (also known as method of loci) are mnemonic devices dating back thousands of years that involve associating information with specific locations within a familiar environment. In alternative education settings, memory techniques like memory palaces can enhance information retention and recall.
To create a memory palace, students choose a familiar location (such as their home or school) and mentally assign different pieces of information to various rooms or objects within that space. When they need to recall the information later on, they mentally navigate through their memory palace, retrieving the associated details as they move from one location to another.
The power of memory palaces lies in their ability to tap into the brain’s natural spatial awareness and visual processing capabilities. By creating vivid mental images that connect new information with pre-existing knowledge stored in long-term memory, alternative learners can strengthen neural connections associated with those concepts.
Other mnemonic devices commonly used in alternative education include acronyms (creating memorable words or phrases using the first letter of each item being memorized), visualization techniques (associating abstract ideas with concrete images), and rhymes or songs (creating rhythmic patterns that aid in remembering).
By providing students with tools like memory palaces and other mnemonic devices, educators empower them to take control of their own learning process by developing personalized methods for retaining important information. These techniques not only improve short-term recall but also contribute to long-term retention and retrieval.
Metacognition and Self-Regulated Learning in Alternative Schooling
Metacognition refers to the ability to think about one’s own thinking processes – reflecting on what we know, understanding how we learn best, and monitoring our own progress. Self-regulated learning is an essential aspect of metacognition that involves setting goals, planning strategies for achieving those goals, monitoring progress along the way, and making adjustments as needed.
In alternative schooling environments where personalized instruction is emphasized, metacognitive skills are crucial for accelerated learning. By developing metacognitive abilities among students, educators empower them to become active participants in their own educational journey.
One way to promote metacognition in alternative education is through regular reflection exercises. Alternative learners can be encouraged to pause and reflect on their learning experiences, asking questions such as: What strategies have been effective for me? How can I improve my study habits? What areas do I need to focus on?
Educators can also help students set realistic goals and develop action plans for achieving those goals. Breaking down larger tasks into smaller, manageable steps allows alternative learners to approach their work systematically and more effectively.
Furthermore, providing opportunities for self-assessment and peer feedback encourages metacognitive reflection. By evaluating their own work or engaging in constructive discussions with peers, students gain a deeper understanding of their strengths and areas needing improvement.
By nurturing metacognitive skills in alternative schooling settings, educators foster independent thinking, self-awareness, and a sense of ownership over the learning process. These attributes contribute to accelerated learning by enabling students to adapt their strategies based on individual needs and continuously refine their approach.
Creative Thinking Exercises to Enhance Learning Outcomes
In alternative education settings where creativity is valued as an essential skillset for success in the modern world, incorporating creative thinking exercises into the curriculum can significantly enhance learning outcomes.
One creative thinking exercise that stimulates divergent thinking is brainstorming. Alternative learners are encouraged to generate as many ideas as possible without judgment or criticism. This technique helps students think beyond conventional solutions or approaches by exploring various possibilities.
Another exercise is “forced connections.” Students are presented with unrelated objects or concepts and challenged to find connections between them. This exercise promotes associative thinking – making connections between seemingly disparate ideas – which enhances problem-solving abilities.
Alternative learners can also benefit from activities that encourage analogical thinking – finding similarities between different situations or problems. For example, presenting students with real-world scenarios from different domains (such as solving a mathematical equation using principles from music theory) challenges them to think creatively about how knowledge learned in one context can be applied elsewhere.
Additionally, incorporating activities that foster imagination and storytelling can enhance learning outcomes. Students can be encouraged to create narratives or role-play scenarios related to the subject matter being studied, allowing them to engage emotionally with the material and make personal connections.
By including creative thinking exercises in alternative education settings, educators nurture innovation, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills – all of which are essential for accelerated learning in a rapidly changing world.
Mnemonic Devices for Remembering Complex Information
In alternative education settings where students may encounter complex information or concepts, mnemonic devices offer effective strategies for memory retention and recall.
One commonly used mnemonic device is acronyms – creating memorable words or phrases using the first letter of each item being memorized. For example, to remember the order of operations in mathematics (parentheses, exponents, multiplication/division, addition/subtraction), students might use the acronym PEMDAS (Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally).
Another technique is creating vivid visual images associated with specific pieces of information. By associating abstract ideas with concrete images that evoke strong emotions or engage multiple senses, alternative learners can improve their ability to remember complex details.
The method of loci mentioned earlier as a memory palace technique is another powerful mnemonic device. By mentally navigating through familiar locations while associating specific information with different rooms or objects along the way, students enhance their recall abilities by tapping into spatial awareness and visual processing capabilities.
Wordplay techniques such as rhymes or songs also aid in remembering complex information. The rhythmic patterns created by rhymes help encode details into long-term memory more effectively while making the material more enjoyable to learn.
By providing alternative learners with a range of mnemonic devices suited to their individual preferences and learning styles, educators empower them to take charge of their own retention strategies. These techniques not only improve short-term recall but also contribute to long-term understanding and retrieval.
Using Technology Tools for Accelerated Learning in Alternative Schools
In today’s digital age, technology tools can play a significant role in accelerating learning outcomes in alternative education settings. By leveraging various educational apps and online platforms, alternative learners have access to interactive resources that cater to their individual needs.
One popular technology tool is the use of virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) applications. These immersive experiences allow students to explore subjects visually and interactively, enhancing their understanding by providing a three-dimensional perspective. For example, VR simulations can transport students to historical events or scientific environments for a more impactful learning experience.
Another useful technology tool is adaptive learning software. These programs use artificial intelligence algorithms to personalize instruction based on individual progress and needs. By analyzing students’ performance data and adapting content accordingly, these tools provide tailored support and challenges that match each student’s level of mastery.
Online collaboration platforms also facilitate communication and teamwork among alternative learners. These platforms enable students to work together on projects, share ideas, provide feedback, and collaborate with peers from different locations – all essential skills for success in the digital age.
Furthermore, video lectures or tutorials offer alternative learners the flexibility to review material at their own pace outside traditional classroom hours. Platforms like YouTube or Khan Academy provide free educational videos covering a wide range of topics suitable for self-paced learning.
By integrating appropriate technology tools into the curriculum of alternative schools, educators empower students with engaging resources that enhance comprehension, foster independent exploration, and promote accelerated learning in a digitally connected
Leave a comment