Assessing Progress and Achievement in Self-Directed Learning
Self-directed learning is a powerful approach to education that allows individuals to take control of their own learning journey. It fosters independence, critical thinking, and self-motivation. However, one common concern with self-directed learning is how to assess progress and achievement without traditional measures such as grades or standardized tests. In this article, we will explore various strategies for assessing progress and achievement in self-directed learning.
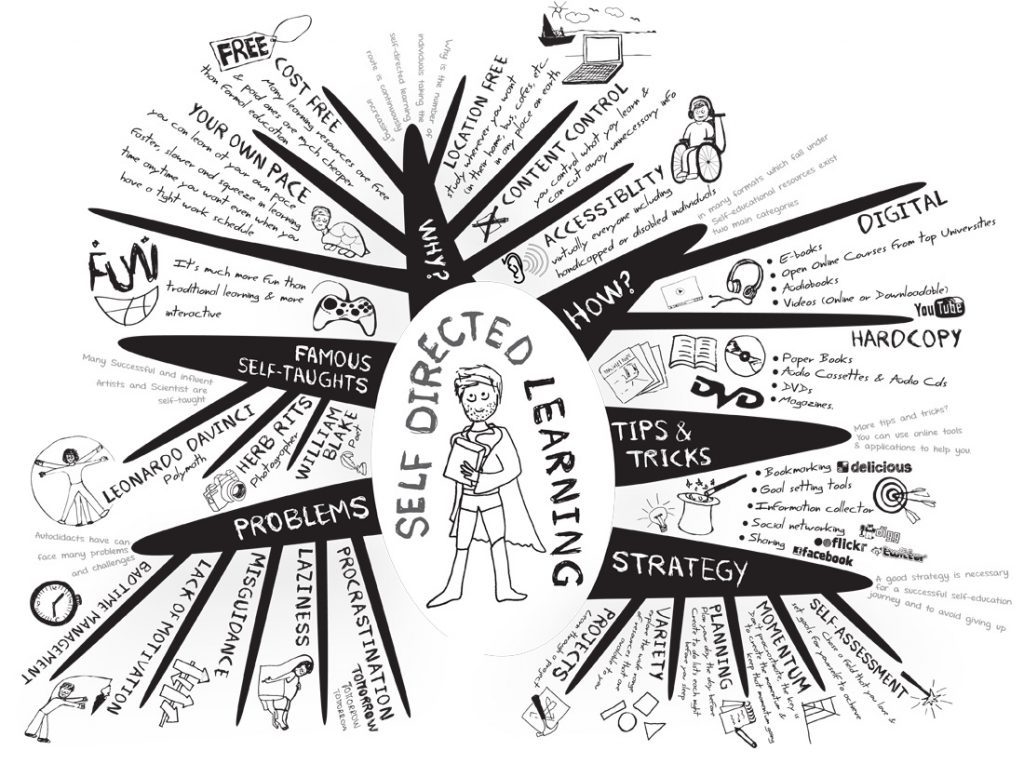
1. Goal Setting
Goal setting is an essential component of self-directed learning. By setting clear goals at the beginning of the learning process, learners can have a sense of direction and purpose. These goals should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). Regularly reviewing these goals helps both learners and educators assess progress towards achieving them.
2. Reflection
Reflection plays a crucial role in self-directed learning assessment. Learners should be encouraged to reflect on their experiences regularly. This can be done through journaling or open discussions with mentors or peers. Reflective exercises help learners recognize their strengths and weaknesses while identifying areas for improvement.
3. Portfolios
Portfolios are an excellent way for learners to showcase their work throughout the self-directed learning journey. They provide tangible evidence of growth over time by collecting samples of completed projects or assignments that demonstrate various skills acquired during the process.
4. Self-Assessment
Empowering learners to assess themselves promotes autonomy in their educational experience. Encourage students to evaluate their progress against predetermined criteria or rubrics provided at the beginning of each project or unit of study. Self-assessment not only allows learners to take ownership but also develops metacognitive skills necessary for lifelong learning.
5. Peer Evaluation
Peer evaluation encourages collaboration among learners while providing opportunities for constructive feedback from peers who share similar interests and goals within a particular subject area or project focus.
6.Problem-solving activities
Design problem-solving activities that require students to apply their knowledge and skills in real-world scenarios. These activities can be open-ended, allowing students to demonstrate their ability to think critically, analyze information, and propose innovative solutions.
7. Performance-based Tasks
Performance-based tasks are an effective way of assessing progress and achievement in self-directed learning. These tasks ask learners to demonstrate what they have learned through practical applications or performances rather than relying solely on written exams. Examples include presentations, debates, exhibitions, or simulations.
8. Mentor/Teacher Feedback
Mentor or teacher feedback is crucial for guiding learners’ progress in self-directed learning. Regular check-ins with mentors or teachers can provide valuable insights into areas where improvement is needed while offering constructive guidance and support throughout the process.
9. Individual Learning Plans (ILPs)
Individual Learning Plans (ILPs) are personalized plans that outline goals and strategies for each learner based on their unique strengths, interests, and needs. ILPs act as a roadmap for both learners and educators to monitor progress effectively.
10.Recognition of Skills Acquired Outside Traditional Settings
Self-directed learning often takes place outside traditional classroom settings. It’s essential to recognize skills acquired through extracurricular activities such as volunteering, internships, online courses, or community projects. Encourage learners to document these experiences by providing certificates of completion or recommendation letters from supervisors.
In conclusion, assessing progress and achievement in self-directed learning requires a shift from traditional methods towards more individualized approaches that focus on personal growth rather than standardized metrics like grades or tests. By implementing goal setting, reflection exercises, portfolios, self-assessment tools along with peer evaluation opportunities combined with performance-based assessments supported by mentor/teacher feedback and recognition of skills acquired outside traditional settings will help assess progress accurately in individuals engaged in self-directed learning journeys
Leave a comment