Experiential Learning: Unlocking the Power of Hands-On Education
In today’s rapidly changing world, traditional forms of education are being challenged by alternative approaches that prioritize hands-on learning and real-world experiences. One such approach gaining traction is experiential learning, a methodology that encourages students to learn through active engagement and reflection.
What is Experiential Learning?
Experiential learning is an educational philosophy that emphasizes the importance of direct experience in the learning process. It recognizes that individuals acquire knowledge best when they actively engage with their environment, make connections between theory and practice, and reflect on their experiences.
Unlike traditional classroom settings where information is passively received, experiential learning provides opportunities for students to immerse themselves in authentic situations relevant to their studies. This type of education fosters critical thinking skills, problem-solving abilities, creativity, collaboration, and adaptability – all essential qualities for success in today’s complex world.
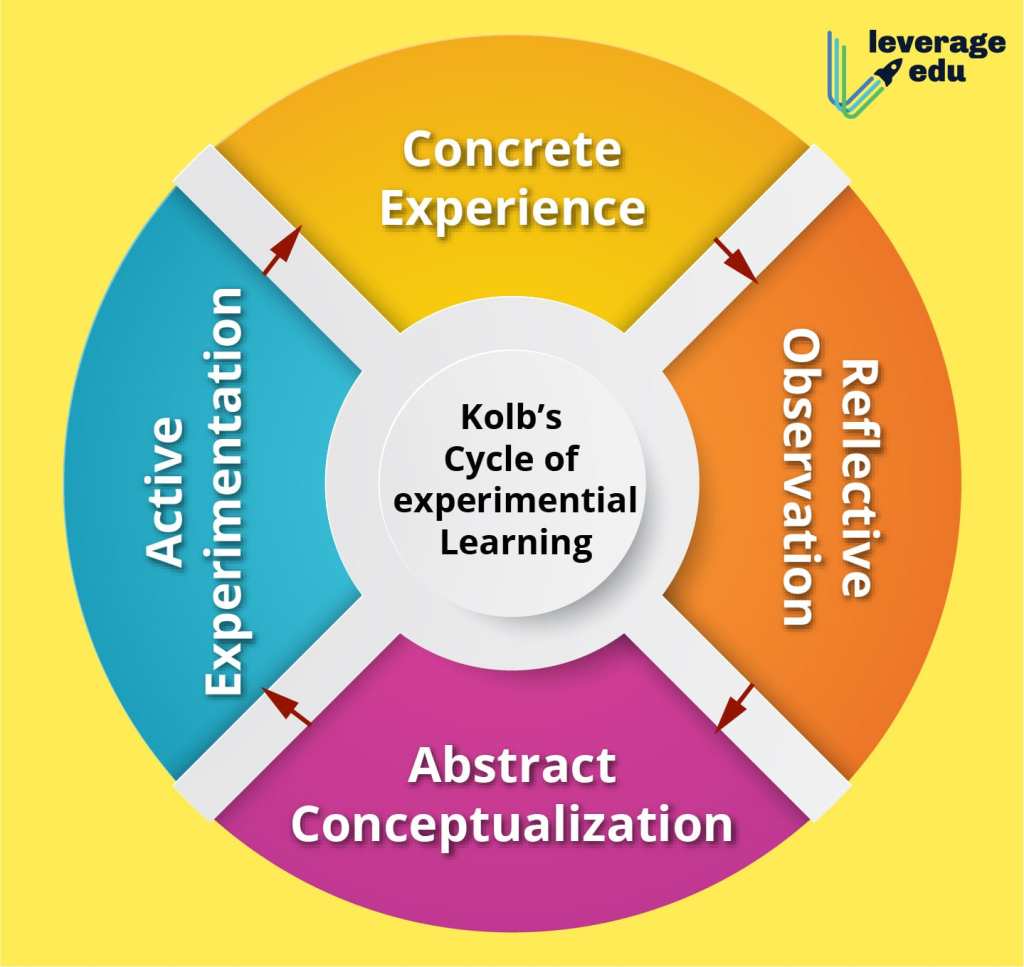
The Four Stages of Experiential Learning
David A. Kolb developed a widely accepted model known as the Experiential Learning Cycle that outlines four stages involved in this process:
1. Concrete Experience: Students engage in hands-on activities or encounter real-world situations related to their area of study. This stage sets the foundation for subsequent reflections.
2. Reflective Observation: Learners reflect upon their experiences by considering what happened during the activity or situation.
3. Abstract Conceptualization: Students form abstract concepts based on their observations and draw connections with pre-existing knowledge.
4. Active Experimentation: Learners test these concepts by applying them to new situations or scenarios.
These four stages create a continuous cycle of experiential learning where each phase builds upon the previous one to deepen understanding and promote lifelong learning.
Types of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning takes various forms depending on its application within different fields or contexts:
1. Project-Based Learning (PBL): In PBL, students work on extended projects that require them to investigate and solve real-world problems. This approach allows for interdisciplinary learning, collaboration, and the application of knowledge in practical ways.
2. Field Trips and Site Visits: Taking students out of the classroom and into real-world environments provides valuable firsthand experiences. Whether it’s visiting a museum, nature reserve, or local business, these excursions offer unique opportunities for exploration and discovery.
3. Internships and Apprenticeships: Placing students in professional settings related to their studies allows them to gain practical skills under the guidance of experienced mentors. Internships and apprenticeships bridge the gap between theory and practice while building important industry connections.
4. Simulations: Simulations create artificial scenarios that mimic real-life situations where learners can apply theoretical knowledge to solve problems or make decisions without facing actual consequences. These immersive experiences help develop critical thinking skills in a risk-free environment.
Benefits of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning offers numerous benefits beyond traditional educational methods:
1. Active Engagement: By actively participating in hands-on activities, students become more engaged with their studies compared to passively receiving information through lectures or textbooks.
2. Real-World Relevance: Experiences gained through experiential learning are directly applicable to real-life situations, making education more meaningful for students.
3. Critical Thinking Skills: Experiential learning promotes critical thinking by encouraging learners to analyze problems from different perspectives, explore possible solutions, evaluate outcomes, and adjust accordingly.
4. Collaboration and Communication: Many experiential learning activities involve teamwork, fostering effective communication skills as students work together towards common goals.
5. Emotional Connection: Hands-on experiences elicit emotional responses that enhance memory retention and understanding of concepts covered during the activity.
6. Self-Reflection: The reflection stage of experiential learning encourages self-awareness as learners assess their strengths, weaknesses, biases, and areas for growth.
7. Transferable Skills: Experiential learning develops skills such as adaptability, problem-solving, decision-making, leadership, and creativity – all highly sought-after attributes in today’s job market.
Implementing Experiential Learning
To successfully incorporate experiential learning into educational practices, certain considerations should be taken into account:
1. Curriculum Design: Educators need to design curricula that integrate experiential learning opportunities while aligning with academic standards.
2. Authentic Assessments: Traditional exams may not effectively evaluate the skills developed through experiential learning. Alternative assessment methods like portfolios, presentations, or reflective essays can better capture students’ growth and understanding.
3. Teacher Training: Teachers should receive professional development training to understand how to facilitate experiential learning effectively and provide guidance during each stage of the cycle.
4. Community Partnerships: Establishing partnerships with local businesses, organizations, or community members allows for a wider range of authentic experiences beyond the classroom walls.
Success Stories in Experiential Learning
Experiential learning has yielded remarkable outcomes in various contexts around the world:
1. High Tech High (HTH): HTH is a network of charter schools in California that prioritize project-based learning and student-centered approaches. Students engage in long-term projects where they tackle real-world challenges by collaborating with professionals from relevant fields.
2. Outward Bound: Outward Bound offers wilderness-based programs that challenge participants physically and emotionally while fostering teamwork and personal growth.
3. European Schoolnet Academy: The European Schoolnet Academy provides online courses for teachers to enhance their knowledge of innovative pedagogies such as experiential learning.
Conclusion
Experiential learning represents a paradigm shift towards more engaging forms of education that cater to the needs of our rapidly changing world. By providing immersive experiences tied directly to real-life situations, this approach equips learners with essential skills needed for success in their personal and professional lives. As we continue to explore alternative approaches to education, experiential learning stands out as a powerful tool for unlocking the potential of every student.
Leave a comment