Experiential Learning: An Alternative Approach to Education
Introduction:
Education is a critical aspect of human development, providing individuals with the necessary knowledge and skills to thrive in society. However, traditional education methods often rely heavily on classroom-based instruction and theoretical learning. While this approach has its merits, it may not cater to the diverse needs and learning styles of all students.
Experiential learning presents an alternative approach that focuses on hands-on experiences and active involvement in the learning process. This method emphasizes practical application over rote memorization, allowing students to develop essential life skills while gaining subject knowledge. In this article, we will explore the concept of experiential learning, its benefits for students, and how it can be implemented in various educational settings.
What is Experiential Learning?
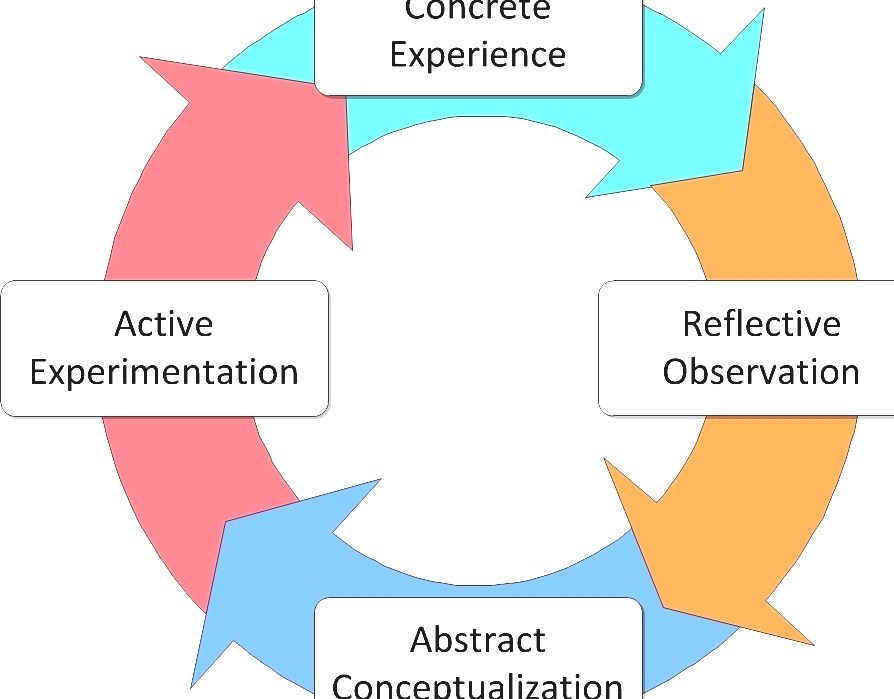
Experiential learning is an educational philosophy that centers around direct engagement with real-world experiences as a primary means of acquiring knowledge. It encourages learners to actively participate in activities related to their studies rather than passively receiving information through lectures or textbooks.
This approach recognizes that individuals learn best when they are personally invested in their education. By connecting theory with practice, experiential learning offers students opportunities for reflection, problem-solving, critical thinking, collaboration, and decision-making – all crucial skills for success beyond academia.
Benefits of Experiential Learning:
1. Enhanced Understanding:
Engaging directly with concepts allows students to understand them more deeply compared to simply reading about them or listening to lectures. When learners experience firsthand how theories work in real-life situations, they gain a holistic understanding that goes beyond textbook definitions.
2. Practical Application:
Experiential learning bridges the gap between theory and practice by encouraging students to apply what they have learned in real-world scenarios. By practicing their skills or knowledge within authentic contexts, learners develop a sense of relevance and applicability.
3. Active Engagement:
Traditional classroom environments often struggle with maintaining student engagement. Experiential learning addresses this issue by involving students actively in their education. Through hands-on experiences, learners take ownership of their learning journey, leading to increased motivation and attentiveness.
4. Skill Development:
Experiential learning fosters the growth of essential life skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, collaboration, and adaptability – skills that cannot be fully developed through passive learning alone. These skills are vital for success in today’s rapidly evolving world.
5. Emotional Connection:
Real-world experiences evoke emotions that enhance memory retention and overall engagement with the subject matter. By connecting emotionally with what they are learning, students build stronger connections between knowledge acquisition and personal meaning.
Implementing Experiential Learning:
Experiential learning can be implemented across various educational settings – from traditional schools to alternative schooling systems or even homeschooling environments. Here are a few ways educators can incorporate experiential learning techniques into their teaching strategies:
1. Field Trips:
Taking students on field trips provides them with opportunities to observe real-life applications of classroom concepts. Whether visiting a science museum or exploring historical sites, field trips enable students to engage directly with subjects they have learned about in class.
2. Hands-On Projects:
Assigning hands-on projects allows learners to apply theoretical knowledge while developing practical skills simultaneously. For instance, instead of merely reading about chemistry experiments, students could conduct experiments themselves under proper supervision.
3. Service-Learning:
Engaging in community service projects not only benefits society but also offers valuable lessons for students involved. Service-learning combines academic instruction with meaningful community service activities that address local needs while fostering personal growth and empathy.
4. Simulations and Role-Playing:
Simulations provide immersive experiences where learners enact scenarios relevant to their studies or future careers. This approach allows individuals to step into different roles and make decisions based on the information available – thus building critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
5. Internships and Apprenticeships:
Encouraging students to participate in internships or apprenticeships gives them the opportunity to apply classroom knowledge in professional settings. This real-world experience helps bridge the gap between academia and the job market, preparing students for future careers.
Challenges of Experiential Learning:
While experiential learning offers numerous benefits, it is essential to acknowledge potential challenges that educators may face when implementing this approach:
1. Resource Constraints:
Certain experiential learning initiatives, such as field trips or hands-on projects, require additional resources that may not always be readily available within educational institutions. Funding constraints or logistical issues can limit the scope of these experiences.
2. Time Management:
Planning and executing experiential learning activities often require more time compared to traditional teaching methods. Teachers must allocate adequate time for preparation, implementation, reflection, and assessment – a factor that needs careful consideration within existing curricula.
3. Assessment Methods:
Assessing student progress through experiential learning can be challenging due to its subjective nature. Traditional grading systems may not effectively capture the full range of skills developed during hands-on experiences or reflect individual growth accurately.
Conclusion:
Experiential learning provides an alternative approach to education that fosters deeper understanding, practical application of knowledge, active engagement among learners, skill development, emotional connection with subjects, and ultimately prepares individuals for success beyond school walls.
By incorporating various techniques like field trips, hands-on projects, service-learning opportunities, simulations/role-playing exercises, internships/apprenticeships into their teaching strategies; educators can create dynamic learning environments where students actively participate in their own education journey while acquiring crucial life skills necessary for their future endeavors.
While there are challenges associated with implementing experiential learning methods within existing educational systems such as resource constraints or time management concerns; the long-term benefits far outweigh these obstacles. By embracing experiential learning, we can create a more engaging and impactful educational experience for all learners.
Leave a comment