The Socratic method is a powerful tool that can be used in various educational settings to promote student-centered learning, critical thinking skills, and meaningful dialogue. In alternative education schools, where innovative approaches to teaching and learning are embraced, incorporating the Socratic method can have profound effects on student engagement and academic growth.
1. The Role of Questioning in Student-Centered Learning
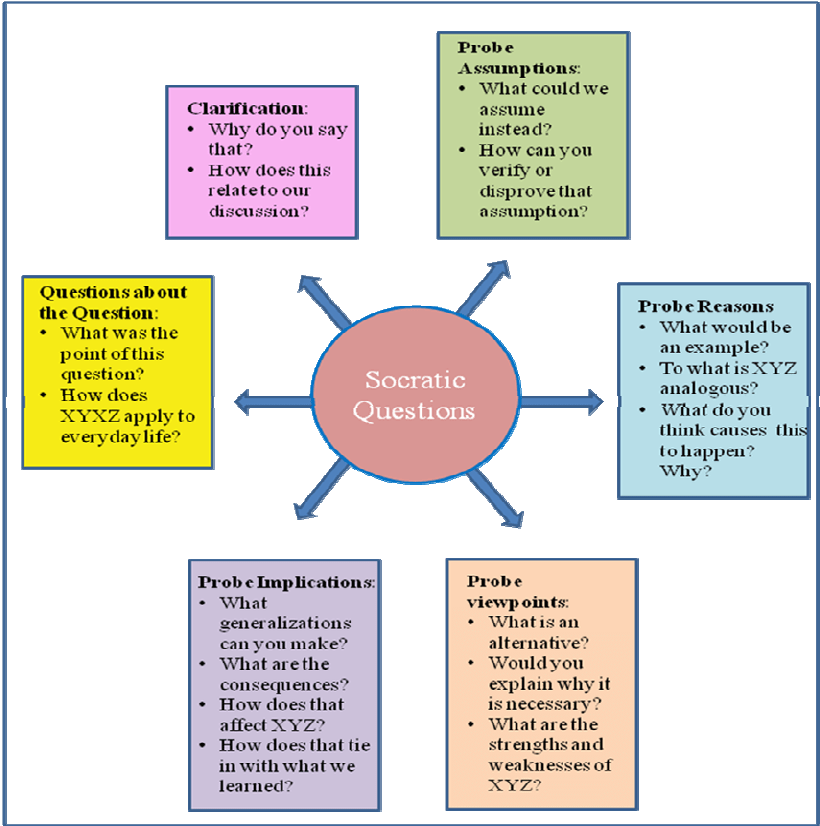
At the heart of the Socratic method lies the art of questioning. By asking thought-provoking questions, teachers encourage students to think deeply about a topic or problem and arrive at their own conclusions through active participation. This process shifts the focus from mere memorization of facts to fostering a deeper understanding and critical analysis.
In student-centered learning environments, where students take ownership of their learning journey, questioning plays a central role. Instead of simply providing answers or information, teachers facilitate discussions by asking open-ended questions that stimulate curiosity and encourage exploration. This allows students to develop their own ideas and perspectives while engaging with diverse viewpoints.
2. Incorporating Socratic Seminars in Alternative Education Settings
Socratic seminars provide an ideal platform for incorporating the Socratic method into alternative education settings. These seminars involve small groups of students engaging in thoughtful conversation guided by essential questions related to a specific text or topic.
During these seminars, participants are encouraged to actively listen to one another’s perspectives while respectfully challenging assumptions and exploring multiple viewpoints. The facilitator’s role is crucial in guiding the discussion without dominating it, ensuring all voices are heard.
By implementing Socratic seminars within alternative education schools, educators create opportunities for deep reflection on complex issues while nurturing important communication skills such as active listening and respectful dialogue.
3. Adapting the Socratic Method for Project-Based Learning
Project-based learning (PBL) is an effective approach employed in many alternative education settings due to its emphasis on real-world application of knowledge and collaborative problem-solving skills.
By integrating elements of the Socratic method into PBL, students are encouraged to think critically about the project’s driving questions and reflect on their progress. Teachers can guide this process by posing Socratic questions that prompt students to evaluate their research methods, analyze data, and make connections between different aspects of the project.
This adaptation of the Socratic method in project-based learning not only leads to a deeper understanding of the topic at hand but also fosters skills such as self-reflection, metacognition, and effective communication.
4. Using the Socratic Method to Develop Critical Thinking Skills in Students
Critical thinking is a fundamental skill for success in both education and life beyond the classroom. The Socratic method provides an excellent framework for developing critical thinking skills by challenging assumptions, encouraging evidence-based reasoning, and promoting logical analysis.
Through Socratic questioning techniques such as probing for evidence, examining underlying assumptions, exploring counterarguments, and evaluating implications, students learn how to approach problems from multiple perspectives.
By incorporating regular opportunities for Socratic dialogue within alternative education schools, educators can nurture critical thinking skills that empower students to become independent learners and thoughtful contributors to society.
5. Exploring the Historical Origins of the Socratic Method and Its Relevance Today
The Socratic method takes its name from Greek philosopher Socrates who used questioning as a means of guiding his students towards discovering truth through self-examination. While it has ancient roots, its relevance remains undeniable in contemporary educational settings.
In today’s rapidly changing world where information is readily available but discernment is crucially needed, teaching students how to ask meaningful questions becomes even more important. The ability to engage with complex issues critically allows individuals to navigate diverse perspectives effectively while making informed decisions.
Understanding the historical origins of the Socratic method helps educators appreciate its timeless value in empowering students with intellectual curiosity and open-mindedness.
6. Applying the Socratic Method to Foster Empathy and Understanding in Classrooms
Empathy is another vital skill often fostered in alternative education schools. By incorporating the Socratic method, educators can guide students to develop empathy by encouraging them to consider multiple perspectives and understand the underlying motivations or experiences of others.
Through carefully crafted questions that prompt students to explore different viewpoints, teachers create opportunities for students to challenge their own assumptions and engage in compassionate dialogue. This practice not only enhances understanding but also cultivates a sense of empathy and respect for diverse perspectives among students.
7. Utilizing Technology to Enhance Socratic Discussions in Alternative Education
Incorporating technology into Socratic discussions can enhance engagement, collaboration, and accessibility within alternative education settings.
Online platforms such as discussion boards or video conferencing tools allow for asynchronous or synchronous discussions, respectively. These digital tools enable a broader range of student voices to be heard while providing opportunities for reflection before contributing to the conversation.
Additionally, online resources like e-books or multimedia content can serve as prompts for Socratic questioning sessions, expanding the scope of topics that can be explored with students.
8. Integrating the Socratic Method into Interdisciplinary Curriculum Design
Alternative education often emphasizes interdisciplinary learning experiences that transcend traditional subject boundaries. The Socratic method aligns perfectly with this approach by promoting critical thinking across various disciplines.
By integrating the Socratic method into interdisciplinary curriculum design, educators encourage students to make connections between different subjects and apply critical thinking skills universally. This integration enables students to see how knowledge is interconnected rather than compartmentalized.
9. Addressing Cultural Diversity Through the Socratic Method in Alternative Schools
Cultural diversity is an essential aspect of alternative education settings where inclusivity is valued. The use of the Socratic method provides a platform where cultural differences can be acknowledged and celebrated through respectful dialogue.
Educators should pose questions that invite perspectives from diverse backgrounds while fostering an environment where all opinions are valued equally. This practice not only enhances cultural sensitivity but also promotes equity and inclusion within classrooms.
10. Examining the Impact of Teacher Facilitation on Socratic Dialogue in Education
The role of the teacher as a facilitator is crucial in Socratic dialogues. The way educators guide and structure discussions can significantly impact student engagement and learning outcomes.
Effective facilitation involves creating a safe and inclusive environment, asking thought-provoking questions, managing time effectively, encouraging active participation from all students, and providing constructive feedback.
By continuously reflecting on their facilitation techniques and seeking professional development opportunities related to the Socratic method, teachers can enhance their ability to foster meaningful dialogue among students.
11. Enhancing Student Engagement Through Active Participation in Socratic Discussions
Active participation is essential for successful implementation of the Socratic method. By actively engaging with questions posed by teachers or peers, students take ownership of their learning process while developing critical thinking skills.
To enhance student engagement during Socratic discussions, educators should create a supportive classroom culture that encourages risk-taking and values diverse perspectives. Additionally, incorporating small-group activities or incorporating multimedia resources can further stimulate active involvement from all students.
12. The Benefits of Incorporating Ethical Dilemmas into Socratic Questioning Sessions
Ethical dilemmas provide rich opportunities for exploring moral reasoning through the lens of the Socratic method. By presenting challenging scenarios or case studies that require thoughtful analysis and consideration of ethical principles, educators promote ethical decision-making skills among students.
Engaging in these discussions helps develop empathy, cultural sensitivity, responsible citizenship, and ethical leadership qualities – all essential attributes for individuals navigating an increasingly complex world.
13. Promoting Democratic Values and Civic Engagement through the Socratic Method
Alternative education schools often strive to empower students as active participants in democratic society. The use of the Socratic method aligns perfectly with this goal by fostering civic engagement through informed discussions about social issues and public policy decisions.
By posing questions related to democratic principles such as justice, equality, freedom of speech or assembly within a safe classroom environment, educators can encourage students to critically examine their own values and engage in responsible citizenship.
14. Supporting Social-Emotional Development through Reflective Questioning Techniques
Social-emotional development is a vital aspect of alternative education that focuses on the whole child. The Socratic method provides an avenue for supporting social-emotional growth by prompting self-reflection and emotional intelligence.
Through reflective questioning techniques, teachers create opportunities for students to explore their emotions, motivations, and reactions in response to different scenarios or texts. This practice enhances self-awareness, empathy towards others, and the ability to regulate emotions effectively.
15. The Role of Metacognition in Deepening Understanding during Socratic Dialogues
Metacognition refers to the ability to think about one’s own thinking processes. By incorporating metacognitive strategies within Socratic dialogues, educators help students develop awareness of their own learning approaches and become more effective learners.
Encouraging students to reflect on their thinking patterns during Socratic discussions promotes higher-order thinking skills such as analysis, evaluation, and synthesis. It also helps develop self-regulation skills necessary for independent learning beyond the classroom.
16. Using Literature as a Catalyst for Meaningful Socratic Conversations in Classrooms
Literature provides a rich source of material for engaging Socratic discussions within alternative education classrooms. By using novels, short stories, poetry or plays as catalysts for critical analysis and reflection, educators invite deep exploration of themes related to identity, society or human nature.
Through close reading practices coupled with thoughtful questioning techniques inspired by the Socratic method, students learn how literature can illuminate complex human experiences while encouraging empathy and understanding among diverse perspectives.
17. Nurturing Creativity and Divergent Thinking through Open-Ended Questioning Strategies
The Socratic method not only fosters critical thinking but also nurtures creativity by encouraging divergent thinking – generating multiple possibilities or solutions instead of focusing solely on finding one correct answer.
By employing open-ended questioning strategies that promote creative thinking, educators create an environment where students feel empowered to explore unconventional ideas and perspectives. This practice enhances problem-solving skills and encourages innovative approaches to learning.
18. Implementing Peer-Led Socratic Circles for Collaborative Learning Experiences
Peer-led Socratic circles provide a unique opportunity for collaborative learning experiences within alternative education settings. By allowing students to take turns facilitating discussions, this approach empowers them with leadership skills while promoting active engagement among peers.
Through peer-led Socratic circles, students learn from one another’s perspectives, develop communication skills, and build confidence in their ability to contribute meaningfully to the conversation. Educators play a supportive role by providing guidance and feedback during these sessions.
19. Exploring Different Variations of the Socratic Method across Alternative Educational Approaches
Alternative education encompasses a wide range of educational approaches such as Montessori, Waldorf, democratic schools or homeschooling. While each approach differs in its implementation, they all share a common goal – fostering student-centered learning environments.
Educators within alternative educational settings can explore different variations of the Socratic method that align with their specific pedagogical approaches. Adapting the essence of the Socratic method to suit the unique needs of each approach ensures its successful integration into alternative education classrooms.
20. Fostering Inclusive Classroom Environments through Equitable Participation in Socratic Discussions
Inclusivity is essential within alternative education schools where diversity is celebrated and valued. The use of equitable participation strategies during Socratic discussions promotes inclusivity by ensuring that all voices are heard and respected equally.
Teachers should create structures that allow for equal opportunities for participation regardless of gender, cultural background or personality traits. Additionally, incorporating norms that encourage active listening and valuing diverse perspectives further fosters an inclusive classroom environment.
21. Incorporating Mindfulness Practices into the Socratic Dialogue Process
Mindfulness practices have gained recognition as effective tools for promoting self-regulation, emotional well-being, and focus within educational settings. Integrating mindfulness techniques into the Socratic dialogue process can enhance student engagement and deepen understanding.
By incorporating moments of reflection or guided mindfulness exercises before or during Socratic discussions, educators create a calm and focused atmosphere that encourages active listening, empathy, and thoughtful responses.
22. Assessing Student Learning Outcomes using Authentic Assessments within a Socratic Framework
Assessing student learning outcomes is an integral part of any educational approach. Within a Socratic framework, authentic assessments provide valuable insights into students’ critical thinking skills, ability to articulate complex ideas, and depth of understanding.
Authentic assessments may include performance-based tasks such as debates, presentations or written reflections that allow students to demonstrate their mastery of content knowledge while showcasing their ability to engage in meaningful dialogue.
23. The Relationship between Inquiry-Based Learning and the Principles of the Socratic Method
Inquiry-based learning shares many similarities with the principles underlying the Socratic method. Both approaches emphasize curiosity-driven exploration, critical thinking skills development, and collaborative problem-solving.
Educators can leverage this relationship by integrating inquiry-based learning strategies within Socratic dialogues. By posing open-ended questions that prompt investigation and discovery while guiding students through structured inquiry processes such as research or experimentation, teachers foster deeper engagement with academic content.
24. Developing Effective Questioning Techniques for Guiding Productive Classroom Discussions
Effective questioning lies at the core of successful implementation of the Socratic method in alternative education classrooms. By honing their questioning techniques, educators can guide productive discussions that promote critical thinking while fostering respectful collaboration among students.
Some key considerations when developing effective questioning techniques include clarity of purpose behind each question posed; asking open-ended questions to encourage diverse perspectives; sequencing questions strategically to scaffold understanding; providing wait time for thoughtful responses; and modeling active listening throughout the conversation.
25. Cultivating Intellectual Humility and Curiosity through Ongoing Use of the Socratic Approach
Cultivating intellectual humility is a valuable outcome of ongoing use of the Socratic method in alternative education settings. By encouraging students to engage in peer-to-peer dialogue, challenging their own assumptions, and being open to revising their beliefs based on evidence and reasoned arguments, educators foster an environment where intellectual growth thrives.
Furthermore, by promoting curiosity through thought-provoking questions and encouraging students to pursue deeper understanding beyond surface-level answers, the Socratic approach nurtures lifelong learners who embrace continuous exploration and personal growth.
In conclusion, the Socratic method holds immense potential for enhancing student-centered learning experiences within alternative education schools. By incorporating questioning techniques inspired by its principles across various disciplines and contexts, educators can empower students with critical thinking skills, empathy towards others’ perspectives, civic engagement values, creativity, and a deep passion for learning.
Leave a comment