Experiential Learning: A Hands-On Approach to Education
In recent years, there has been a growing recognition of the limitations of traditional classroom-based education. As students become increasingly disengaged and disconnected from their learning experiences, educators and parents are seeking alternative methods that foster deep understanding and real-world application of knowledge. One such approach gaining popularity is experiential learning.
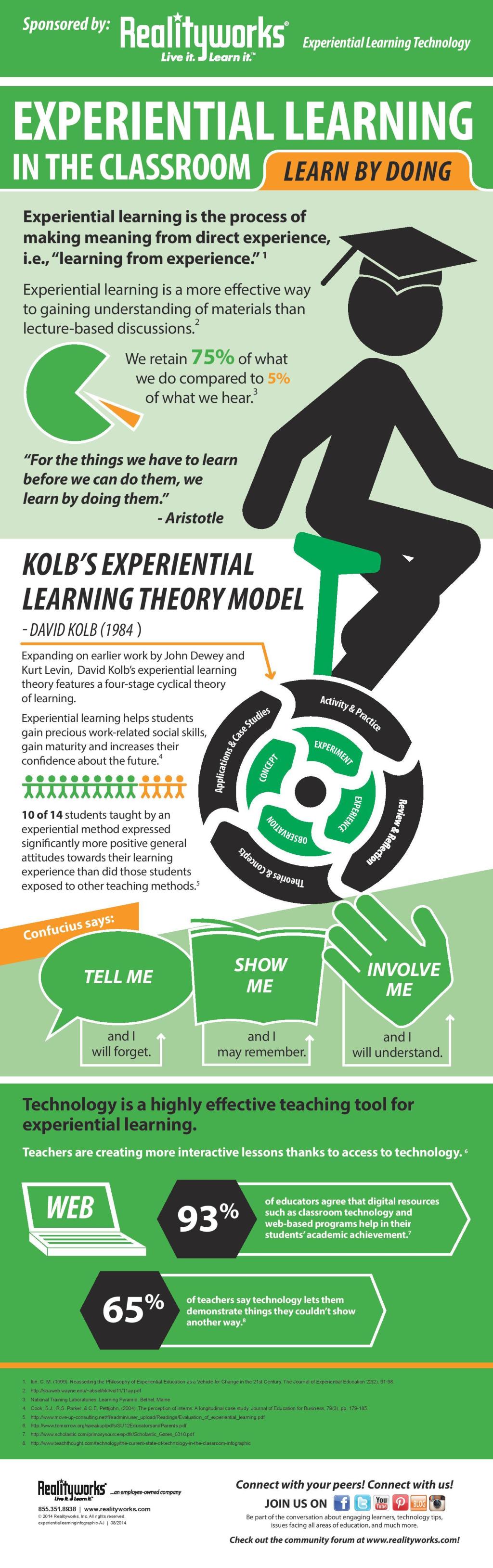
Experiential learning is an immersive educational philosophy that emphasizes hands-on experiences as the primary vehicle for acquiring knowledge, skills, and attitudes. It goes beyond textbooks and lectures by providing opportunities for students to actively engage with the subject matter in meaningful ways. Whether it’s through field trips, projects, or simulations, experiential learning encourages students to take an active role in their own education.
The roots of experiential learning can be traced back to philosopher John Dewey, who believed that education should be practical and relevant to real-life situations. He argued that learners must engage in authentic experiences to fully grasp concepts and develop critical thinking skills. Over time, this concept has evolved into various models and approaches used by alternative schools around the world.
One popular model is the project-based learning (PBL) approach. In PBL classrooms, students work on extended projects that require them to investigate complex questions or problems related to a specific topic or theme. These projects often involve collaboration with peers and experts outside the classroom setting. By working on real-world challenges, students not only gain subject-specific knowledge but also develop essential skills such as problem-solving, communication, creativity, and teamwork.
Another form of experiential learning is service-learning. This approach integrates community service with academic instruction by linking classroom content with real-life issues faced by communities or organizations. Through service-learning projects like volunteering at local charities or conducting research for non-profit organizations, students learn about social responsibility while applying what they have learned in class to make a positive impact on society.
Simulations are yet another powerful tool used in experiential learning. Whether it’s a historical reenactment, a business simulation, or a scientific experiment, simulations provide students with an immersive and interactive experience that allows them to apply theoretical knowledge in practical contexts. These simulated experiences often involve decision-making, problem-solving, and critical thinking skills – all essential for success in the real world.
Field trips are also an integral part of experiential learning. Taking students outside the confines of the classroom allows them to observe and experience firsthand what they have learned theoretically. Whether it’s visiting a museum, exploring nature reserves, or going on cultural excursions, field trips provide opportunities for sensory engagement and multisensory learning – tapping into different modes of understanding.
One unique aspect of experiential learning is its focus on reflection. After engaging in hands-on experiences, students are encouraged to reflect on their actions and outcomes critically. This reflective process helps them make connections between theory and practice while gaining insights into their own strengths and areas for improvement. By actively reflecting on their experiences, students deepen their understanding and enhance metacognitive skills – fostering self-awareness and lifelong learning habits.
The benefits of experiential learning extend beyond academic achievement. Research has shown that this approach enhances motivation by making learning more enjoyable and relevant to students’ lives. It promotes active engagement through student-centered activities that cater to various senses and learning styles. Experiential learning also nurtures important life skills such as problem-solving, adaptability, collaboration, empathy, creativity – all valuable assets in today’s rapidly changing world.
While experiential learning offers numerous advantages over traditional education methods, implementing it requires careful planning from educators. Teachers must design authentic experiences aligned with curriculum objectives while balancing time constraints within the classroom setting. Additionally, assessing student progress becomes more nuanced as traditional tests may not adequately capture the breadth of skills developed through hands-on experiences.
In conclusion,
experiential learning offers a transformative approach to education, shifting the focus from passive consumption of knowledge to active participation and application. By integrating real-world experiences into the curriculum, students develop a deeper understanding of subjects while acquiring essential skills for success in their personal and professional lives. As alternative schooling gains traction, experiential learning emerges as a powerful tool to engage students and prepare them for the challenges of an ever-evolving world.
Leave a comment