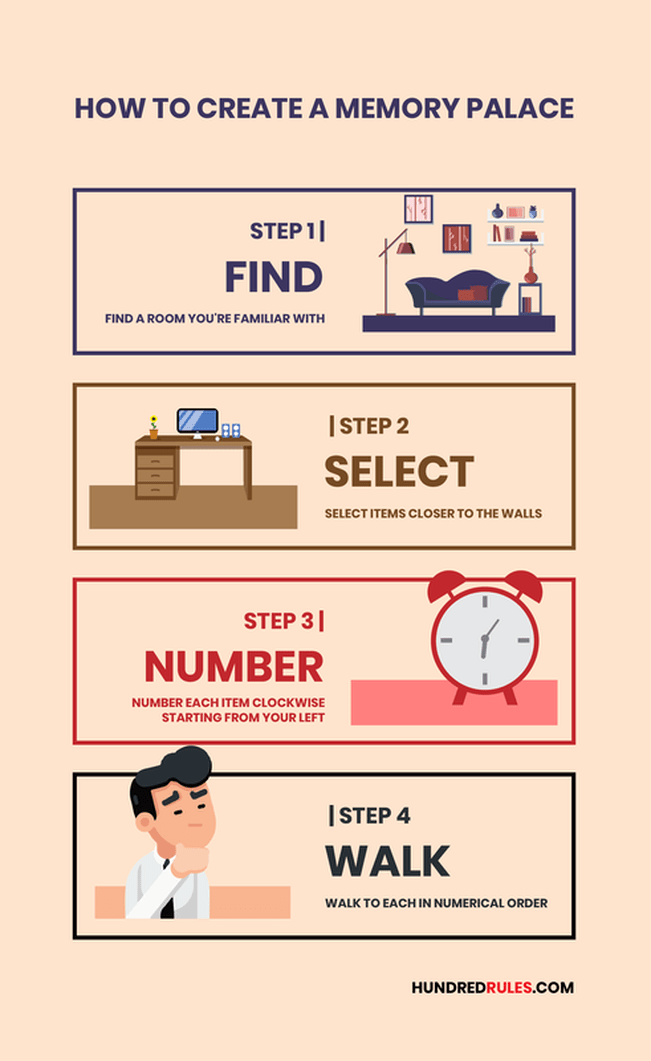
Memory palaces have been used for centuries as a powerful mnemonic device to aid in remembering information. This technique involves mentally visualizing a familiar place, like your home, and associating specific pieces of information with different rooms or objects within that space. By mentally walking through this memory palace, you can easily recall the information tied to each location.
Dual coding theory suggests that combining verbal and visual information can enhance learning and retention. When you use both words and images to represent concepts, you are engaging multiple areas of the brain, making it easier to remember the material later on.
Spaced repetition is a study technique where you review material at increasing intervals over time. By spacing out your practice sessions rather than cramming all at once, you reinforce your memory more effectively and retain the information for longer periods.
Chunking involves breaking down large amounts of information into smaller chunks or groups. Our brains can only hold so much in working memory at one time, so organizing data into manageable chunks makes it easier to process and remember.
Retrieval practice is a method where instead of simply reviewing material passively, you actively try to recall it from memory. This effortful process strengthens neural pathways associated with that information, leading to better long-term retention.
The Feynman technique is named after physicist Richard Feynman and involves explaining a concept in simple terms as if teaching it to someone else. By doing so, you identify gaps in your understanding and solidify your knowledge on the subject.
Mind mapping is a visual tool that helps organize thoughts and ideas around a central topic using branches or nodes connected by lines. This method aids in brainstorming, note-taking, and synthesizing complex information into a more digestible format.
Speed reading techniques aim to increase reading speed without sacrificing comprehension. Strategies like minimizing subvocalization (pronouncing words silently) or using peripheral vision can help improve reading rate while maintaining understanding.
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. Learning new skills or challenging the mind through mental exercises can promote neuroplasticity and enhance cognitive function.
Metacognition strategies involve thinking about one’s own thinking processes such as planning how to approach learning tasks, monitoring comprehension during studying, and evaluating performance afterward. By being aware of how we learn best, we can optimize our study habits for improved outcomes.
The Pomodoro technique breaks study sessions into short intervals (usually 25 minutes) separated by brief breaks. This structured approach helps maintain focus and productivity by incorporating regular rest periods into study sessions.
Research has debunked the idea of distinct “learning styles” (e.g., visual learners vs auditory learners), suggesting instead that individuals benefit from multimodal approaches utilizing various sensory inputs for optimal learning outcomes.
Flow state occurs when individuals are fully immersed in an activity with intense focus leading them to experience deep enjoyment while performing said task; this heightened state promotes efficient learning experiences due increased engagement levels during activities
Sleep plays a crucial role in memory consolidation; during sleep cycles memories are transferred from short-term storage sites located within hippocampus towards long-term storage within cerebral cortex enhancing overall retention rates
Eating nutritious foods rich in antioxidants omega-3 fatty acids vitamins minerals supports healthy brain function improving cognition mood concentration levels aiding effective learning mechanisms
Technology tools such as Anki flashcards Quizlet platforms offer digital solutions practicing spaced repetition ensuring consistent review materials promoting long term memory retention
Physical exercise boosts cognitive functions releasing endorphins reducing stress anxiety sharpening focus attention enhancing overall academic performance
Music has been shown impact cognitive abilities stimulating creative thinking improving mood reducing stress levels fostering conducive environment effective studying
Mindfulness practices including meditation deep breathing exercises cultivate focused attention awareness reduce distractions enhance concentration levels facilitating absorption assimilation complex subjects
Gamification adds elements game design principles educational settings making learning interactive engaging motivating students progress challenges rewards driving sustained interest participation educational content
Leave a comment