Project-Based Learning: Unlocking the Potential of Alternative Education
Introduction:
In a world that is constantly evolving, so too must our approach to education. Traditional methods of teaching and learning have their merits, but they often fail to fully prepare students for the challenges and opportunities that await them beyond the classroom walls. As a result, alternative forms of education are gaining popularity, with Project-Based Learning (PBL) emerging as one of the most effective ways to engage students in meaningful and impactful learning experiences. In this article, we will explore what PBL is all about, its benefits, and how it can revolutionize education.
What is Project-Based Learning?
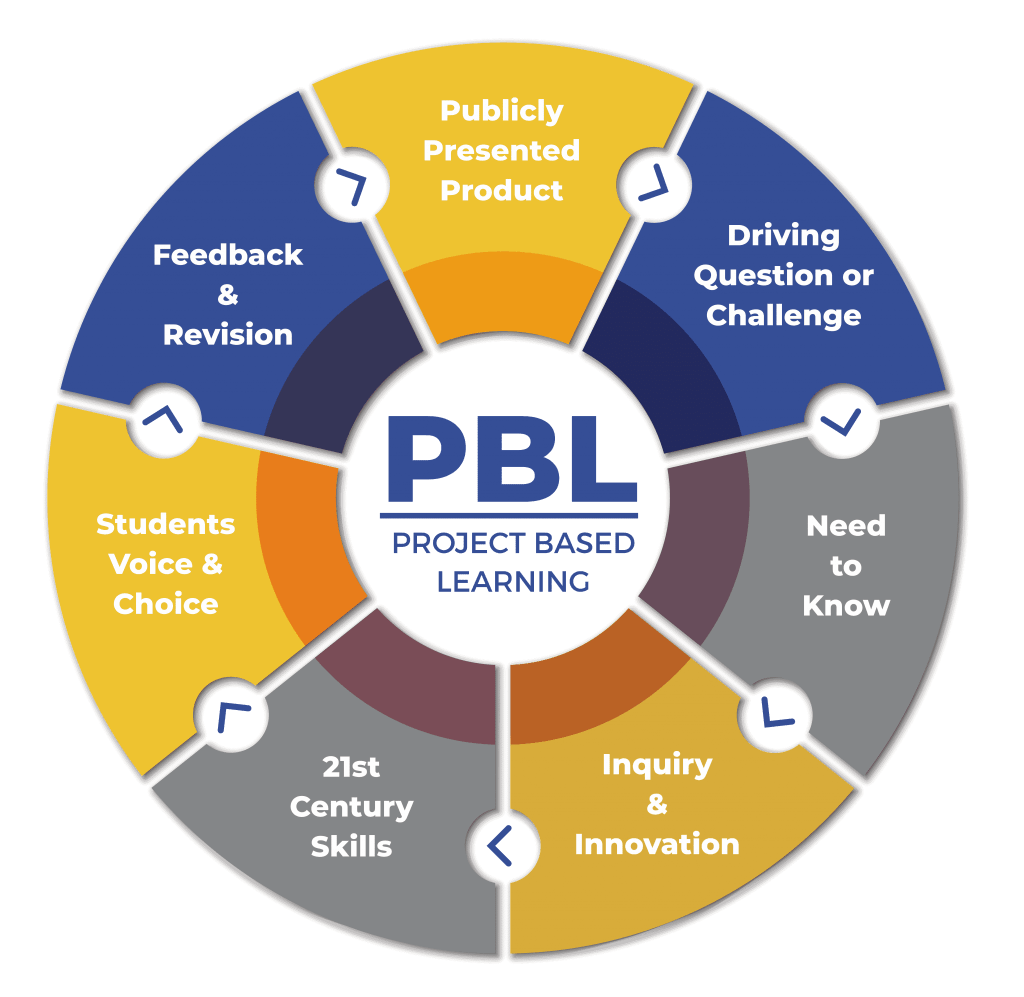
At its core, Project-Based Learning is an instructional method that allows students to learn through hands-on projects or tasks that are relevant and meaningful to them. Unlike traditional approaches where teachers dispense knowledge from textbooks or lectures, PBL puts students at the center of their own learning by empowering them to take ownership over their education.
In a project-based classroom setting, teachers act as facilitators rather than lecturers. They guide students through open-ended questions and encourage critical thinking skills while providing support and structure when needed. Projects can span across various subjects or disciplines – be it science, math, history or even art – allowing for interdisciplinary learning that mirrors real-world problem-solving scenarios.
The Benefits of Project-Based Learning:
1. Engaged Learners: One of the key advantages of PBL is its ability to captivate student interest by making learning relevant and applicable in real-world contexts. By working on projects that reflect issues they care about or problems they want to solve, students become deeply engaged in their studies.
2. Authentic Assessments: PBL assessments go beyond traditional tests or exams; instead, they focus on evaluating a student’s ability to apply knowledge creatively in practical settings. Through presentations, demonstrations or portfolios showcasing their work process and final product outcomes, learners develop crucial communication skills essential in professional and personal life.
3. Collaboration: PBL encourages students to work together, fostering collaboration, teamwork, and communication skills that are highly valued in the workplace. By collaborating with peers on projects, learners gain exposure to diverse perspectives and learn how to navigate challenges as a team – an invaluable skill for success in the 21st-century workforce.
4. Critical Thinking Skills: Projects often require students to tackle complex problems where there may be no clear-cut answers. This pushes learners to think critically, analyze information from various sources, evaluate options, make decisions and defend their choices – skills that are indispensable for lifelong learning.
5. Creativity and Innovation: PBL provides an environment where creativity thrives. As they design solutions or create products related to their project topic, students have the freedom to express themselves creatively and explore innovative ideas without fear of failure or judgment.
6. Long-Term Knowledge Retention: Research has shown that when students actively participate in their learning through hands-on experiences like those found in PBL classrooms, they retain knowledge at a deeper level compared to passive learning methods such as lectures or memorization-based assessments.
Implementing Project-Based Learning:
To successfully implement PBL in schools requires careful planning and support from administrators, teachers, parents/guardians, and the wider community. Here are some key considerations:
1. Professional Development: Teachers need training on how to effectively facilitate project-based classrooms by understanding its principles and methodologies. Providing ongoing professional development opportunities ensures educators have the necessary skills needed for successful implementation.
2. Curriculum Alignment: Aligning projects with curriculum standards is crucial; this ensures that content is covered while allowing room for student choice within defined parameters set by educational institutions.
3. Resources: Accessible resources play a vital role in executing well-designed projects effectively. Schools should invest in materials such as technology tools (computers/laptops), art supplies or scientific equipment depending on project requirements.
4. Community Engagement: Engaging the local community and leveraging its resources can enhance project outcomes. Experts from various fields, mentors or community spaces can provide additional guidance, support and authentic learning experiences.
5. Reflection and Feedback: Regular opportunities for students to reflect on their learning journey and receive constructive feedback are essential components of PBL. This helps learners refine their skills, self-assess growth areas, set goals for improvement and build a lifelong love for learning.
Conclusion:
Project-Based Learning is an exciting approach that challenges traditional educational norms by placing students at the forefront of their education. By fostering engagement, critical thinking skills, collaboration, creativity, and innovation – PBL equips learners with the knowledge and competencies necessary to thrive in a rapidly changing world. As alternative forms of education continue to gain traction worldwide, project-based classrooms offer a promising solution to ensure students develop the skills they need to succeed beyond school walls.
Leave a comment