The impact of sleep deprivation on brain function
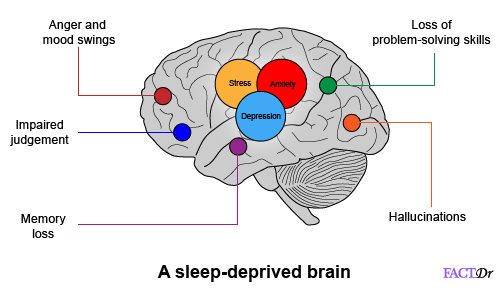
Sleep is a crucial component of overall brain health and function. Numerous studies have shown that sleep deprivation can have detrimental effects on cognitive abilities, attention, memory, and problem-solving skills. When we don’t get enough sleep, our brain’s ability to process information efficiently is compromised.
During sleep, the brain consolidates memories and clears out waste products through a process called synaptic pruning. Without adequate restorative sleep, these processes are disrupted, leading to difficulties in learning and retaining new information. Sleep deprivation also affects the prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for decision-making and impulse control. This can result in poor judgment and increased risk-taking behaviors.
Neuroplasticity and its role in alternative education
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. This concept has significant implications for alternative education settings as it suggests that students’ brains are not fixed entities but rather malleable structures that can be shaped through experiences.
Alternative education often emphasizes individualized instruction and hands-on learning experiences. By providing opportunities for students to engage in meaningful activities that stimulate their senses and challenge their thinking, educators can promote neuroplasticity. This approach allows students to develop essential skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity, and adaptability.
Brain-based strategies for teaching mathematics
Mathematics can be a challenging subject for many students. However, understanding how the brain processes mathematical concepts can inform effective instructional strategies.
Research has shown that incorporating visual aids, manipulatives (such as blocks or counters), real-life examples, and storytelling into math lessons engages multiple regions of the brain involved in spatial reasoning, pattern recognition, logic processing, and memory retrieval.
Furthermore,
active participation through interactive games,
collaborative problem-solving activities,
and regular practice with varied exercises
can enhance mathematical understanding by reinforcing neural pathways associated with numerical processing.
By employing brain-based strategies, educators can create a supportive and engaging learning environment that fosters mathematical skills acquisition and promotes long-term retention.
Enhancing creativity through brain-based learning approaches
Creativity is an essential skill for success in the 21st century. Brain-based learning approaches can effectively nurture and enhance creativity in students.
Firstly, it is important to understand that creativity involves both divergent thinking (generating multiple ideas) and convergent thinking (evaluating and selecting ideas). Alternative education settings often provide opportunities for open-ended projects and problem-solving tasks that encourage divergent thinking. This allows students to explore various possibilities without fear of judgment or failure.
Additionally, incorporating arts-based activities such as visual arts, music, drama, and dance into the curriculum stimulates different areas of the brain associated with imagination, emotional expression, pattern recognition, and innovation.
Brain breaks or moments of unstructured play during the school day allow students’ minds to wander freely. This state of relaxed attention has been linked to increased creative insights.
Overall,
alternative education environments that prioritize flexible thinking,
encourage risk-taking,
provide exposure to diverse experiences,
and foster a supportive atmosphere
can effectively promote creativity by harnessing the power of neuroplasticity and engaging multiple regions of the brain involved in creative processes.
Leave a comment