Peer Assessment for Self-Regulated Learning: A Valuable Tool for Alternative Schooling
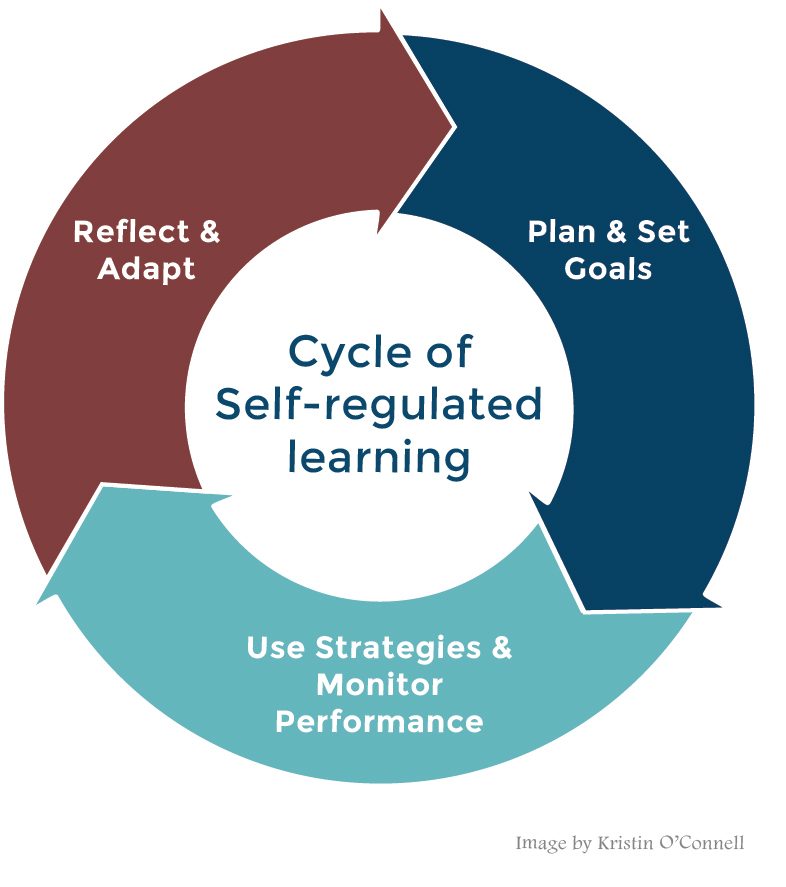
In alternative schooling and education, the focus is often placed on fostering self-regulated learning among students. Self-regulated learners are able to take control of their own learning process, set goals, monitor their progress, and make adjustments as necessary. One effective tool that can support the development of self-regulation skills is peer assessment.
What is Peer Assessment?
Peer assessment involves students evaluating and providing feedback on each other’s work. It can be used in various educational settings, including traditional classrooms and alternative schools. In this approach, students become active participants in the learning process by taking on both roles – assessor and assessee.
How Does Peer Assessment Support Self-Regulated Learning?
1. Reflection: Through peer assessment activities, students have the opportunity to reflect on their own work as well as that of others. By critically analyzing their peers’ work, they gain a deeper understanding of what constitutes quality work themselves. This reflection helps them identify areas where they might need improvement or further practice.
2. Goal Setting: When engaging in peer assessment, students are encouraged to set specific criteria or rubrics for evaluating each other’s work. This process requires them to think about what should be included in an exemplary piece of work and what steps they need to take to achieve that level themselves.
3. Monitoring Progress: Peer assessment provides a valuable means for monitoring progress towards achieving individual goals. As students review their peers’ work against established criteria or rubrics, they can compare it with their own performance and determine how far they have come in reaching their objectives.
4. Feedback Loop: Through giving constructive feedback to peers and receiving feedback from them in return, students develop essential communication skills while also gaining insights into different perspectives and approaches within a collaborative setting.
5. Metacognition: Engaging in peer assessment requires metacognitive thinking – thinking about one’s own thinking. Students must understand their own strengths and weaknesses, as well as those of others, in order to provide meaningful feedback. This metacognitive awareness enhances self-regulation skills.
Tips for Implementing Peer Assessment:
1. Clear Guidelines: Establish clear guidelines and expectations for peer assessment activities, including criteria or rubrics for evaluation.
2. Training: Provide guidance and training on how to effectively give constructive feedback and evaluate peers’ work.
3. Scaffolded Approach: Start with simpler tasks and gradually increase the complexity of assessments as students become more comfortable with the process.
4. Reflection Time: Allow time for students to reflect on the feedback they receive from peers and make adjustments accordingly.
5. Teacher Support: While peer assessment is primarily student-driven, teachers should play an active role by monitoring the process, providing guidance when needed, and ensuring fairness in evaluations.
Peer assessment can be a valuable tool in alternative schooling environments where self-regulated learning is highly valued. By engaging in this practice, students not only develop important skills such as reflection, goal setting, monitoring progress, providing constructive feedback but also foster a sense of autonomy and ownership over their own learning journey.
Leave a comment