Assessing Collaboration and Teamwork Skills: Unlocking the Potential of Alternative Education
In today’s rapidly evolving world, collaboration and teamwork have become essential skills for success in both personal and professional spheres. Traditional educational systems often focus primarily on individual achievement, leaving little room for students to develop these critical abilities. However, alternative schooling and education approaches recognize the importance of fostering collaboration skills from an early age.
Assessing collaboration and teamwork skills is a multifaceted task that requires a holistic approach. It involves evaluating not only students’ ability to work effectively with others but also their communication, problem-solving, leadership, and adaptability skills. This article explores various methods used by alternative schools to assess collaboration and teamwork skills among their students.
1. Project-Based Learning:
Project-based learning (PBL) is at the core of many alternative educational models. In PBL, students engage in real-world projects that require them to collaborate with peers towards a common goal. Throughout the project duration, educators observe how well individuals contribute to group discussions, share responsibilities, seek consensus when making decisions, and communicate effectively.
To assess collaboration within PBL frameworks accurately, teachers may use rubrics that outline specific criteria such as active listening, constructive feedback giving/receiving abilities or regular reflections on group dynamics.
2. Cooperative Learning Structures:
Cooperative learning structures provide opportunities for students to interact positively with their peers while working towards academic objectives together. These structures range from simple pair-share activities to more complex group projects where each member has assigned roles or tasks.
During cooperative learning activities or projects like jigsaw puzzles or debates structured by teachers in alternative education settings; educators can observe how well participants collaborate by assessing their ability to actively listen to others’ ideas respectfully debate opinions without resorting to personal attacks or showing empathy towards fellow teammates.
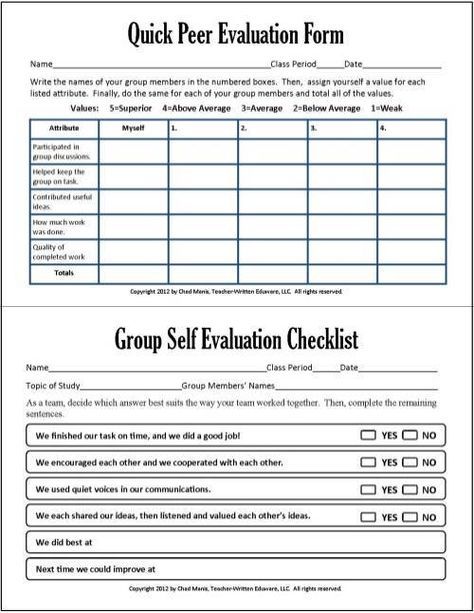
3. Peer Evaluation:
Peer evaluation allows students themselves to assess each other’s contributions during collaborative tasks actively. This not only encourages self-reflection but also promotes a sense of accountability and responsibility among students. Peer evaluations can be conducted through structured questionnaires, interviews, or even group discussions facilitated by an educator.
Alternative education models often integrate peer evaluation as a regular practice, providing valuable feedback to individuals about their collaboration skills. This process fosters self-awareness and encourages students to reflect on their strengths and areas for improvement.
4. Experiential Learning:
Experiential learning immerses students in real-world scenarios where they must collaborate with others to solve problems or achieve specific goals. These experiences can range from outdoor adventure activities to community service projects or internships.
Assessing collaboration during experiential learning involves observing how well students adapt to new situations, work effectively within diverse teams, demonstrate leadership when necessary, and communicate with stakeholders outside the classroom environment. Educators may use reflective journals, personal interviews, or group presentations as assessment tools for these experiences.
5. Collaborative Reflection:
Reflection plays a crucial role in assessing collaboration skills. Alternative schools often provide dedicated time and space for collaborative reflection sessions where students discuss their teamwork experiences openly. During these sessions, educators facilitate conversations that encourage participants to identify successful strategies used within the team dynamic while also addressing challenges faced along the way.
Collaborative reflections help individuals recognize their growth areas and develop action plans for future collaborations better. Educators may document key takeaways from these discussions as part of the assessment process while also making note of individual contributions towards facilitating meaningful dialogue within the group.
In conclusion, assessing collaboration and teamwork skills is an essential aspect of alternative schooling and education approaches that aim to prepare students for success in today’s world. Through project-based learning, cooperative structures, peer evaluation techniques, experiential learning opportunities, and collaborative reflection sessions; alternative schools offer comprehensive methods for evaluating collaboration abilities among their learners.
By incorporating these varied assessment practices into their curricula; alternative educational institutions foster an environment that values collaboration, encourages empathy, and equips students with the skills necessary to thrive in collaborative settings throughout their lives.
Leave a comment