Response to intervention (RTI) is a multi-tiered approach used in education to identify students who are struggling academically and provide them with appropriate interventions. It aims to address students’ needs promptly and effectively, ensuring that they receive the support necessary to succeed in their academic journey. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of RTI and how it benefits both students and educators.
1. What is RTI?
RTI is an evidence-based framework designed to identify, monitor, and support struggling learners through a tiered system of interventions. It operates on the principle that early intervention can prevent long-term academic difficulties.
2. How does RTI work?
The process begins by screening all students to assess their skills in areas such as reading or math. Based on these assessments, students are placed into different tiers based on their level of need for additional support.
3. What are the tiers in RTI?
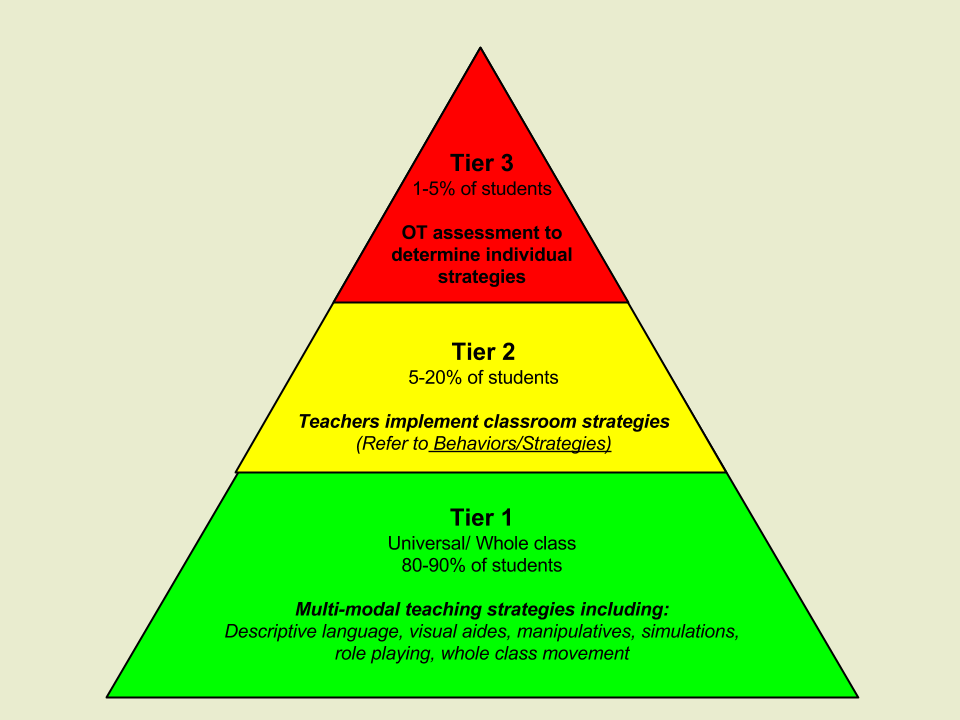
RTI typically consists of three tiers:
– Tier 1: Core instruction provided within the general education classroom setting.
– Tier 2: Targeted small-group interventions for students who require more focused support than what is available in Tier 1.
– Tier 3: Intensive individualized interventions for students who continue to struggle despite targeted Tier 2 intervention.
4. Who implements RTI?
RTI involves collaboration among various stakeholders, including teachers, administrators, special education professionals, and parents/guardians. This collaborative effort ensures that student progress is monitored consistently across different settings.
5. What are some advantages of using RTI?
Implementing RTI offers several benefits:
– Early identification of learning difficulties
– Tailored supports based on individual needs
– Reduced over-reliance on special education referrals
– Improved communication between teachers and other professionals involved
6. How does data play a role in RTI?
Data collection plays a crucial role at each tier of RTI. Teachers use ongoing assessments to monitor student progress, identify areas of need, and evaluate the effectiveness of interventions. This data-driven decision-making guides instructional planning and intervention strategies.
7. What types of interventions are used in RTI?
Interventions vary based on students’ specific needs but can include targeted instruction, adaptations to classroom materials or teaching methods, additional practice opportunities, and supplemental supports like tutoring or small-group instruction.
8. Is RTI only for academic struggles?
While RTI is primarily focused on addressing academic difficulties, it can also be adapted to support students with behavioral challenges or socio-emotional needs. By providing appropriate interventions in these areas, schools create a holistic approach to student support.
9. Can parents request RTI for their child?
Parents play an essential role in the RTI process. If they have concerns about their child’s progress, they should communicate with teachers or school administrators to discuss possible interventions and supports that could be implemented.
10. How does RTI impact special education services?
RTI is designed as a preventative measure that aims to reduce the number of unnecessary special education referrals by providing early intervention support at Tier 1 and Tier 2 levels. However, if a student continues to struggle despite intensive interventions at Tier 3, a referral for an evaluation for special education may be made.
11. Are there any potential challenges with implementing RTI?
Like any educational framework, implementing RTI comes with its own set of challenges such as ensuring consistent implementation across all tiers, adequate resources and training for educators involved in delivering interventions effectively.
12. How do schools ensure fidelity in implementing RTI?
To ensure fidelity in implementing RTI practices consistently throughout the school system:
– Schools provide professional development opportunities for teachers
– Consistent monitoring and review processes are established
– Collaboration between general education and special education staff is encouraged
In conclusion, Response to Intervention (RTI) is an evidence-based approach that helps identify and support struggling students in a timely manner. By providing tiered interventions tailored to individual needs, RTI aims to improve student outcomes and reduce the number of unnecessary special education referrals. Through collaboration among teachers, administrators, and parents/guardians, RTI ensures that all students receive the necessary support to succeed academically.
Leave a comment