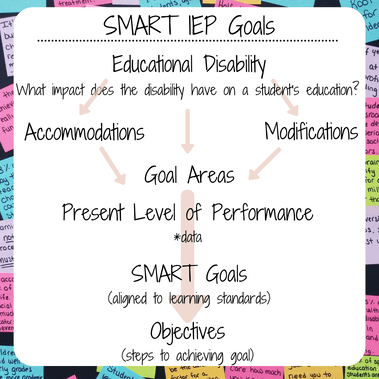
Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) are crucial documents that outline the unique needs and goals of students with disabilities in educational settings. These comprehensive plans are tailored to address a student’s specific learning requirements, accommodations, and services to ensure they have access to a free and appropriate public education. In recent years, there has been a significant shift towards creating more inclusive and supportive IEPs that not only focus on academic achievement but also encompass the social-emotional well-being and overall development of the student.
Transition planning is an essential component of IEP development for students approaching graduation or transitioning between different educational levels. This process involves setting goals related to post-secondary education, employment, independent living skills, and community involvement. By incorporating transition planning into the IEP early on, educators can better prepare students for life beyond school and support them in achieving their long-term aspirations. For more insights, check out our article on Creative Font Keyboards: A Surprisingly ….
Assistive technology plays a vital role in supporting students with disabilities in reaching their full potential. Including assistive technology devices and services in an IEP can help bridge learning gaps, enhance communication skills, improve access to curriculum materials, and promote independence in daily tasks. Educators must consider each student’s unique needs when determining the most suitable assistive technology tools to include in their IEP. You might also find The Hidden Cost of People-Pleasing (And How to Rec… interesting. For more insights, check out our article on Screen Time Boundaries That Actually Wor….
Culturally responsive IEPs recognize the diversity of students’ backgrounds, languages, cultures, beliefs, and experiences. It is crucial for educators to collaborate with families from diverse cultural backgrounds to develop IEPs that respect and incorporate their values while addressing their children’s educational needs effectively. By fostering cultural competence within the IEP process, schools can create more inclusive environments where all students feel valued and supported.
Trauma-informed IEP development acknowledges the impact of adverse childhood experiences on a student’s learning abilities and behavior. By adopting trauma-sensitive practices within the IEP framework, educators can provide appropriate support systems for students who have experienced trauma or high levels of stress. Creating safe spaces within schools that prioritize emotional well-being can help mitigate the effects of trauma on academic performance and foster resilience among students.
Behavior intervention plans (BIPs) are designed to address challenging behaviors that may impede a student’s learning progress or disrupt classroom dynamics. When developing BIPs within an IEP, it is essential for educators to conduct thorough functional behavior assessments to identify triggers for undesirable behaviors accurately. Implementing proactive strategies alongside positive reinforcement techniques can help modify behaviors effectively while promoting a positive school climate conducive to learning.
Gifted and talented students also benefit from having individualized goals outlined in their IEPs that cater to their advanced cognitive abilities or special talents. By providing enrichment opportunities, acceleration options, or specialized instruction within the framework of an IEP plan tailored specifically for gifted learners,…
Social-emotional learning (SEL) goals integrated into an Individualized Education Program (IEP) are instrumental in nurturing emotional intelligence,…
Tools You Might Love:
To make your educational materials more accessible through audio, [ElevenLabs](https://try.elevenlabs.io/w95mzlppyxor) offers professional voice generation technology.
Many productivity enthusiasts find valuable tools and resources at [Smorgi Apps](https://smorgi.app) to optimize their daily routines.
Leave a comment