Neurodiversity is a concept that acknowledges and celebrates the wide range of neurological differences among individuals. It encompasses conditions such as autism, ADHD, dyslexia, and more, recognizing them not as disorders but as natural variations in the human brain. In the realm of education, understanding and embracing neurodiversity can lead to more inclusive and effective teaching practices that cater to the unique needs of neurodivergent students.
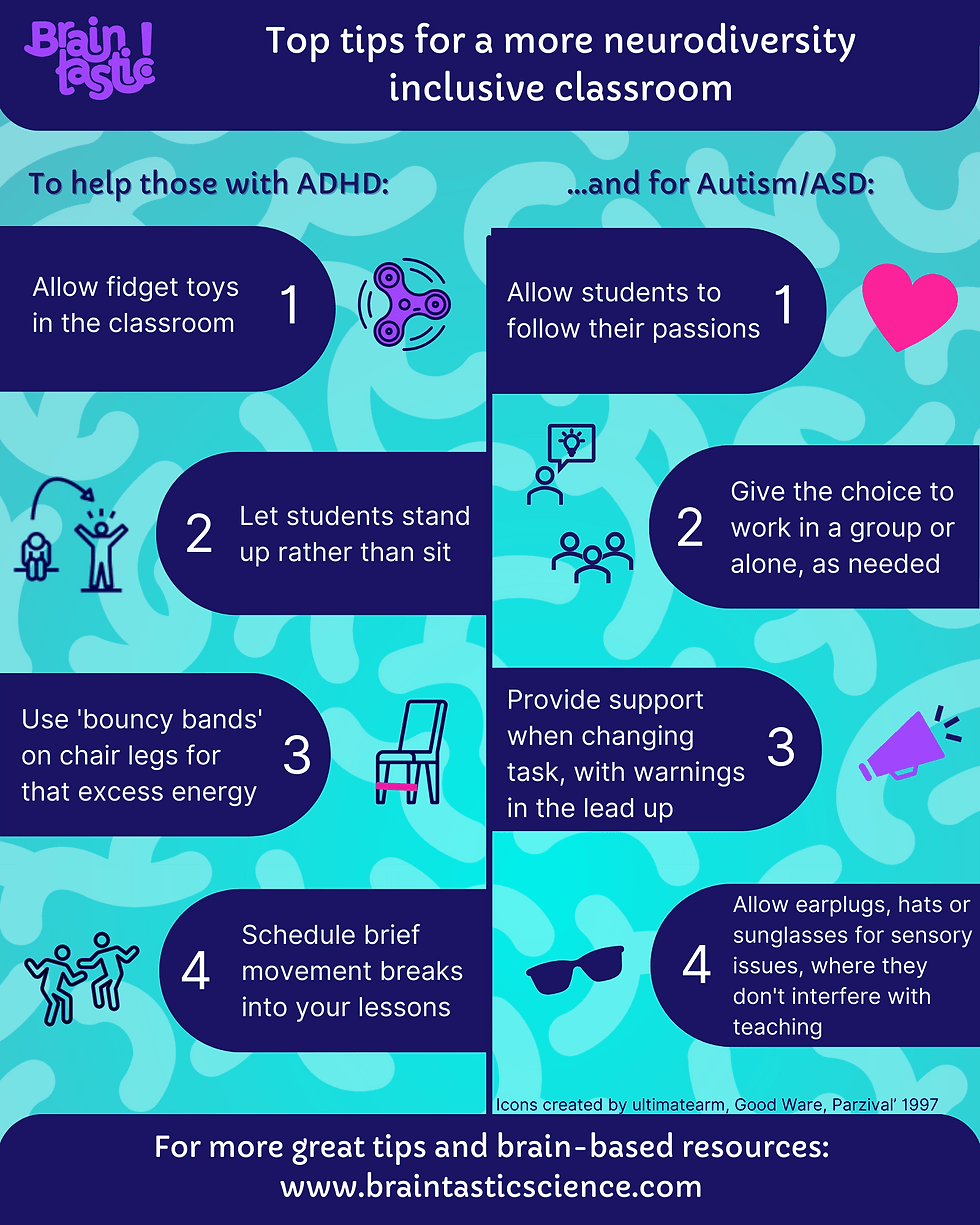
One key aspect of neurodiversity in education is sensory processing differences. Many neurodivergent individuals experience sensory sensitivities or differences in how they perceive and respond to sensory stimuli. For example, someone with autism may be hypersensitive to noise or touch, while someone with ADHD might have difficulty filtering out distractions. Educators can support these students by providing accommodations such as quiet spaces, fidget tools, or visual schedules to help regulate their sensory experiences and enhance their learning environment.
Creativity is another area where neurodiversity shines in education. Research has shown that neurodivergent individuals often possess unique creative talents and thinking styles. By embracing different ways of processing information and solving problems, educators can tap into the creativity of these students and foster a rich learning environment that values diverse perspectives. You might also find Why Journaling Beats Overthinking Every Single Tim… interesting. For more insights, check out our article on Creative Font Keyboards: A Surprisingly …. For more insights, check out our article on Screen Time Boundaries That Actually Wor….
Gender identity intersects with neurodiversity in complex ways. Neurodivergent individuals may navigate gender identity issues differently due to their unique cognitive processes and social interactions. Educators play a crucial role in creating inclusive environments where all students feel accepted and supported in expressing their gender identities authentically.
Social skills development is an important focus for many neurodivergent students who may struggle with communication or interpersonal interactions. Alternative communication methods such as visual supports, social stories, or assistive technology can aid these students in building relationships and navigating social situations effectively.
Physical education presents its own set of challenges for neurodiverse learners who may face coordination difficulties or sensory sensitivities during physical activities. Adaptations like modified equipment, individualized goals, or sensory breaks can make physical education more accessible and enjoyable for these students.
The arts offer a valuable outlet for self-expression and creativity for neurodivergent learners. By supporting them through adaptive techniques tailored to their specific needs – whether through music therapy for emotional regulation or visual arts for fine motor skill development – educators can empower these students to showcase their talents and boost their confidence.
Environmental influences also impact the learning experiences of neurodiverse individuals. Factors such as classroom setup, lighting levels, noise levels, and seating arrangements can significantly affect their ability to focus and engage with academic tasks. By creating a supportive environment that accommodates these factors proactively, educators can optimize learning outcomes for all students.
Holistic approaches are essential when educating neurodivergent learners because they require comprehensive support across various domains – academic, social-emotional, behavioral – to thrive in educational settings successfully. This involves collaboration between educators, therapists, families, and community resources to address the diverse needs of each student comprehensively.
Executive functioning challenges often accompany certain neurodevelopmental conditions like ADHD or autism spectrum disorder (ASD), impacting skills such as time management,
organization
skills,
attention
to detail,
task initiation
and completion,
and
problem-solving abilities
Culturally responsive teaching practices recognize the importance of acknowledging cultural diversity within classrooms – including those related specifically towards understanding how culture shapes student’s perceptions regarding disability & difference thereby promoting respect towards varying perspectives on special educational provisions offered at school-settings
In conclusion,
advocacy plays a vital role
in ensuring
inclusive practices
for
neurodiferse populations.
Alternative schooling settings provide opportunities
for innovative approaches
that cater
to the diverse needs
of
neurodervirgent learners.
By fostering an inclusive educational environment
that values each student’s strengths
and supports areas needing growth,
educators pave way
for success
amongst all learners,
regardless
of neurological differences they may possess
Leave a comment