Student-Centered Learning:
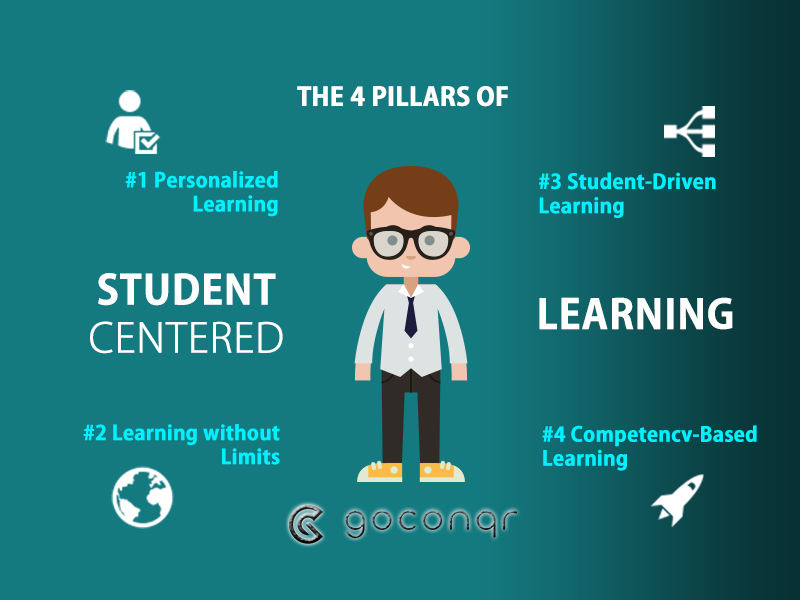
Student-centered learning is an educational approach that prioritizes the needs, interests, and abilities of individual students. It shifts the focus from a teacher-centric model to one where students actively engage in their own learning process. In student-centered classrooms, educators act as facilitators rather than direct instructors, allowing students to take ownership of their education.
In a student-centered learning environment, students have more control over how they learn and demonstrate their understanding of concepts. This can be achieved through various strategies such as personalized learning plans, project-based assignments, and flexible grouping. By giving students agency in their education, they become active participants who are motivated to learn and explore topics that interest them.
Democratic Decision-Making Processes in Schools:
Democratic decision-making processes involve all members of the school community having a voice in shaping policies and practices. This includes not only teachers and administrators but also students, parents/guardians, and support staff. The goal is to create an inclusive environment where everyone’s perspectives are valued and decisions are made collectively.
In democratic schools, decision-making often takes place through regular meetings or assemblies where all stakeholders can participate. This may involve voting on issues such as curriculum choices, disciplinary policies, or even hiring decisions. By involving different perspectives in decision-making processes, schools can promote transparency and equity while fostering a sense of ownership among all members.
Self-Directed Learning:
Self-directed learning empowers students to take responsibility for their own education by setting goals and managing their progress towards achieving them. It recognizes that individuals have unique strengths, interests, and preferred learning styles which should be respected throughout the educational journey.
In self-directed learning environments, teachers serve as guides or mentors who provide resources and support to help students navigate their chosen paths. Students have the freedom to choose what they want to learn based on their passions while being encouraged to develop crucial skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving abilities, time management skills,and self-reflection.
Project-Based Learning:
Project-based learning (PBL) is an instructional approach that centers around real-world problems and challenges. Students engage in hands-on projects that require them to apply knowledge and skills acquired in various subjects to solve complex problems or create meaningful products.
In project-based learning, students collaborate with their peers to investigate, design, and present their findings or solutions. This approach fosters critical thinking, creativity, communication skills,and collaboration among students while promoting a deeper understanding of the subject matter. It also allows for student voice and choice in determining the direction of their projects.
Community Involvement in Education:
Community involvement plays a vital role in education as it strengthens the connection between schools and the broader community. By involving parents/guardians, local organizations, businesses, and volunteers, schools can tap into additional resources and expertise to enhance the educational experience for all students.
Community involvement can take many forms such as guest speakers sharing their professional experiences or conducting workshops on specific topics. It can also involve partnerships with local organizations for internships or service-learning opportunities which provide students with valuable real-world experiences beyond the classroom walls. Additionally, involving parents/guardians through parent-teacher associations or committees ensures that there is ongoing dialogue between home and school.
Restorative Justice in Schools:
Restorative justice is an alternative approach to discipline that focuses on repairing harm caused by wrongdoing rather than simply punishing offenders. In restorative justice practices within schools,judicial processes shift from being punitive towards being healing-oriented.
Restorative justice encourages open dialogues where everyone affected by an incident comes together to discuss its impact on individuals and the community as a whole. The goal is to hold individuals accountable while also providing opportunities for growth,resolution,and reconciliation among all parties involved.This approach helps build empathy,cultural competency,and conflict resolution skills among students while creating safer and more inclusive school environments.
Holistic Education Approaches:
Holistic education approaches recognize that learners are multifaceted individuals with physical, emotional, social, and intellectual needs. These approaches aim to nurture the whole child by integrating academic instruction with a focus on personal development and well-being.
Holistic education emphasizes the importance of promoting self-awareness, emotional intelligence,and character development alongside academic achievement. It encourages educators to create supportive learning environments that foster positive relationships,nurture creativity,and provide opportunities for physical activity and mindfulness practices. By addressing all aspects of a student’s well-being,holistic education helps develop resilient,self-confident learners who are equipped to thrive in all areas of their lives.
Democratic Classroom Management Strategies:
In democratic classrooms,classroom management strategies shift from authoritarian models towards more collaborative and inclusive approaches. This involves involving students in decision-making processes regarding classroom rules,routines,and consequences.
By involving students in setting expectations for behavior within the classroom environment,they feel a sense of ownership and responsibility which leads to increased engagementand accountability. Teachers can use techniques such as class meetings or restorative circles where students have an equal voice in discussing concerns,resolving conflicts,and contributing ideas for improvement.By fostering open communication and respect,democratic classroom management strategies promote autonomy,self-discipline,and mutual respect among students.
Education for Social Justice and Equity:
Education for social justice and equity aims to address inequalities within educational systems while empowering students to become agents of change in their communities.To achieve this goal,it is essential to examine issues related to race,class,gender,ability,status,religion,and other forms of oppression that may exist within society.
Educational programs focused on social justice help students develop critical thinking skills,cultural competency,perspective-taking abilities,and empathy.They encourage discussions about power dynamics,injustice,bias,stereotypes,tolerance,and human rights.Students learn how they can challenge systemic injustices through activism,social action projects,research projects,event planning,campaigns or community service initiatives.Education for social justice promotes inclusivity,fosters empathy,tolerance,social awareness,and prepares students to become informed,engaged citizens who can advocate for a more equitable and just society.
Experiential Learning Methods:
Experiential learning methods involve hands-on experiences that actively engage students in the learning process. These methods are based on the idea that individuals learn best when they can apply their knowledge and skills in real-world contexts.
Examples of experiential learning include field trips, simulations, internships,service-learning projects or outdoor expeditions.Through these activities,studen explore new environments,gain practical skills,and develop critical thinking abilities.Experiential learning helps make connections between theoretical concepts and real-life situations while promoting creativity,problem-solving,collaboration,and adaptability.
Student Voice and Agency in Curriculum Design:
Involving students in curriculum design allows for a more personalized educational experience where their interests,perspectives,and cultures are valued.This approach recognizes that students have unique strengths and passions which should be incorporated into the curriculum.
By incorporating student voice into the design process,curriculum becomes relevantand meaningful.Students feel motivated to learn because they see themselves reflectedin what they study.They also develop important skills such as communication,negotiation,critical thinking,and collaboration.In addition,having agency over their education fosters a sense of ownership,responsibilityand empowerment among students.
Collaborative Learning Environments:
Collaborativelearning environments promote peer-to-peer interaction as an essential component of the learning process.They encourage active participation,cooperation,multidisciplinary approaches,and shared responsibility within groups.Working together allowsstudents to benefit from each other’s perspectives,knowledge,and expertise.Collaborativelearningenvironmentspreparestudentsforreal-worldcollaborationsinwhichtheywilllikelyencounterdiverseopinionsandinclusiveworkspaces.Bycultivatingtheseskillssuchascommunication,negotiation,time-managementandsocial-awareness,collaborativelearningfostersaninclusiveandalternativemodelforacquiringknowledgeanddevelopingcriticalskills.
Assessment Practices in Democratic Education Settings:
In democratic education settings, assessment practices focus on more than just academic achievement. They also emphasize the development of skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, creativity, and collaboration.
Assessment methods may include portfolios, exhibitions, presentations, project-based assessments or self-reflection journals. These approaches allow students to demonstrate their understanding and growth in various ways while promoting metacognition and self-assessment. By involving students in the assessment process through peer feedback or student-led conferences, they become active participants in evaluating their own learning progress.
Teacher-Student Relationships in Alternative Schooling Models:
Alternative schooling models often prioritize building positive relationships between teachers and students. These models recognize that strong teacher-student relationships are crucial for creating a safe and supportive learning environment where all students can thrive.
Teachers who foster positive relationships with their students cultivate trust,respect,and empathy.They take time to get to know each student as an individual,to understand their strengths,challenges,and interests.Teachers provide personalized support,enablingstudents to feel valuedand understood.Students who have positive teacher-student relationships tend to be more engaged,independent,and motivated learners.They feel comfortable asking questions,taking risks,and seeking help when needed.
Conflict Resolution Skills for Students and Educators:
Conflict resolution skills are essential for fostering healthy communication,self-awareness,resilience,and empathy among individuals within educational settings.These skills enable individuals to resolve conflicts constructively while maintaining positive relationships with others.
Educators play a crucial role in teaching conflict resolution skills by modeling effective communication strategies.They can incorporate activities,such as role-playing exercises or restorative justice circles,to help students develop these skills.Students learn howto express themselves respectfully,address differing viewpoints,negotiate solutions,and seek common ground.Conflict resolution training creates a peaceful school climatewhere disputes are resolved peacefullyand where disagreementsbecome opportunitiesforlearning,growth,andunderstanding.
Multicultural Education and Diversity Awareness:
Multicultural education promotes respect,appreciation,and understanding of diverse cultures,languages,religions,and perspectives within educational settings.It recognizes that diversity enriches the learning experience and prepares students to thrive in a globalized world.
Educators who incorporate multicultural education into their practice expose students to a variety of cultural experiences, literature,music,artforms or historical events through curriculum design and classroom activities.They encourage open discussions about social justice,inclusion,toleranceand bias.Through these efforts,studen developcross-culturalcompetence,empathy,criticalthinkingabilitiesandrespectfordifference.Multiculturaleducationhelpscreateinclusiveandsafelearningenvironmentswhereallstudentsfeelvaluedandrepresented.
Democratic Governance Structures in Schools:
Democratic governance structures involve all members of the school community having a voice in decision-making processes related to policy development,school budgets,hiring practices or curriculum design.These structures aim to distribute power,responsibility,and authority among stakeholders.
Examplesofdemocraticgovernanceincludeteacher-ledschoolcommittees,parent-teacherassociationswithvotingrightssubcommitteeorgoverningboards.Democraticgovernanceencouragesparticipation,equityandtransparency.Membersoftheschoolcommunityareabletocontributetheirideastothedecision-makingprocess,takingsownershipoftheirschoolexperience.Thisresultsinmutualrespect,bettercommunicationamongstakeholdersenhancedaccountabilitywhilefosteringasenseofsatisfactionandbelongingwithintheschoolcommunity.
Emotional Intelligence and Social-Emotional Learning:
Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to recognize,understand,and manage one’s own emotions as well as those of others.Social-emotional learning (SEL) focuses on developing skills such as self-awareness,self-management,responsible decision-making,social awareness,and relationship-building. Emotional intelligence and SEL are integral components of holistic education approaches which recognize the importance of addressing students’ social and emotional needs.
Educators who incorporate emotional intelligence and SEL into their practice create safe,emotionally supportive learning environments. They teach students how to manage stress,navigate conflicts,and develop empathy.The development of these skills helps students build positive relationships while equipping them with tools for lifelong success in both personal and professional realms.
Outdoor and Nature-Based Education:
Outdoor and nature-based education emphasizes learning experiences that take place outside traditional classroom settings.Students connect with nature,explore natural ecosystems,and engage in hands-on activities such as gardening,experiments,hikes or wildlife observation.These experiences foster a sense of wonder,critical thinking,sustainability-awarenessand environmental stewardship.
Through outdoor education,students gain an appreciation for the natural world while developing important skills such as problem-solving,inquiry-based learning,self-reflection,and collaboration.Research has shown that outdoor education can enhance academic achievement,motivation,creativity,and overall well-being.It provides opportunities for experientiallearning,inclusivityandsocialconnectionswithboththephysicalenvironmentandotherindividuals.Thisapproachcanbeappliedtoanysubjectareaandofteninspiresastudent’sloveforlearninginamemorableway.
Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills Development:
Critical thinkingandproblem-solvingskillsaredesirableoutcomesofeducationas they enablestudents to analyze complex issues,differentiateperspectives,synthesizeinformation,andmakeinformeddecisions.Criticalthinkinggoesbeyondmereacquisitionoffactsorrecallabilities;itrequiresstudents to applyreasoning,strategize,take risksandexamineproblemsfrommultipleangles.Problem-solvingskillsemphasizetheabilitytoidentifychallenges,gatherinformation,developsolutions,teststrategiesandexperimentwithdifferentapproaches.Enhancingcriticalthinkingandproblem-solvingskillspreparestudentsforchallengestheywillfaceintheirliveswhilecultivatinginitiativeandcreativity.
Technology Integration in Democratic Classrooms:
Technology integration in democratic classrooms aims to leverage digital tools and resources to enhance teaching and learning experiences.Technology can facilitate collaboration,communication,research,and creativity.It also provides access to a variety of educational materials,including online courses,virtual field trips,or multimedia presentations.
In democratically-run schools,technology is used as a tool for empowering students. It allows them to explore their interests,pursue self-directed learning,and engage in meaningful projects.Technologycanalsofacilitatestudentvoiceandagencyincurriculumdesignanddecision-makingprocesses.Inaddition,itprovidesflexibilityforstudentswithdiverselearningneedswhileequippingthemwith21st-centurydigitalskillssuchasinformationliteracy,criticalthinking,andcollaboration.
Educating for Sustainable Development:
Educatingforsustainabledevelopmentaims topromoteawarenessoftheinterconnectednessofsocial,economicandenvironmentalissues.Studentslearnaboutsustainabilityconceptsthroughexploringtopicslikewaterconservation,renewableenergy,wastemanagement,biodiversity or climatechange.Theydevelopanunderstandingofhowtheiractionsaffect theplanetwhileexaminingwaystoaddresschallengesandsolutionsforasustainablefuture.
Sustainabl education helps students become environmentally responsiblecitizenswhoarecapableoftakingactiontocontributepositivelytowardstheirlocalcommunitiesandtheglobalcommunity.Atthesametime,itencouragesacriticalappreciationfortheimportanceofsocioeconomicjustice,inclusivityandequityinsustainabilityefforts.Teacherswhoincorporateeducatingforsustainabledevelopmentintothecurriculumpreparestudentsbecomechangemakerswhoareequippedtocreateapositiveimpactontheworldaroundthem.
Arts Integration and Creative Expression in Education:
Artsintegrationinandcreativeexpressionineducationrecognizesthattheartsplayacrucialroleinthedevelopmentofacreative,well-roundedindividual.Theartsprovideuniqueopportunitiesforself-expression,criticalthinking,andproblem-solving.Theyalsofosterimaginativeandinnovativethinkingwhilecultivatingemotionalintelligenceandempathy.
Educatorswhoincorporateartintegrationintotheircurriculumrecognizethevalueofincorporatingvisualarts,music,drama,danceorcreative writingintolearningexperiences.Studentsareencouragedtoexploretheircreativeside,take risks,andengageinmeaningfulprojects.Art-basedactivitiesstimulatestudents’imaginations,allowthemtothinkoutsidethebox,anddevelopuniquesolutionsto problems.Beyondacademicachievement,artintegrationenhancesstudents’confidence,self-esteemandsenseofbelongingwhilepromotingculturalawarenessandinclusivity.
Mindfulness Practices for Students and Teachers:
Mindfulnesspracticesinvolvebeingpresentinthemomentwithawaresnesstothoughts,feelings,body sensations,andtheenvironment.Theseprovidespaceforreflection,self-regulation,stressreduction,andimprovedmentalwell-being.Ineducationalsettings,mindfulnesspracticesbenefitbothstudentsandteachersbycreatingahealthierlearningenvironmentthatpromotesfocus,resilience,andemotionalintelligence.
Teacherscanincorporatemindfulnessactivitiesinsidetheclassroom,suchasdeep-breathing exercises,body-scans,meditation breaks or gratitude practices.Studentslearnhowtomanagestressandanxiety,becomebetterlistenersandcommunicators,reduceself-judgmentandexperienceincreasedcompassion.Mindfulnesshasbeenshowntoimproveattention,focus,social-emotionalskillsandoverallacademicperformance.Itcreatesasafehavenforthedevelopmentofmentallyhealthyindividualsandcontributes topositiveclassroomclimate.
Inclusive Education Practices within Democratic Frameworks:
Inclusiveeducationisaprominentaspectwithinademocraticframework.Itaimstoprovideequalopportunitiesandaccessforstudentsofallabilities,backgrounds,anddiverselifeexperiences.Inclusiveschoolingpromotesrespect,equality,socialjustice,andacademicachievementforallstudents.
Educatorswhoadoptinclusiveeducationpracticesstrivetocreatelearningenvironmentsthataccommodateindividualdifferences.Teachingmethodologiesandsupportservicesareadaptedtoaddressstudents’uniquelearningneeds.Studentsfeelvaluedandincluded,internurturingapositiveidentity,self-confidenceandempathytowar
Leave a comment