Mentorship is a powerful tool that can have a significant impact on the lives of students. It provides guidance, support, and encouragement to help them navigate through various challenges and achieve their goals. While mentorship programs are commonly associated with traditional educational settings, they also play a crucial role in alternative schooling environments.
Alternative schools cater to students who may not thrive in mainstream education due to various reasons such as learning disabilities, behavioral issues, or personal circumstances. These schools offer a different approach to education, focusing on individualized instruction and providing additional support services. Mentorship programs within these alternative schools serve as an essential component of holistic student development.
One area where mentorship has proven to be beneficial is for students interested in STEM fields (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics). Many alternative schools recognize the importance of fostering interest and proficiency in these subjects among their students. By pairing them with mentors who are professionals working in STEM-related industries or pursuing higher education in these fields, students can gain valuable insights into potential career paths and develop the necessary skills.
The LGBTQ+ community often faces unique challenges both inside and outside of the classroom. Providing mentorship opportunities specifically tailored to LGBTQ+ students can help create safe spaces where they can explore their identities while receiving guidance from supportive individuals. Mentors who identify as LGBTQ+ themselves or have experience working with this community can provide invaluable advice on navigating societal pressures, coming out experiences, mental health concerns, and accessing resources.
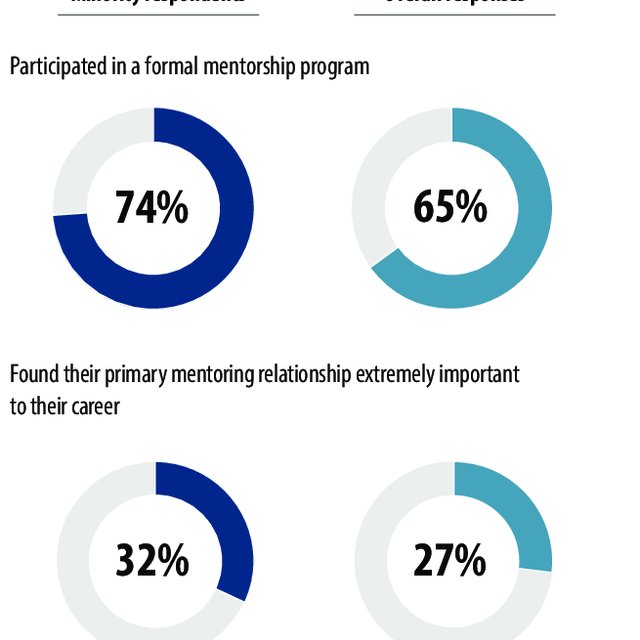
Similarly, minority students face specific obstacles that mentors well-versed in cultural sensitivity can address effectively. These mentors serve as role models who understand firsthand the difficulties faced by marginalized communities. They offer guidance on overcoming systemic barriers while empowering mentees to embrace their identity proudly. Through mentorship relationships built on trust and understanding, minority students are encouraged to pursue their dreams despite external limitations.
First-generation college-bound students often lack access to resources that would typically be available through family connections or prior knowledge. Mentorship programs designed for these students can help bridge the gap by providing guidance on college applications, financial aid, and navigating the higher education system. Mentors who have themselves been first-generation college students are well-equipped to provide personalized support and understanding throughout the entire process.
Non-traditional adult learners, such as those returning to school later in life or pursuing education while working full-time, also benefit greatly from mentorship opportunities. These individuals often face unique challenges such as balancing multiple responsibilities and adapting to new learning environments. Mentors who have successfully navigated similar paths can offer valuable advice on time management, goal setting, and overcoming obstacles specific to adult learners.
In today’s digital age, online mentorship programs have become increasingly popular due to their accessibility and convenience. These programs connect students with mentors from various locations around the world through virtual platforms. Online mentorship resources offer a wide range of benefits, including flexibility in scheduling sessions, access to a diverse pool of mentors with specialized expertise, and the ability to cater specifically to individual needs.
Building effective mentor-mentee relationships is essential for successful outcomes in any mentoring program. It requires open communication, active listening skills, empathy, and trust-building exercises. Mentor training programs play a crucial role in equipping mentors with these necessary skills so they can effectively guide their mentees towards personal growth and success.
The role of mentors within alternative schooling environments extends beyond academic guidance; they also play a vital part in nurturing social-emotional development among students. Many alternative schools focus on creating supportive communities that address not only academic challenges but also emotional well-being. By fostering positive relationships between mentors and mentees based on mutual respect and understanding, students feel more connected to their school community.
Peer-to-peer mentoring models are particularly effective within alternative schooling environments because they create an atmosphere of shared experiences among students facing similar challenges or circumstances. This type of mentoring allows for genuine empathy between peers while encouraging personal growth and accountability. Peer mentors can provide valuable insights and advice based on their own experiences, enabling mentees to feel understood and supported.
Mentoring programs that promote career exploration and readiness are crucial for students in alternative education settings. These programs expose students to different career paths, help them identify their strengths, set educational goals, develop job-related skills, and build professional networks. Mentors who work in the industry or possess relevant expertise guide students through these processes and offer real-world insights into potential careers.
Research consistently shows that mentorship has a positive impact on academic achievement. Mentors act as advocates for their mentees by providing support tailored to individual learning styles and needs. They encourage goal setting, monitor progress, offer constructive feedback, instill confidence in students’ abilities, and help them navigate potential challenges or setbacks along the way.
Culturally responsive mentoring practices are essential within alternative schooling environments to ensure inclusivity and understanding among diverse student populations. Mentors who receive training in cultural competence can effectively address the unique needs of students from different cultural backgrounds while promoting mutual respect and appreciation for diversity.
Behavioral challenges often arise within alternative education settings due to various factors such as trauma history or undiagnosed learning disabilities. Mentorship serves as a tool to address these challenges by offering personalized support tailored to meet each student’s specific needs. Mentors trained in behavioral management techniques can provide guidance on emotional regulation strategies, conflict resolution skills, self-advocacy techniques, and building healthy relationships with peers.
Parent involvement is crucial for successful mentoring programs at alternative schools. Parents play an integral role in supporting mentor-mentee relationships by providing additional insight into their child’s strengths, weaknesses, interests, and goals outside of school hours. Regular communication between parents/guardians and mentors ensures alignment between home-based support systems and school-based initiatives.
Finally , mentor training opportunities should be readily available to mentors working within alternative schooling environments so they can continually develop their skills and stay updated on best practices. Professional development programs should cover topics such as effective communication, active listening, cultural competence, goal setting, behavioral management strategies, and building strong mentor-mentee relationships.
In conclusion, mentorship programs play a vital role in alternative schooling environments by providing guidance, support, and encouragement to students facing unique challenges. These programs cater to various student populations including those interested in STEM fields, LGBTQ+ students, minority students, first-generation college-bound students, non-traditional adult learners. Online mentorship resources offer flexibility and accessibility while peer-to-peer mentoring models foster empathy and personal growth. Mentorship promotes academic achievement while addressing social-emotional development needs. Culturally responsive practices ensure inclusivity and understanding among diverse student populations. Mentoring also addresses behavioral challenges through personalized support. Parent involvement is crucial for successful mentoring programs at alternative schools, and mentor training opportunities are essential for ongoing professional development.
By recognizing the importance of mentorship within alternative education settings and implementing robust programs that address specific student needs effectively, we can empower students to overcome obstacles and achieve success in their educational journeys.
Leave a comment