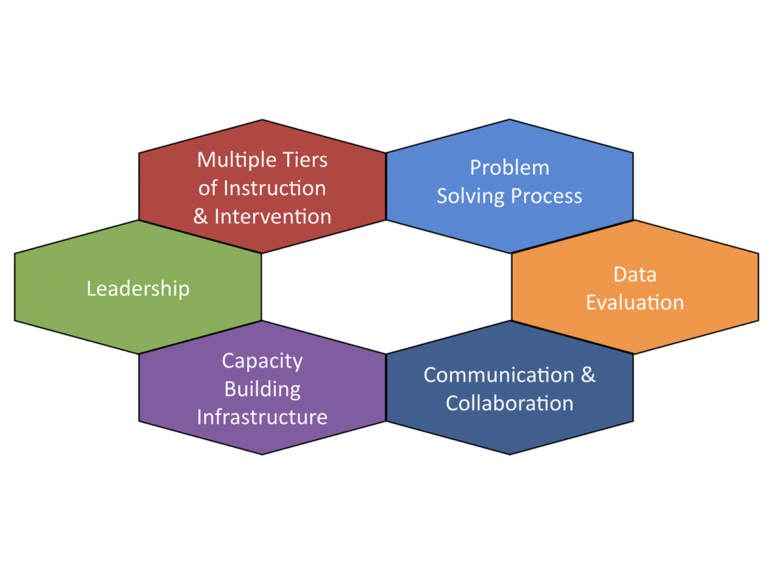
Multi-tiered systems of support (MTSS) are a comprehensive framework that aims to provide targeted interventions and support to meet the diverse needs of students in schools. This approach, also known as Response to Intervention (RTI), has gained popularity in recent years due to its effectiveness in promoting academic achievement and positive behavior.
In this article, we will explore 15 key components of MTSS that make it an essential tool for educators and administrators seeking to create inclusive learning environments.
1. Universal Screening: The first step in MTSS is conducting universal screenings or assessments to identify students who may need additional support. These screenings help educators understand the specific areas where individual students may be struggling academically or behaviorally.
2. Data-driven Decision Making: MTSS relies on data analysis to inform decision-making at all levels. Educators use multiple sources of information, such as formative assessments, progress monitoring tools, and behavior logs, to identify trends and make informed decisions about interventions.
3. Tiered Interventions: MTSS operates on a tiered system with three levels of intervention – Tier 1 (universal), Tier 2 (targeted), and Tier 3 (intensive). In Tier 1, all students receive high-quality instruction aligned with grade-level standards. If additional support is needed, students move through the tiers for more intensive interventions.
4. Evidence-based Practices: Interventions within each tier should be evidence-based – meaning they have been proven effective through research – and tailored to meet individual student needs. This ensures that resources are allocated efficiently while maximizing student outcomes.
5. Progress Monitoring: Regular progress monitoring helps educators determine if interventions are effective or if adjustments need to be made. It involves collecting data frequently and using it to track growth over time so that appropriate changes can be implemented when necessary.
6. Collaborative Problem Solving: MTSS promotes collaboration among teachers, specialists, administrators, families, and students themselves. By working together, stakeholders can develop effective strategies and interventions that address the unique needs of each student.
7. Professional Development: Implementing MTSS effectively requires continuous professional development for educators. This ensures that teachers have the necessary knowledge and skills to identify struggling students, implement evidence-based interventions, and monitor progress effectively.
8. Early Intervention: One of the key strengths of MTSS is its focus on early intervention. By identifying and addressing potential difficulties at an early stage, educators can prevent academic or behavioral problems from escalating further.
9. Family Engagement: Parents and families play a crucial role in supporting their child’s education within an MTSS framework. Regular communication with families helps create a shared understanding of goals, interventions, and progress monitoring strategies.
10. Culturally Responsive Practices: MTSS acknowledges the importance of cultural responsiveness in meeting the needs of diverse student populations. Educators strive to incorporate diverse perspectives into instruction and intervention practices while respecting individual cultural backgrounds.
11. Social-Emotional Learning (SEL): Recognizing that social-emotional well-being is essential for academic success, MTSS integrates SEL programs into its framework. These programs promote self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making.
12. Individualized Education Plans (IEPs): For students with disabilities or exceptionalities who require specialized support beyond Tier 3 interventions, IEPs are developed as part of MTSS implementation to ensure their unique needs are addressed comprehensively.
13. Data Management Systems: Effective implementation of MTSS relies on robust data management systems that allow educators to store, analyze, and visualize data easily across multiple tiers and over time.
14. Continuous Improvement Cycle: Implementing MTSS involves ongoing cycles of planning, implementing interventions tailored to individual student needs based on data analysis results monitoring progress regularly evaluating outcomes adjusting interventions as needed
15.Sustainability: Successful implementation requires commitment from school leadership to embed MTSS practices within the school’s culture. This includes allocating resources, providing ongoing support to educators, and continuously monitoring fidelity of implementation.
In conclusion, MTSS provides a comprehensive framework for schools to meet the diverse needs of students through evidence-based interventions. By incorporating data-driven decision-making, tiered interventions, and collaboration among stakeholders, MTSS promotes academic achievement and positive behavior while ensuring that no student falls through the cracks. With its focus on early intervention and continuous improvement, MTSS has become an invaluable tool in creating inclusive learning environments that support all students’ success.
Leave a comment