Social-emotional learning (SEL) refers to the process of developing and understanding one’s emotions, managing relationships, and making responsible decisions. It is a crucial component of education that helps students develop important life skills beyond academic knowledge. In this Q&A style post, we will explore some common questions about social-emotional learning.
Q: What are the core competencies of social-emotional learning?
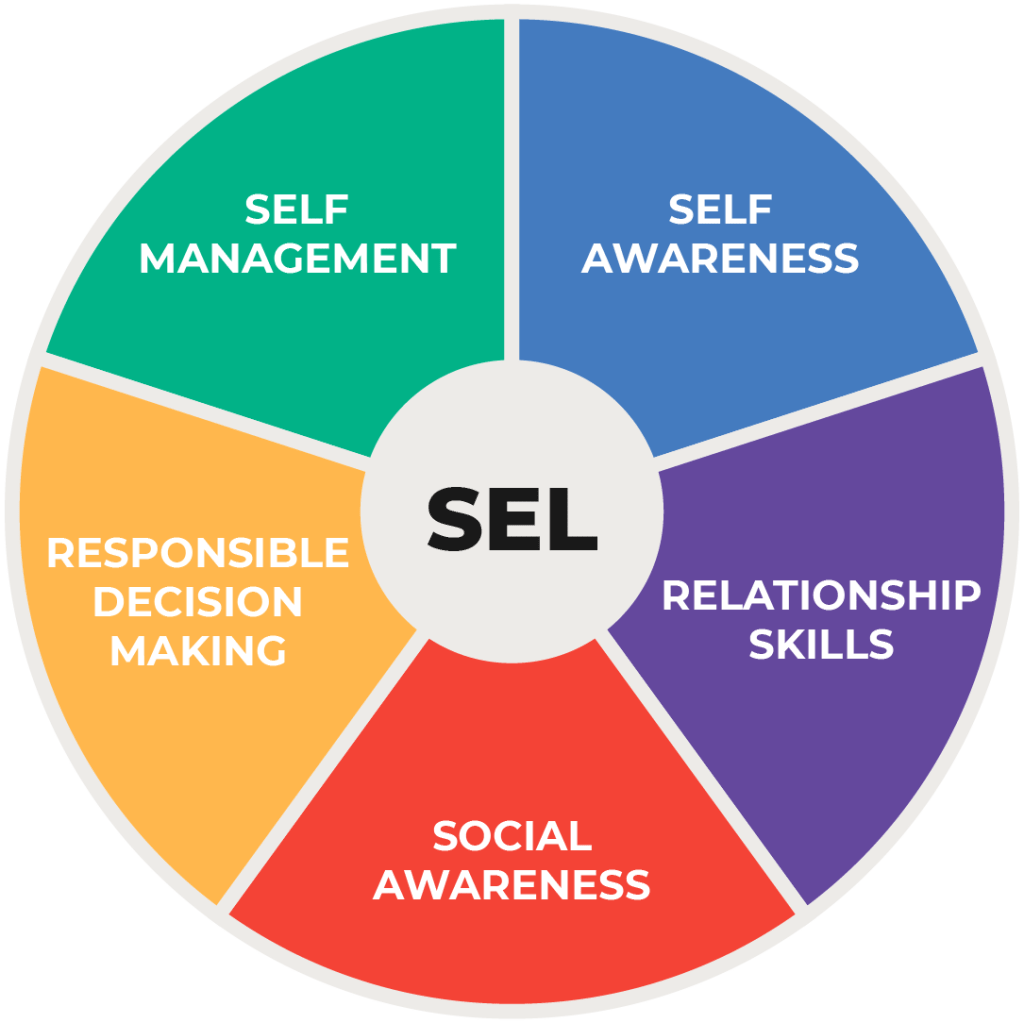
A: The Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning (CASEL) has identified five core competencies of SEL:
1. Self-awareness: This involves recognizing one’s own emotions, strengths, weaknesses, values, and goals.
2. Self-management: It includes regulating emotions effectively, setting personal goals, and demonstrating self-discipline.
3. Social awareness: This competency focuses on empathizing with others’ perspectives and experiences while appreciating diversity.
4. Relationship skills: These skills involve establishing positive relationships through effective communication,
cooperation, negotiation conflict resolution.
5. Responsible decision-making: This competency emphasizes making ethical choices by considering the well-being
of oneself and others.
Q: How does social-emotional learning benefit students?
A: Research shows that incorporating SEL into education has numerous benefits for students. It helps improve academic performance as students gain better focus and attention in classroom settings. SEL also enhances interpersonal skills such as empathy and teamwork which are essential for building healthy relationships both inside and outside school environments. Furthermore, it equips students with problem-solving abilities that enable them to handle conflicts constructively.
Q: How can schools integrate social-emotional learning into their curriculum?
A: Schools can incorporate SEL into their curriculum in various ways:
1. Dedicated lessons or programs focused explicitly on SEL.
2. Infusing SEL principles within existing subjects like English or Social Studies by discussing characters’
emotions or societal issues.
3. Creating a positive school climate where respect for diversity is fostered through inclusive practices
and anti-bullying initiatives.
4. Providing opportunities for cooperative learning and teamwork activities.
5. Encouraging reflection and self-assessment through journaling or other reflective practices.
Q: Can parents support social-emotional learning at home?
A: Absolutely! Parents play a crucial role in supporting their child’s SEL development. Some ways parents can contribute include:
1. Modeling emotional intelligence by recognizing, expressing, and managing their emotions effectively.
2. Engaging in open communication with their children, actively listening to them, and validating their feelings.
3. Establishing routines that promote self-discipline and responsibility.
4. Encouraging empathy by discussing others’ perspectives or engaging in community service together.
5. Setting clear expectations for behavior while allowing room for mistakes and growth.
Q: Is social-emotional learning only relevant during school years?
A: No, social-emotional learning is a lifelong process that continues beyond school years. The skills acquired during childhood serve as a foundation for emotional well-being throughout adulthood. SEL competencies are essential in various aspects of life such as career success, building healthy relationships, managing stress, and making responsible decisions.
In conclusion, social-emotional learning is an integral part of education that equips students with essential life skills beyond academic knowledge. By incorporating SEL into the curriculum both at schools and within families, we can help our children develop into well-rounded individuals who are capable of navigating challenges successfully throughout their lives
Leave a comment