Differentiating Instruction in IEPs:
Individualized Education Programs (IEPs) are designed to provide specialized support and accommodations for students with disabilities. One essential aspect of developing effective IEPs is differentiating instruction to meet the unique needs of each student.
Differentiation involves tailoring instruction, content, and assessment to match a student’s abilities, learning style, and interests. In the context of an IEP, differentiation allows educators to address specific academic goals while considering the student’s individual strengths and challenges.
To differentiate instruction within an IEP, teachers can employ various strategies such as flexible grouping, tiered assignments, and modified materials. Flexible grouping involves forming small groups based on students’ skill levels or learning preferences. This approach allows teachers to provide targeted instruction that meets individual needs.
Tiered assignments involve providing different levels of complexity or depth for students within the same lesson or activity. By offering varied entry points and scaffolding options, teachers can accommodate diverse learners while maintaining high expectations.
Modifying materials may include adapting reading texts or using assistive technology tools like text-to-speech software or alternative communication devices. These modifications ensure that students can access curriculum content at their instructional level.
Transition Planning for Students with IEPs:
Transition planning is a critical component of an IEP that focuses on preparing students for life beyond school. It aims to facilitate successful transitions into post-secondary education or employment by setting appropriate goals and providing necessary support.
Transition planning should start early in a student’s educational journey to allow sufficient time for exploration, skill development, and goal-setting. The process typically involves collaboration between educators, parents/guardians, vocational specialists, community resources agencies,and the student themselves when appropriate
During transition planning meetings,discussions often revolve around identifying career interests,personal skills inventory ,exploring post-secondary education options,researching vocational programs available locally as well as understanding eligibility criteria.The team discusses possibilities for gaining work experience through internships, job shadowing, or vocational training programs.
Accommodations and Modifications in IEPs:
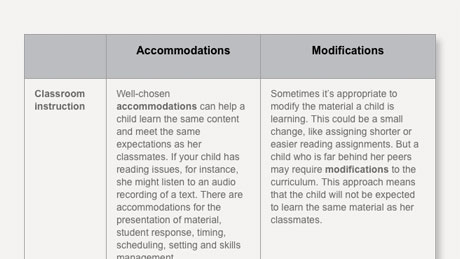
Accommodations and modifications are essential components of an IEP that aim to support students’ access to the general education curriculum. Accommodations refer to changes made in how a student learns or demonstrates knowledge without altering the content. These may include extended time for assignments or tests, preferential seating, use of assistive technology devices, or visual aids.
Modifications involve altering the curriculum standards themselves, allowing students to learn at their instructional level. This might include simplifying reading materials, reducing the number of math problems required for mastery, or providing alternative assessments.
Individualized Goal-Setting in IEPs:
IEPs should include individualized goals that address each student’s unique needs and abilities. These goals should be specific, measurable, attainable,relevant,and time-bound (SMART). Goals can encompass various areas such as academic achievement, social-emotional development,self-help skills,speech/language development,motor skills(daily living activities) ,and behavior management.
Collaborating with Parents and Guardians on IEP Development:
Parents/guardians play a vital role in developing effective IEPs as they possess invaluable insights into their child’s strengths,challenges,and preferences. Collaboration between parents/guardians and school staff fosters a shared understanding of the child’s needs and supports ongoing communication throughout the process.
To enhance collaboration,person-centered planning meetings should take place where parents/guardians actively participate along with educators.School personnel must ensure that parents/guardians feel welcomed,valued,and empowered during these discussions.Parental contribution helps create comprehensive plans tailored to each student’s requirements while also promoting a sense of ownership among all stakeholders
Assistive Technology in IEPs:
Assistive technology (AT) refers to tools,digital resources,equipment,and software designed to support students with disabilities.Assistive technology can enhance communication,access to information,learning opportunities and promote greater independence in various learning environments.
IEPs can include provisions for using assistive technology based on the student’s specific needs.Accessibility options might include text-to-speech software,speech-to-text programs,communication devices with alternative input methods such as switches or eye-gaze systems,and specialized equipment like mobility aids or hearing amplification devices.
The integration of assistive technology within IEPs promotes inclusion and empowers students to participate more fully in educational activities. It is essential that teachers receive training on how to effectively implement assistive technology tools and strategies to maximize their impact on student learning outcomes.
Leave a comment