Personalized Learning Plans
In today’s rapidly evolving educational landscape, traditional schooling models are being challenged and alternative approaches to education are gaining popularity. One such approach is personalized learning, which tailors education to the unique needs, interests, and abilities of each individual student.
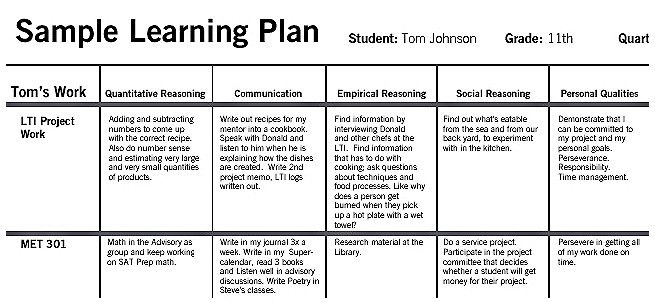
Personalized learning plans (PLPs) are at the core of this approach. PLPs outline a roadmap for students’ academic journey, taking into account their strengths, weaknesses, goals, and aspirations. These plans provide students with a sense of ownership over their education and allow them to take control of their learning process.
The key advantage of personalized learning plans is that they promote student-centered instruction. Instead of following a one-size-fits-all curriculum, PLPs enable educators to design customized lessons that cater to individual student needs. This targeted instruction ensures that students receive the support they need in areas where they struggle while also allowing them to excel in subjects where they have natural talents or interests.
Project-Based Learning
Project-based learning (PBL) is an innovative teaching method that engages students through hands-on projects and real-world problem-solving activities. PBL shifts the focus from rote memorization and passive absorption of information towards active participation and application of knowledge.
In a project-based learning environment, students collaborate on meaningful projects that require critical thinking skills, creativity, communication abilities, and teamwork. By working on these projects autonomously or in groups under the guidance of teachers or mentors, students develop important 21st-century skills such as collaboration and problem-solving.
Competency-Based Education
Competency-based education (CBE) focuses on mastery rather than seat time or completion of coursework within a specific timeframe. In CBE programs, students progress based on demonstrated proficiency in specific competencies rather than simply advancing grade levels based on time spent in class.
This approach allows learners to move at their own pace by focusing on mastering essential knowledge and skills before moving forward. It eliminates the pressure of “keeping up” with peers and promotes a deeper understanding of concepts.
Gamification in Self-Paced Learning
Gamification is the integration of game elements and mechanics into non-game contexts, such as education. In self-paced learning environments, gamification can be used to enhance student engagement and motivation.
By incorporating elements like points, badges, leaderboards, and rewards into the learning process, educators can tap into students’ natural inclination towards competition and achievement. Gamified self-paced learning platforms provide immediate feedback, encourage goal-setting, and create a sense of accomplishment that motivates students to continue their educational journey.
Peer-to-Peer Collaboration in Alternative Schooling
Collaboration is an essential skill for success in today’s interconnected world. Alternative schooling approaches emphasize the importance of peer-to-peer collaboration as a means to foster social skills, teamwork abilities, empathy, and communication.
In alternative education settings, students are encouraged to work together on projects or participate in group discussions where they can exchange ideas, learn from one another’s experiences and perspectives while developing essential interpersonal skills.
Self-Assessment and Reflection Techniques
Self-assessment is a valuable tool for promoting metacognition – the ability to reflect on one’s own thinking processes. By engaging students in regular self-assessment activities such as journaling or reflective writing exercises after completing tasks or projects, educators help them develop a deeper understanding of their strengths and weaknesses.
These techniques encourage students to take ownership of their learning by identifying areas that need improvement or further exploration. Self-reflection also fosters critical thinking skills as learners evaluate their progress towards goals and consider strategies for improvement.
Using Technology for Self-Paced Learning
Technology has revolutionized education by providing new tools for personalized instruction. In self-paced learning environments specifically designed around technology platforms or online resources offer opportunities for individualized instruction tailored to each student’s needs.
Educational software applications enable adaptive learning experiences that adjust content based on individual progress levels. Online platforms provide access to vast resources, interactive simulations, and virtual laboratories that enhance the learning experience beyond the traditional classroom limitations.
Incorporating Mindfulness Practices in Alternative Education
Mindfulness practices are gaining recognition for their potential in promoting emotional well-being, reducing stress, enhancing focus, and improving overall mental health. Integrating mindfulness techniques into alternative education models can help students develop emotional self-regulation skills and increase their resilience in the face of challenges.
Practices such as mindful breathing exercises or guided meditations can be incorporated into daily routines to create a calm and focused learning environment. Mindful movement activities like yoga or tai chi can also help students release physical tension and improve body awareness.
Differentiated Instruction in Self-Paced Learning Environments
Differentiated instruction is an approach that recognizes and accommodates diverse student needs within the same classroom. In self-paced learning environments, differentiated instruction becomes even more crucial as learners progress at their own pace.
Teachers must design instructional materials that cater to different learning styles, preferences, abilities, interests, and prior knowledge levels. By providing multiple pathways to mastery through varied instructional methods (e.g., visual aids, hands-on activities), educators ensure that all students have equal opportunities for success.
Building Resilience and Perseverance Through Self-Paced Learning
Self-paced learning settings offer unique opportunities for developing resilience – the ability to bounce back from setbacks – and perseverance – sticking with tasks until completion. These qualities are essential for success both academically and personally.
In self-paced environments where learners have more control over their educational journey, they encounter challenges such as time management issues or difficulty grasping complex concepts independently. Overcoming these obstacles requires resilience-building strategies such as maintaining a growth mindset (believing intelligence is not fixed) or seeking support from peers or mentors when needed.
Balancing Structure and Flexibility in Alternative Schooling
Alternative schooling models often strive to strike a balance between structure – necessary for creating a supportive and productive learning environment – and flexibility – allowing students to take ownership of their education.
While structure provides a framework for learning goals, deadlines, and expectations, flexibility allows for personalized pacing, individual interests, and exploration. Finding the right balance between these elements ensures that students have the guidance they need while still having room for self-direction and autonomy.
Supporting Students with Special Needs in Self-Paced Learning Settings
Self-paced learning can be particularly beneficial for students with special needs as it allows them to progress at their own pace without feeling rushed or left behind. However, additional support may be required to cater to their unique needs effectively.
Teachers must ensure that instructional materials are accessible and adaptable according to individual requirements. Providing assistive technologies, accommodations, or modifications can empower students with special needs to fully participate in the self-paced learning experience.
Fostering Creativity and Innovation in Alternative Education Models
Creativity is a vital skill in today’s rapidly changing world. Alternative education models provide opportunities for fostering creativity by encouraging open-ended projects or problem-solving activities that require innovative thinking.
By incorporating arts-based activities such as visual arts, music, drama into the curriculum or providing freedom within assignments for creative expression through writing or design projects educators foster imagination and originality among learners.
Cultivating a Growth Mindset in Self-Paced Learners
A growth mindset is the belief that intelligence is not fixed but can be developed through effort and perseverance. In self-paced learning environments where learners face challenges independently, cultivating a growth mindset becomes crucial for success.
Educators play an essential role in promoting this mindset by providing constructive feedback that focuses on effort rather than outcome. Encouraging reflection on mistakes as opportunities for growth helps learners develop resilience when faced with setbacks.
Social-Emotional Learning Strategies for Alternative Schooling
Social-emotional learning (SEL) refers to acquiring skills related to emotional intelligence, empathy development, relationship building, responsible decision-making, and self-awareness. Alternative schooling models often prioritize SEL as a means to develop well-rounded individuals.
Educators can incorporate SEL strategies into the curriculum by explicitly teaching skills such as active listening, conflict resolution, or emotional regulation. Creating a safe and inclusive classroom environment that promotes open dialogue and empathy also supports social-emotional growth among students.
Integrating Arts and Culture into Self-Paced Learning Curricula
Arts and culture play a crucial role in fostering creativity, critical thinking, cultural appreciation, and personal expression. Integrating arts-based activities or cultural studies into self-paced learning curricula enriches the educational experience beyond traditional subjects.
By exploring different art forms (e.g., painting, music) or studying diverse cultures’ history and traditions, learners develop a broader perspective of the world while nurturing their own creativity.
Promoting Inclusivity and Diversity in Alternative Education
Inclusivity is an essential aspect of alternative education models. These approaches strive to create inclusive environments where all learners feel valued regardless of their backgrounds, abilities, gender identities, or socio-economic status.
Educational materials should reflect diversity through culturally responsive teaching practices that acknowledge students’ unique experiences. Encouraging respectful discussions about diversity issues fosters understanding among peers while promoting inclusivity within alternative schooling settings.
Developing Critical Thinking Skills Through Self-Directed Learning
Critical thinking skills are fundamental for problem-solving, analysis, decision-making – skills required for success in academic pursuits as well as everyday life. In self-paced learning environments where students take charge of their educational journey independently,
educators must design tasks that require higher-order thinking skills such as analyzing information from multiple sources or evaluating arguments based on evidence. Providing opportunities for inquiry-based learning encourages curiosity while developing critical thinking abilities.
Nurturing Student Autonomy and Independence in Alternative Schooling
One key benefit of alternative schooling approaches is empowering students to take ownership of their education by cultivating autonomy and independence. Learners are encouraged to set goals, manage their time, make choices about the pace and direction of their learning.
Teachers act as facilitators or guides, providing support and resources when needed. This autonomy fosters self-confidence, self-motivation, and a sense of responsibility for one’s own learning journey.
Addressing Challenges of Motivation and Accountability in Self-Paced Learning
While self-paced learning offers flexibility and personalization benefits, it also presents challenges related to motivation and accountability. Without traditional classroom structures or external pressure,
some students may struggle with staying motivated or meeting deadlines. To address these challenges educators can incorporate strategies such as goal-setting exercises, regular check-ins with students or peer-to-peer accountability systems.
Exploring Non-Traditional Assessment Methods for Alternative Education
Alternative schooling models often call for non-traditional assessment methods that go beyond standardized tests or quizzes. These approaches focus on assessing learners’ practical skills, creativity levels,
problem-solving abilities through portfolios, presentations, performances or project-based assessments. This shift allows educators to evaluate a broader range of competencies while encouraging student-centered instruction.
Creating a Positive Classroom Culture Within a Self-Paced Environment
In alternative education settings where students work independently at their own pace creating a positive classroom culture becomes essential for fostering collaboration,
supportive environments within which students feel comfortable asking questions seeking guidance from peers without fear of judgment. Educators can create this culture by promoting respect empathy among classmates celebrating achievements encouraging teamwork.
Encouraging Lifelong Learning Habits Through Alternative Schooling Approaches
Alternative schooling approaches aim to instill lifelong learning habits that extend beyond formal education years. By emphasizing the value of curiosity exploration independent thinking,
alternative education models prepare learners to adapt thrive in an ever-changing world encourages them to continue seeking knowledge throughout their lives regardless of age occupation.
Supporting Parental Involvement and Engagement in Self-Paced Education
Parental involvement is crucial for educational success especially in self-paced learning environments where parents play a significant role in supporting their child’s learning journey.
Educators can foster parental involvement by regularly communicating sharing progress updates involving parents in goal-setting activities providing resources or workshops that support parents in facilitating their child’s education at home.
Examining the Role of Mentors and Coaches in Alternative Educational Settings
Mentors coaches play a significant role in alternative educational settings by guiding learners offering personalized support guidance throughout their educational journey. These individuals provide expertise,
motivation, emotional support, and accountability as students navigate self-paced learning environments. The mentor-coach relationship helps learners set goals develop strategies for success while building essential life skills such as communication problem-solving abilities.
In conclusion, alternative schooling approaches offer innovative solutions to traditional education challenges. Personalized learning plans, project-based learning competency-based education, gamification peer-to-peer collaboration,
self-assessment and reflection techniques technology integration mindfulness practices differentiated instruction resilience-building inclusive strategies critical thinking development autonomy fostering are some key components alternative schooling models. By implementing these approaches educators create engaging supportive environments where students thrive become lifelong learners equipped succeed beyond classroom walls
Leave a comment