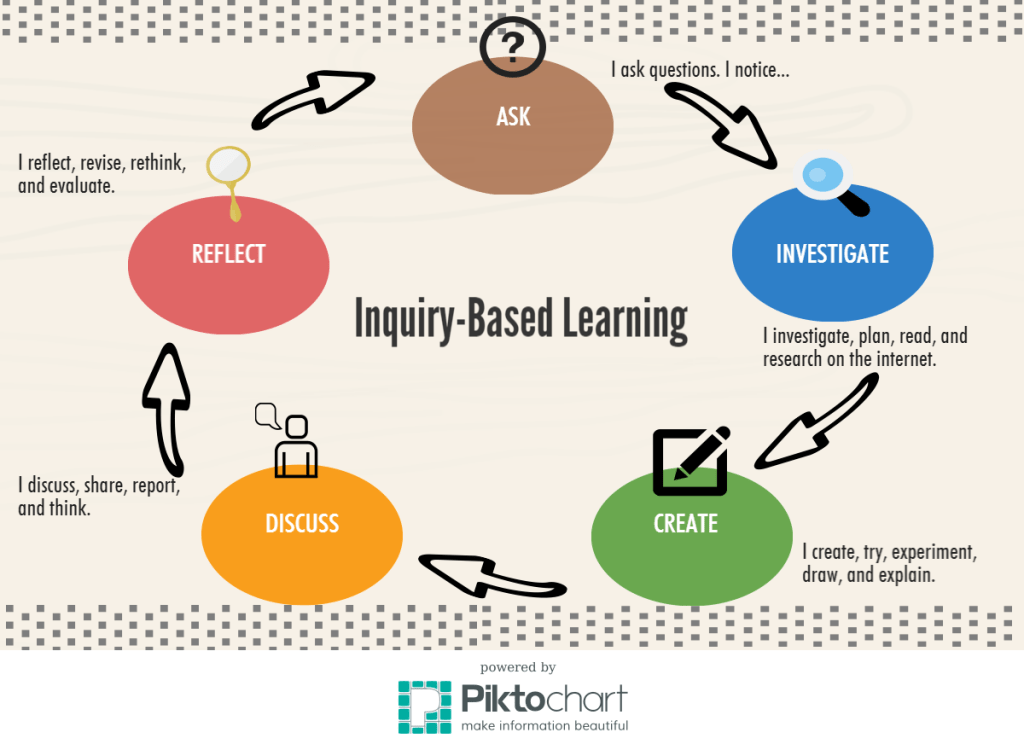
Inquiry-based learning, also known as inquiry-driven instruction, is a student-centered approach to education that fosters curiosity, critical thinking, and deep understanding. It encourages students to actively engage in their own learning process by posing questions, investigating topics of interest, and seeking answers through research and exploration. This method goes beyond rote memorization and promotes lifelong learning skills that are essential for success in the 21st century.
At its core, inquiry-based learning is centered around asking questions. Instead of being passive recipients of information delivered by teachers, students become active participants in constructing their knowledge. They learn how to ask meaningful questions about the world around them and develop strategies for finding solutions. By nurturing this natural sense of curiosity within each student, inquiry-based learning creates a foundation for independent thinking and problem-solving abilities.
One key aspect of inquiry-based learning is encouraging students’ autonomy. Rather than following a rigid curriculum or set lesson plans dictated by the teacher, learners have the freedom to explore topics that interest them personally. This individualized approach allows each student’s unique interests and talents to be recognized and nurtured.
Inquiry-based learning also emphasizes critical thinking skills. Students learn how to analyze information from various sources critically, evaluate its credibility and relevance, synthesize ideas from different perspectives, and make informed judgments based on evidence rather than mere opinions or assumptions. These skills are not only crucial for academic success but also prepare students for real-world challenges where they will need to analyze complex problems before making decisions.
Furthermore, inquiry-based learning promotes collaboration among peers. Students often work together in small groups or larger teams on projects or investigations where they can share ideas, challenge each other’s thinking constructively, solve problems collectively, and communicate effectively with others – all valuable skills needed in today’s interconnected world.
Another advantage of this approach is its ability to foster intrinsic motivation within learners. When students have agency over their education – choosing what they want to study and how they want to explore it – they are more likely to be engaged, enthusiastic, and motivated. Inquiry-based learning taps into students’ intrinsic desire to learn, fostering a passion for knowledge that extends beyond the classroom walls.
Inquiry-based learning also aligns well with modern educational trends such as personalized learning and project-based learning. It allows students to pursue their interests through self-directed projects or investigations while developing important skills in research, critical thinking, problem-solving, and communication.
However, implementing inquiry-based learning requires a shift in traditional teaching practices. Teachers must serve as facilitators rather than instructors by providing guidance and support throughout the inquiry process. They need to create an environment conducive to questioning and exploration where students feel safe to take risks, share ideas openly, and make mistakes without fear of judgment.
Additionally, assessment methods in inquiry-based learning differ from traditional approaches. Instead of relying solely on tests or quizzes that measure memorization of facts, teachers evaluate student progress based on their ability to ask thoughtful questions, conduct research effectively, analyze information critically, collaborate with peers successfully, present findings coherently, and reflect on their own learning journey.
In conclusion, inquiry-based learning is a powerful approach that empowers students as active participants in their education. By nurturing curiosity and critical thinking skills while promoting autonomy and collaboration among learners
Leave a comment