Cooperative learning is a teaching approach that promotes active engagement, collaboration, and shared responsibility among students. It has been shown to enhance academic achievement, social skills development, and overall student satisfaction. In this article, we will explore various aspects of cooperative learning and its applications in different educational settings.
1. Jigsaw method in cooperative learning:
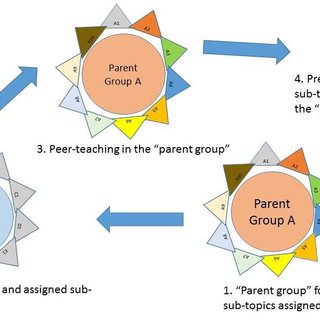
The jigsaw method is a popular cooperative learning technique where students work together in groups to master specific pieces of information and then share their knowledge with the rest of the class. This strategy fosters interdependence as each group member becomes an expert on a particular topic or concept. The jigsaw method encourages active participation, communication skills development, and accountability within the group.
2. Role-playing activities for cooperative learning:
Role-playing activities offer an immersive experience that enables students to step into different roles or perspectives related to a given topic or scenario. Through role-playing exercises, students can develop empathy, critical thinking skills, and problem-solving abilities while working collaboratively towards common goals. This approach promotes cooperation, creativity, and enhances subject understanding through experiential learning.
3. Cooperative learning in physical education classes:
Incorporating cooperative learning strategies into physical education classes can provide numerous benefits beyond simply developing physical fitness. By engaging in team-based games or challenges requiring collaboration and communication between participants, students acquire valuable interpersonal skills such as leadership qualities, effective teamwork abilities, conflict resolution techniques while improving their motor skills simultaneously.
4. Cooperative learning strategies for teaching math concepts:
Mathematics often intimidates many students due to its abstract nature; however, incorporating cooperative learning strategies can make it more accessible and enjoyable for all learners. Group problem-solving tasks encourage peer-to-peer explanations which promote deeper conceptual understanding of mathematical principles rather than rote memorization of formulas or algorithms.
5. Using technology to enhance cooperative learning experiences:
Technology tools such as online platforms or collaborative software enable remote collaboration among students even when physically apart from one another. These digital tools can facilitate group discussions, document sharing, and real-time feedback exchange. Technology-enhanced cooperative learning experiences foster inclusivity, accessibility, and engagement among students.
6. Group investigation approach in cooperative learning:
The group investigation approach involves students working together to explore a particular topic or problem through research, experiments, or fieldwork. This method encourages curiosity, critical thinking skills development, and independent learning within a collaborative context. By dividing tasks and responsibilities among group members while maintaining interdependence on each other’s contributions, students become active investigators of knowledge.
7. Cooperative learning for students with special needs:
Cooperative learning is particularly beneficial for students with special needs as it promotes social integration and peer support while addressing individual learning goals. In inclusive classrooms, cooperative activities enable diverse learners to engage meaningfully with their peers without feeling isolated or stigmatized. Teachers can implement differentiated instructional strategies that accommodate different abilities within the cooperative groups to ensure equitable participation.
8. Implementing cooperative learning in online education settings:
With the rise of online education platforms and remote learning environments, adapting cooperative learning methods becomes crucial for creating engaging virtual classroom experiences. Online discussion forums, breakout rooms in video conferencing applications, or collaborative project management tools are some examples of how teachers can facilitate student collaboration virtually while fostering a sense of community and shared responsibility over the collective outcome.
9. Cooperative learning and project-based assessments:
Project-based assessments provide an opportunity for students to apply their knowledge creatively while developing essential 21st-century skills such as problem-solving ability and communication competence. Collaborative projects allow students to work together towards a common goal by leveraging each other’s strengths and expertise in order to produce high-quality outcomes that reflect shared ownership.
10.The impact of teacher-student relationships on cooperative learning outcomes:
The quality of teacher-student relationships plays a significant role in the success of cooperative learning initiatives. When teachers establish positive rapport with their students based on trust, respect, and support, students feel more motivated to actively participate in group activities. Strong teacher-student relationships foster a sense of belonging, enhance social skills development, and contribute to a positive classroom climate that is conducive to cooperative learning.
11. Cross-age tutoring as a form of cooperative learning:
Cross-age tutoring involves pairing older students with younger ones to facilitate peer teaching and learning experiences. This approach benefits both the tutor and the tutee by promoting knowledge consolidation for the tutor while providing individualized guidance and support for the tutee. Cross-age tutoring encourages responsibility, empathy, leadership qualities, and strengthens intergenerational bonds within the school community.
12. Peer feedback and assessment in cooperative learning groups:
Peer feedback is an integral component of cooperative learning as it fosters self-reflection, critical thinking skills development, and promotes active engagement among group members. By providing constructive feedback on each other’s work or contributions within a safe environment guided by clear criteria or rubrics, students learn how to give and receive feedback effectively while enhancing their own understanding of the subject matter.
13. Culturally responsive approaches to cooperative learning:
Culturally responsive cooperative learning practices acknowledge and value diverse cultural backgrounds within the classroom setting. Teachers can incorporate culturally relevant content into their instructional materials or encourage students to share their unique perspectives during collaborative activities. Culturally responsive approaches promote inclusivity, respect for diversity, empathy building, prejudice reduction while fostering academic achievement among all learners.
14.Cooperative learning and social-emotional development:
Cooperative learning environments provide opportunities for students to develop essential social-emotional skills such as communication skills, conflict resolution abilities, empathy building techniques while fostering positive interpersonal relationships with their peers. Students learn how to navigate different personalities within a group setting which contributes positively towards emotional intelligence development.
15.Problem-solving techniques within cooperative learning structures:
Problem-solving techniques are central components of many cooperative learning activities as they encourage critical thinking abilities amongst learners working collaboratively towards solving complex problems. By engaging in group discussions, brainstorming sessions, and analyzing multiple perspectives within a cooperative learning framework, students learn to approach challenges creatively while developing effective problem-solving strategies.
16.The role of self-regulation skills in successful cooperative learning:
Self-regulation skills such as goal setting, time management, and task prioritization are essential for successful participation in cooperative learning activities. Students need to manage their own contributions effectively within the group context to ensure equitable distribution of workload and maximize collective outcomes. Cooperative learning environments provide opportunities for students to develop and refine these self-regulation skills through continuous practice and reflection.
17.Cooperative learning and student motivation:
Cooperative learning has been shown to enhance student motivation by providing meaningful tasks that promote active engagement with the subject matter. The sense of shared responsibility and interdependence within cooperative groups fosters a collaborative spirit that motivates students to actively participate, contribute their best efforts, and take ownership of their own learning process.
18.Differentiating instruction within a cooperative learning framework:
Cooperative learning allows teachers to differentiate instruction based on individual needs or abilities within heterogeneous classroom settings. Group members can support each other by sharing different perspectives or approaches towards problem-solving tasks while accommodating diverse learner profiles simultaneously. Teachers can design flexible instructional activities that cater to various levels of readiness or interest among students without compromising the collaborative nature of the exercise.
19.Cooperative learning and the development of critical thinking skills:
Critical thinking is an essential skill required in today’s complex world; cooperative learning provides an ideal platform for its development. Through collaborative discussions, analysis of multiple viewpoints, evaluation of evidence-based arguments, and constructive critique exchange among peers during group work activities- students learn how to think critically about information sources while making informed decisions backed by logical reasoning.
20.Incorporating mindfulness practices into cooperative learning activities:
Mindfulness practices can enhance the effectiveness of cooperative learning experiences by promoting focus, attentional control, emotional regulation abilities amongst participants. By incorporating short mindfulness activities such as breathing exercises, guided imagery, or reflective journaling at the beginning or end of cooperative learning sessions – teachers can create a calm and conducive environment for optimal engagement while fostering present-moment awareness and self-reflection skills among learners.
In conclusion, cooperative learning is a powerful teaching approach that fosters active engagement, collaboration, and shared responsibility among students. It has numerous benefits across various educational settings and subject areas. Whether through strategies like the jigsaw method or role-playing activities, cooperative learning promotes social-emotional development, critical thinking skills acquisition, motivation enhancement while creating inclusive environments where all learners can thrive. By implementing cooperative learning techniques effectively within different contexts and embracing its core principles of interdependence and mutual support, educators can empower their students to become successful lifelong learners.
Leave a comment