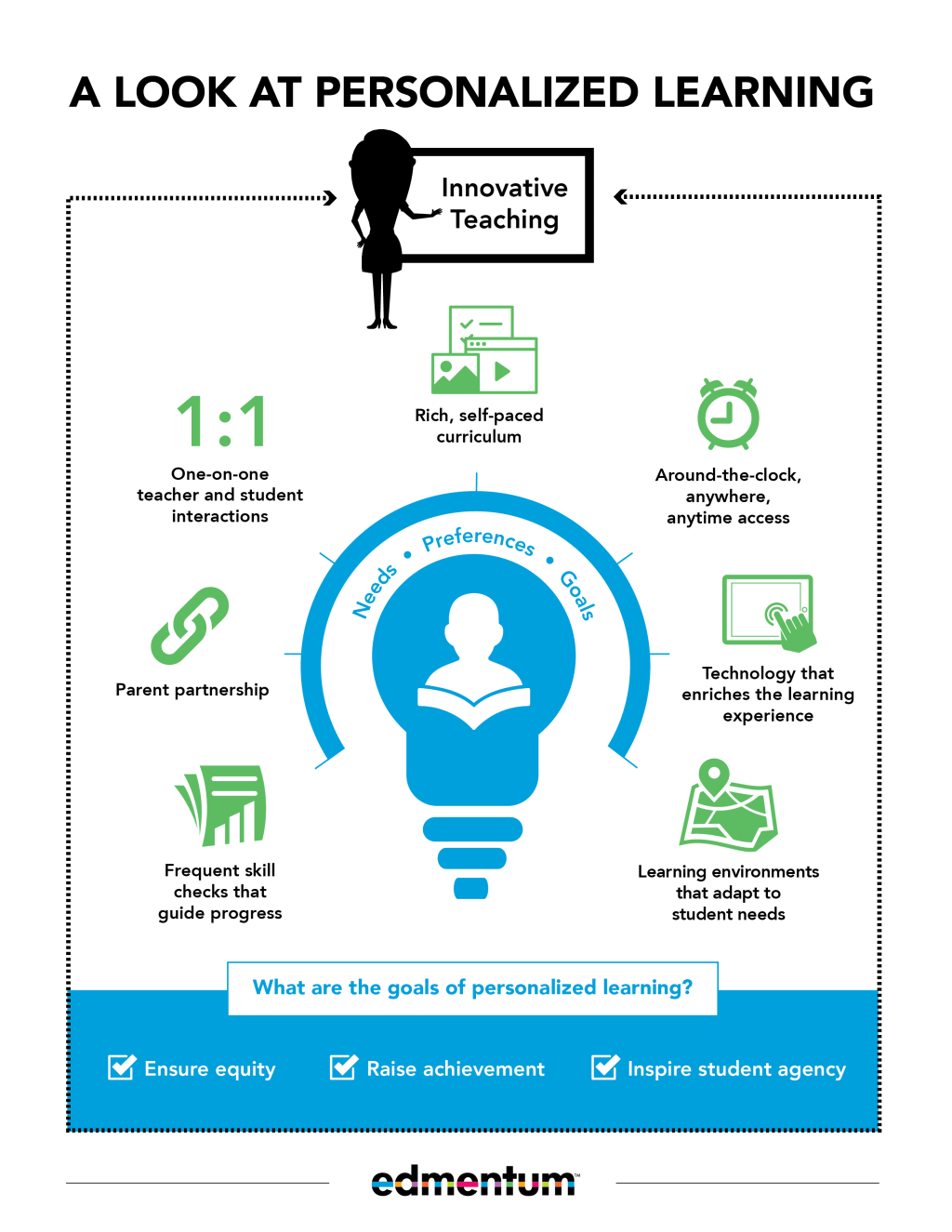
Differentiated instruction, individualized learning plans, and self-paced learning are all key components of personalized education. These approaches recognize that students have different strengths, weaknesses, and learning styles, and aim to tailor instruction to meet their specific needs. In alternative schools, where the focus is often on providing a more individualized and flexible educational experience for students, these strategies can be particularly effective.
1. Differentiated Instruction:
Differentiated instruction involves modifying teaching methods, materials, and assessments to accommodate the diverse learning needs of students. This approach acknowledges that students learn at different paces and through various modalities. In alternative schools, educators may use a variety of instructional techniques such as small group work or one-on-one tutoring to deliver content in ways that resonate with each student.
2. Individualized Learning Plans (ILPs):
Individualized learning plans are customized roadmaps that outline specific goals, objectives, and strategies for each student’s education journey. ILPs take into consideration a student’s interests, strengths, weaknesses, and aspirations to create personalized pathways toward academic success. Alternative schools often utilize ILPs as a way to empower students in taking ownership of their education.
3. Self-Paced Learning:
Self-paced learning allows students to progress through material at their own speed rather than adhere to a fixed schedule imposed by traditional classroom settings. This approach recognizes that learners differ in terms of readiness levels and preferred pace of learning. Alternative schools may offer online courses or digital platforms where students can access resources independently and move through lessons according to their own abilities.
4. Project-Based Learning in Alternative Schools:
Project-based learning (PBL) is an instructional method that promotes active engagement by presenting real-world problems or challenges for students to solve collaboratively using critical thinking skills. In alternative schools where creativity and experiential learning are emphasized, PBL plays an integral role in fostering deeper understanding of concepts while promoting teamwork among peers.
5. Personalized Assessment Methods:
Personalized assessment methods go beyond traditional tests and exams to evaluate student learning. These approaches allow students to demonstrate their understanding through various means, such as portfolios, presentations, or performances. Alternative schools often prioritize authentic assessments that reflect real-life scenarios and provide a more comprehensive view of students’ abilities.
6. Adaptive Technology for Personalized Learning:
Adaptive technology refers to digital tools and software that adapt content and delivery based on individual needs, preferences, and progress. In alternative schools, adaptive technology can be used to tailor instruction in real-time by providing personalized feedback, scaffolding support, and offering additional resources when needed.
7. Social-Emotional Learning (SEL) in Alternative Education Settings:
Social-emotional learning focuses on developing students’ emotional intelligence, self-awareness, empathy, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making abilities. In alternative education settings where the emphasis is on holistic development rather than just academic achievement, SEL is integrated into the curriculum to nurture well-rounded individuals.
8. Personalized Learning for Students with Special Needs:
Personalized learning can greatly benefit students with special needs by accommodating their unique challenges and strengths. Individualized education plans (IEPs) are commonly used in alternative schools to address specific learning disabilities or developmental differences effectively.
9. Personalized Learning for Gifted and Talented Students:
Gifted and talented students also require personalized learning experiences that challenge them intellectually while nurturing their talents further. Alternative schools often offer accelerated programs or enrichment opportunities tailored specifically for these high-achieving learners.
10. Personalized Learning and Student Motivation:
Personalization has been shown to increase student motivation as it allows learners to connect with material that aligns with their interests and goals directly. By tailoring instruction to individual needs in alternative schooling environments, educators can cultivate a sense of ownership over one’s education which leads to increased engagement.
11.Personalized Learning And Student Engagement Strategies:
Student engagement strategies play a vital role in personalized education. Alternative schools employ various techniques such as hands-on activities, flipped classrooms, and project-based learning to actively involve students in their own learning process.
12. Personalized Learning And Student Agency:
Personalized learning fosters student agency by giving learners more autonomy and choice in their educational journey. In alternative schools that prioritize student-centered approaches, students are encouraged to set goals, make decisions about their learning paths, and reflect on their progress regularly.
13. Peer Collaboration In Personalized Learning Environments:
Collaboration with peers is an essential component of personalized learning as it provides opportunities for students to learn from one another, develop social skills, and gain different perspectives. Alternative schools often create structures and spaces that facilitate peer collaboration through group projects or cooperative learning activities.
14. Teacher Roles In Personalized Learning Settings:
In personalized education settings, teachers play the role of facilitators rather than traditional instructors who deliver content knowledge exclusively. They guide students’ individual journeys by providing support, resources, feedback, and helping them set achievable goals.
15. Parent Involvement In Personalized Education:
Parent involvement is crucial for successful personalized education implementation. Alternative schools often foster strong partnerships between parents and educators through regular communication channels like parent-teacher conferences or workshops where parents can learn about personalized approaches used in the school.
16.Personalized Learning And Cultural Responsiveness:
Cultural responsiveness involves acknowledging and valuing diverse cultural backgrounds within the educational context while adapting teaching practices accordingly. In alternative schooling models that serve a wide range of student populations with varying cultural identities, incorporating culturally responsive strategies into personalized instruction is vital for creating an inclusive environment.
17.Personalized Learning And Inclusive Practices:
Inclusive practices ensure that all students have equal access to quality education regardless of their background or abilities. Alternative schools strive to provide tailored supports for learners with diverse needs through individual accommodations or specialized programs designed specifically for underrepresented groups.
18.Competency-Based Education (CBE) In Alternative Schools:
Competency-based education focuses on students mastering specific skills and knowledge rather than simply progressing through a curriculum based on time spent in class. Alternative schools often adopt CBE principles to provide personalized learning experiences where students can progress at their own pace.
19.Micro-Credentials And Badges For Personalized Learning:
Micro-credentials and badges are digital certificates that recognize specific skills or achievements. In alternative schools, these credentials can be used as evidence of individual progress and mastery within personalized learning pathways.
20.Data-Driven Decision Making In Personalized Education:
Data-driven decision making involves using student data to inform instructional practices and personalize learning further. Alternative schools collect and analyze data on student performance, engagement, and growth to make informed decisions about curriculum design, instructional strategies, and interventions.
21.Professional Development For Teachers Implementing Personalized Learning:
To effectively implement personalized learning approaches in alternative schools, teachers require ongoing professional development opportunities. These programs equip educators with the necessary knowledge, skills, and strategies for designing personalized instruction that meets the diverse needs of their students.
22.Equity Considerations In Personalized Education:
Equity is a critical consideration in personalized education to ensure that all students have access to high-quality educational opportunities regardless of socioeconomic status or background. Alternative schools must strive for equitable practices by providing targeted supports for marginalized populations while addressing systemic barriers that impede educational equity.
23.Student Voice And Choice In Alternative Schooling Models:
Alternative schooling models prioritize student voice and choice by involving learners actively in decision-making processes regarding their education. Students are encouraged to express their interests, preferences, concerns, and goals so that their educational experience reflects their unique needs.
24.Flexible Scheduling And Time Management In Personalized Education:
Flexible scheduling allows students in alternative schools to structure their day according to individual preferences while managing time effectively. This flexibility enables learners to engage deeply with content when they are most alert or productive while accommodating personal commitments or interests.
25.Community Partnerships For Personalized Learning Opportunities:
Community partnerships offer alternative schools opportunities to provide real-world learning experiences that complement personalized education. Collaboration with local businesses, organizations, or experts allows students to connect classroom learning with the outside world and gain practical skills.
In conclusion, personalized education in alternative schools encompasses a wide range of strategies and approaches that aim to tailor instruction to meet the diverse needs of students. By implementing differentiated instruction, individualized learning plans, self-paced learning, project-based learning, and other personalized techniques, educators can create an environment where students feel empowered and supported in their educational journey. Additionally, considerations such as cultural responsiveness, inclusive practices, equity considerations, and community partnerships contribute to a holistic approach that fosters student agency and engagement while promoting academic growth.
Leave a comment