Co-op Academic Focus Areas: A Case Study
Introduction:
In recent years, alternative schooling and education have gained popularity due to their innovative approaches and focus on personalized learning. One such model is the Co-operative Education (Co-op) system, which combines academic coursework with practical work experience in a real-world setting. Co-op programs emphasize experiential learning, allowing students to develop essential skills while exploring their areas of interest. In this case study, we will delve into the various academic focus areas offered within the Co-op framework.
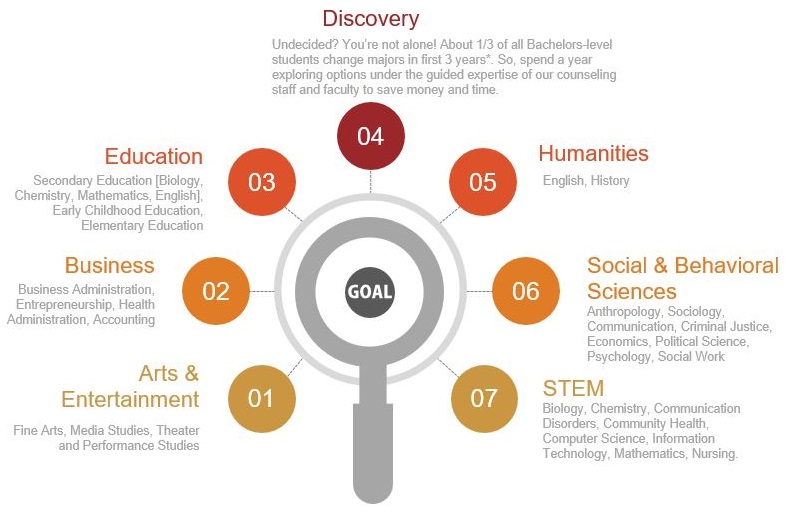
1. STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics):
STEM education plays a vital role in preparing students for careers in rapidly evolving industries. The Co-op approach provides ample opportunities for hands-on learning in STEM fields through collaborations with industry partners. Students engage in research projects, gain technical expertise, and enhance critical thinking skills by applying scientific principles to real-world problems.
2. Business and Entrepreneurship:
Co-op programs offer a unique platform for aspiring entrepreneurs or business professionals to acquire practical experience early on. Through internships at startups or established companies, students learn about market analysis, financial management, marketing strategies, and project management firsthand. This immersive exposure equips them with valuable insights into business operations.
3. Arts and Media:
For those interested in creative pursuits like arts and media production or journalism, co-op programs provide an excellent opportunity to blend theory with practice. Students can intern at renowned art galleries or media organizations where they gain professional experience working alongside experts in their field of interest.
4. Social Sciences:
The social sciences encompass a wide range of disciplines such as psychology, sociology, anthropology, political science etc., where understanding human behavior is key. Co-op placements related to social sciences may involve working with nonprofits or government agencies focused on community development initiatives or policy-making processes.
5 Education:
Cooperative educational experiences also extend beyond traditional classrooms as students explore teaching opportunities during co-op placements at schools or educational institutions. This focus area allows aspiring educators to observe and participate in classroom activities, gain practical teaching skills, and develop an understanding of different learning styles.
Conclusion:
Co-op education programs offer a holistic approach to learning by combining academic coursework with hands-on experience. By offering diverse academic focus areas like STEM, business and entrepreneurship, arts and media, social sciences, and education, co-op programs cater to a wide range of student interests. Through these specialized placements, students acquire valuable skills that prepare them for future careers while also building a network of professional contacts within their chosen fields. The Co-op model serves as an effective alternative schooling option that provides students with practical experiences alongside their academic studies – ultimately shaping well-rounded individuals ready to contribute meaningfully to the workforce upon graduation.
Leave a comment