Project-based learning is an effective approach to alternative schooling that promotes active engagement and deep understanding of concepts. Research shows that students who engage in project-based learning have higher retention rates compared to traditional instructional methods (Thomas, 2000). This method allows students to apply their knowledge and skills to real-world problems or tasks, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving abilities.
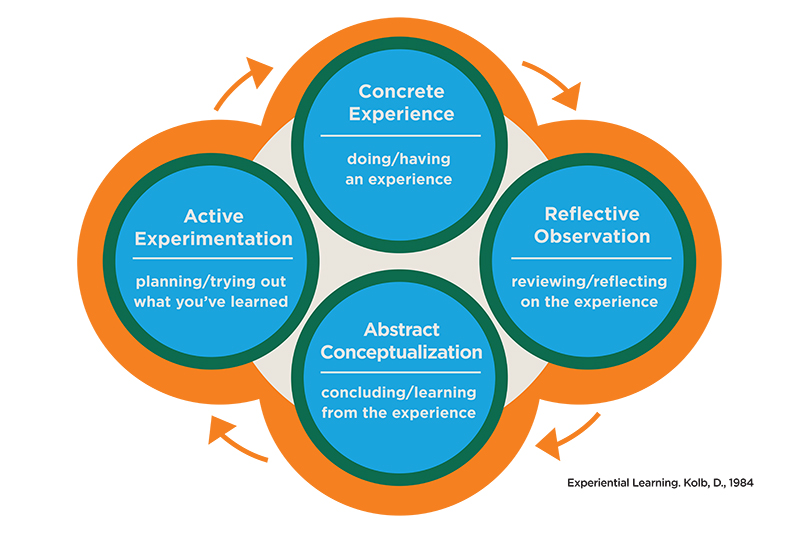
Experiential learning is another valuable strategy in self-directed education. It involves hands-on experiences and reflection on those experiences. Studies have shown that experiential learning enhances student motivation, engagement, and overall academic achievement (Kolb & Kolb, 2017). By engaging with the material directly, learners can develop a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Self-assessment techniques play a crucial role in self-directed learning. They empower learners by allowing them to take ownership of their progress and identify areas for improvement. Self-assessment has been found to enhance student performance and promote lifelong learning habits (Andrade & Du, 2005).
Metacognition and self-reflection are essential skills for self-directed learners. Metacognition refers to the ability to think about one’s own thinking processes. Research suggests that metacognitive strategies improve academic performance across various subjects (Zimmerman & Schunk, 2011). By regularly reflecting on their learning process, students can identify effective strategies while also recognizing areas where they may need additional support.
Personalized learning plans provide a tailored approach to education based on individual strengths, interests, and goals. Studies have shown that personalized instruction leads to improved academic outcomes as it addresses students’ unique needs (Pane et al., 2014).
Peer-to-peer teaching and collaboration foster social interaction among learners while promoting cooperative skills. Collaborative approaches have been found to enhance critical thinking abilities as well as improve communication skills (Johnson et al., 2014).
Goal setting and time management are fundamental aspects of self-directed education. When individuals set goals for themselves, they are more likely to stay motivated and focused on their learning journey. Effective goal setting has been associated with improved academic performance and a sense of personal achievement (Locke & Latham, 2019).
Self-motivation strategies are essential in alternative schooling environments where learners have greater autonomy over their education. Research indicates that self-motivated students demonstrate higher levels of academic success and a deeper passion for learning (Duckworth et al., 2007).
Building a growth mindset is crucial for self-directed learners as it promotes resilience, perseverance, and the belief that abilities can be developed through effort. Studies have shown that individuals with a growth mindset are more likely to embrace challenges and persist in the face of setbacks (Dweck, 2006).
Developing critical thinking skills is vital for independent study. Critical thinkers have the ability to analyze information objectively, make informed decisions, and solve complex problems effectively. Research suggests that critical thinking skills enhance academic performance across various disciplines (Facione et al., 2018).
Effective note-taking methods play an important role in self-directed learning by promoting active engagement with the material. Research shows that well-structured notes aid in comprehension, organization of ideas, and retention of information (Kiewra et al., 1991).
Harnessing technology for self-directed learning allows students to access vast resources beyond traditional textbooks or classroom settings. Technology integration has been found to increase student motivation while enhancing creativity and collaboration skills (Lim & Chai, 2008).
Creating a conducive learning environment at home or in alternative settings is essential for effective self-directed education. Factors such as comfortability, minimal distractions, access to necessary resources or materials contribute to optimal learning experiences.
Balancing structure and freedom helps strike a healthy equilibrium between guidance from educators or mentors while still allowing learners to explore their interests independently.
Cultivating curiosity and love for lifelong learning fosters intrinsic motivation and a passion for seeking knowledge. Research suggests that individuals with a love for learning are more likely to engage in self-directed education (Ryan & Deci, 2000).
Incorporating arts and creativity into self-directed education nurtures innovative thinking, problem-solving skills, and self-expression. Studies indicate that arts integration enhances student engagement, critical thinking abilities, and overall academic achievement (Bamford et al., 2011).
Nurturing emotional intelligence through self-directed learning helps learners develop empathy, self-awareness, and effective interpersonal skills. Emotional intelligence has been associated with improved academic performance and social relationships (Brackett & Katulak, 2006).
Building resilience and perseverance is crucial in the face of challenges encountered during independent study. Research indicates that resilient individuals are better equipped to cope with setbacks or failures while maintaining motivation towards their goals (Masten et al., 1990).
Exploring alternative assessment methods beyond traditional testing allows students to showcase their understanding in diverse ways such as portfolios, presentations or projects which provide a holistic view of their capabilities.
Integrating physical activity and movement into self-directed learning has numerous cognitive benefits such as enhanced memory retention and increased focus (Hillman et al., 2019). Incorporating movement breaks or physical activities can improve overall well-being while supporting the learning process.
Promoting cultural diversity and global awareness through independent study exposes learners to different perspectives, cultures, and world issues. This broadens their horizons while fostering empathy and understanding towards others.
Developing effective research skills prepares students for lifelong learning by equipping them with the ability to find reliable sources of information independently.
Fostering entrepreneurship and innovation encourages learners to think creatively, take risks, solve problems innovatively while cultivating an entrepreneurial mindset even outside traditional business contexts.
Adapting to different learning styles within a self-directed framework recognizes individual differences in how people acquire knowledge best. By catering instruction to various learning styles, educators can ensure that learners are engaged and able to access information effectively.
Exploring non-traditional subjects or disciplines not typically covered in mainstream education allows learners to pursue their passions and develop expertise in unconventional areas. This promotes a well-rounded education that aligns with individual interests and goals.
Understanding the role of mentors in supporting self-directed learners is crucial for successful alternative schooling. Mentors provide guidance, support, and expertise while fostering independence and self-confidence in students (Krampe et al., 2018).
Addressing potential social isolation or lack of peer interaction in alternative schooling environments is important for holistic development. Opportunities for collaboration, group projects, or extracurricular activities can help foster social connections among learners.
Creating opportunities for real-world application of knowledge gained through self-directed learning enhances relevance and deepens understanding. Connecting concepts learned to practical situations helps students see the value of their education beyond the classroom (Hmelo-Silver et al., 2007).
In conclusion, alternative schooling approaches offer a wide range of strategies and techniques aimed at promoting learner autonomy, engagement, critical thinking skills, and personal growth. By incorporating project-based learning, experiential learning, self-assessment techniques, metacognition and self-reflection practices into personalized learning plans with elements such as peer-to-peer teaching and collaboration,
goal setting/time management skills,
self-motivation strategies,
building a growth mindset,
developing critical thinking skills,
effective note-taking methods,
harnessing technology for self-directed learning
creating conducive learning environment at home/alternative settings
balancing structure/freedom,
cultivating curiosity/love for lifelong-learning,
incorporating arts/creativity,
nurturing emotional intelligence,
building resilience/perseverance
exploring alternative assessment methods beyond traditional testing
integrating physical activity/movement into self-directed learning
promoting cultural diversity/global awareness through independent study
develop effective research skills
fostering entrepreneurship/innovation
adapting to different learning styles within a self-directed framework,
exploring non-traditional subjects/disciplines not typically covered in mainstream education,
understanding the role of mentors in supporting self-directed learners
addressing potential social isolation/lack of peer interaction, and
creating opportunities for real-world application,
alternative schooling environments can provide a rich and fulfilling educational experience that supports the holistic development of learners. These approaches empower students to take ownership of their education, cultivate a love for learning, and prepare them for success in an ever-changing world.
Leave a comment