Mnemonic Techniques for Accelerated Learning
In the world of alternative schooling and education, finding effective strategies to enhance learning outcomes is crucial. One such strategy that has gained popularity is the use of mnemonic techniques. Mnemonic devices are memory aids that help individuals remember information more easily by associating it with familiar cues or patterns.
One widely used mnemonic technique is the method of loci, also known as the memory palace technique. This technique involves mentally placing information in different locations within a familiar setting, such as a house or a street. By visualizing these locations and linking specific pieces of information to each spot, learners can recall the information more easily when they mentally walk through their memory palace.
Another powerful mnemonic technique is acronyms and acrostics. Acronyms are formed by taking the first letter of each word in a list and creating a new word from those letters. For example, to remember the order of operations in mathematics (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication/Division, Addition/Subtraction), you could use the acronym PEMDAS. Acrostics work similarly but involve creating sentences where each word begins with one of the initial letters from a list.
Rhymes and songs are also effective mnemonic tools for memorization. Many people find it easier to remember lyrics or rhymes than plain text. For example, many children learn their ABCs through singing them rather than reciting them individually.
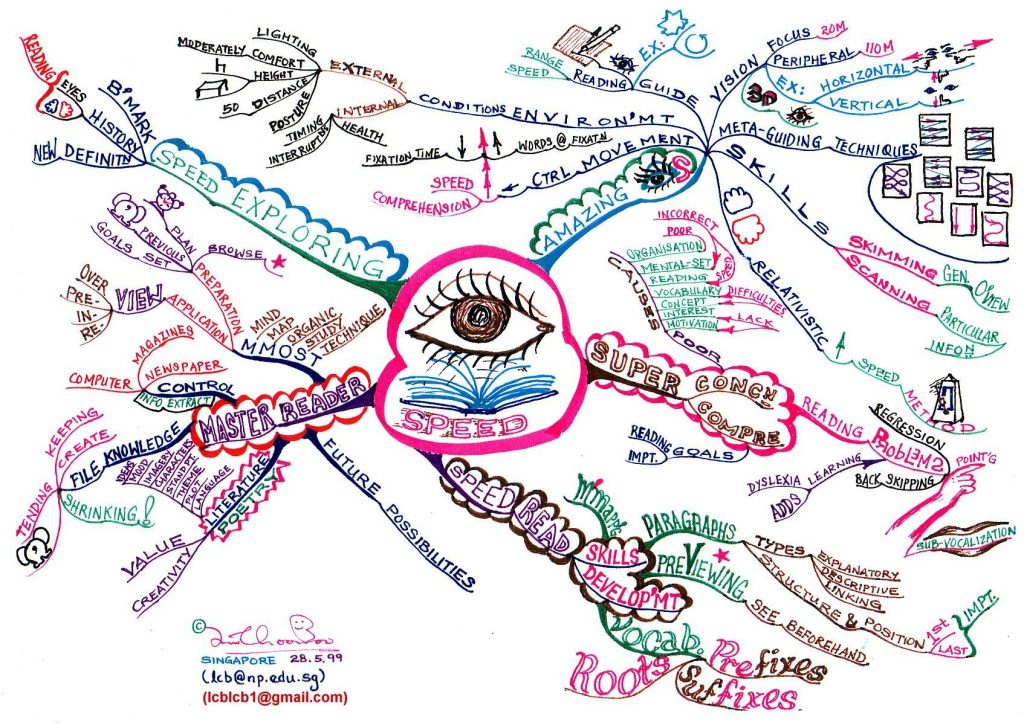
Speed Reading Strategies for Alternative Schooling
Alternative schooling often emphasizes independent learning and self-directed study. In this context, speed reading strategies can be extremely beneficial for students who need to process large amounts of text efficiently.
One popular speed reading technique is called skimming and scanning. Skimming involves quickly running your eyes over an entire page or passage to get an overall sense of its content without focusing on every word individually. Scanning refers to searching for specific keywords or phrases within a text by moving your eyes rapidly across lines while looking for relevant information.
Another effective strategy is chunking. This technique involves grouping words or phrases together and reading them as a single unit, rather than processing each word individually. By training your eyes to see chunks of text instead of individual words, you can increase your reading speed while maintaining comprehension.
Using a pointer or your finger to guide your eyes along the lines as you read can also help improve speed and focus. This technique helps prevent regression (going back to re-read previous sections) and keeps your eyes moving forward consistently.
Additionally, practicing regular reading exercises can enhance both speed and comprehension over time. Gradually increasing the difficulty level of texts and setting specific goals for reading speed can help students track their progress and motivate themselves to improve.
Mind Mapping and Visual Thinking in Accelerated Learning
In alternative schooling environments, where creativity and critical thinking are often prioritized, mind mapping has become a popular tool for organizing ideas, making connections between concepts, and enhancing overall learning experiences.
A mind map is a visual representation of information that allows learners to capture their thoughts in a non-linear way. It typically starts with a central idea or concept at the center of the map, which branches out into subtopics or related ideas. These branches then further extend into more detailed levels of information.
By using colors, images, symbols, keywords, and arrows in their mind maps, students engage both sides of their brain – the logical side for organization and structure, as well as the creative side for visualizing connections between ideas. This holistic approach enhances memory retention by creating multiple associations with the information being learned.
Furthermore, mind mapping encourages active learning by promoting engagement with the material rather than passive consumption. Students actively participate in constructing their own mental models through visualization techniques like mind mapping.
Neuroplasticity: Enhancing Alternative Education Through Brain Plasticity
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to change its structure and function throughout life in response to experiences and learning. This concept has significant implications for alternative schooling, as it suggests that our brains are not fixed entities but rather adaptable and moldable.
Alternative education approaches can leverage neuroplasticity by providing diverse and stimulating learning environments that promote brain development. By engaging students in hands-on activities, real-world problem-solving scenarios, and interdisciplinary projects, alternative schools create rich learning experiences that foster neural connections.
In addition, the use of multi-sensory teaching methods can enhance neuroplasticity. When learners engage their senses simultaneously – such as seeing, hearing, touching, or even smelling – they activate multiple areas of the brain related to those sensory inputs. This multisensory approach strengthens synaptic connections between neurons and facilitates information processing.
Alternative schools can also encourage students to step out of their comfort zones and explore new subjects or skills regularly. Challenging tasks stimulate the release of growth factors in the brain that promote neuronal connections and strengthen existing ones.
By embracing the principles of neuroplasticity within their educational practices, alternative schools have a unique opportunity to optimize students’ cognitive development and provide a solid foundation for lifelong learning.
The Impact of Music on Memory Retention in Accelerated Learning
Music has long been recognized for its ability to evoke emotions and enhance mood. In recent years, research has shown that music can also play a significant role in memory retention and cognitive function – making it an excellent tool for accelerated learning in alternative schooling settings.
Listening to instrumental music while studying or engaging with academic material improves focus by reducing distractions from external noise or internal thoughts. The absence of lyrics prevents interference with verbal processing tasks like reading comprehension or memorization.
Certain types of music have been linked specifically to improved memory retention due to their effects on brainwave activity. Baroque music compositions at approximately 60 beats per minute (BPM), such as those by composers like Bach or Handel, have been found to induce a state of relaxation and increase alpha brainwave activity. This type of brainwave pattern is associated with enhanced concentration, creativity, and memory consolidation.
Moreover, incorporating music into learning activities can make the process more enjoyable and engaging for students. Associating specific information or concepts with musical cues establishes a stronger emotional connection in memory formation.
To harness the benefits of music in accelerated learning, alternative schools can integrate music-based activities into their curriculum. These may include listening to background music during independent study time, using songs or jingles to memorize facts or formulas, or even encouraging students to create their own educational songs as a creative project.
By tapping into the power of music, alternative schools can enhance memory retention and create an optimal learning environment for students.
Gamification in Alternative Schooling: Enhancing Learning Outcomes
In recent years, gamification has gained momentum as a powerful tool for enhancing learning outcomes in various educational contexts. By integrating game elements into traditional curricula, alternative schooling environments can engage students on a deeper level while promoting active participation and intrinsic motivation.
Gamified learning experiences often incorporate features such as points systems, leaderboards, achievements/badges, challenges/quests, personalized avatars/characters, and interactive simulations. These elements provide immediate feedback and reward systems that motivate learners to progress further.
One significant advantage of gamification is its ability to foster problem-solving skills by presenting complex tasks in a playful manner. Games naturally encourage experimentation and trial-and-error approaches without fear of failure – an essential mindset for alternative education focused on fostering creativity and critical thinking abilities.
Furthermore, gamified learning experiences promote collaboration among students through multiplayer games or team-based challenges. Collaboration not only strengthens social bonds but also cultivates important interpersonal skills such as communication, empathy,
and teamwork – all highly valued traits in today’s interconnected world.
Another benefit lies in the adaptability of gamified platforms that allow educators to tailor content based on individual student needs. Personalized learning paths can be created, offering different levels of difficulty or additional support to ensure an optimal learning experience for every student.
While gamification should not replace traditional instruction entirely, it offers alternative schools a valuable tool to engage students actively and enhance their overall educational experience. By employing game elements strategically in the curriculum, alternative educators can create dynamic and immersive learning environments that foster both knowledge acquisition and skills development.
Dual Coding Theory: Enhancing Accelerated Learning with Visuals
Dual coding theory suggests that combining verbal information with visual representations enhances comprehension and memory retention. This theory has significant implications for alternative schooling as it highlights the importance of incorporating visual thinking into instructional practices.
In traditional educational settings, lectures often rely heavily on verbal explanations, leaving little room for visual aids. However, alternative schools can leverage the principles of dual coding by incorporating visuals such as diagrams, charts, infographics, videos, or mind maps into their teaching methods.
Visual aids provide learners with multiple pathways to process information. By simultaneously engaging the auditory and visual channels in the brain, students are more likely to understand complex concepts and remember them over time.
Additionally, visuals help clarify abstract ideas or complex relationships by providing concrete representations that learners can grasp more easily. For example, a diagram showing the water cycle visually conveys how evaporation leads to condensation and precipitation – a concept that might otherwise be challenging to comprehend through words alone.
Alternative schools can also encourage students to create their own visual representations of concepts as part of their learning process. This active engagement strengthens understanding while promoting creativity and critical thinking skills.
By embracing dual coding theory in their instructional strategies, alternative schools empower students to make connections between verbal and visual information effectively – leading to enhanced comprehension and accelerated learning outcomes.
The Benefits of Meditation and Mindfulness Practices for Academic Performance
Amidst increasing academic pressures faced by students today across various schooling systems including alternative education settings – meditation and mindfulness practices have emerged as powerful tools for enhancing focus, reducing stress, and improving overall academic performance.
Meditation involves training the mind to achieve a state of calm and focused awareness. Mindfulness, on the other hand, refers to intentionally paying attention to present moment experiences without judgment. Both practices have been shown to positively impact cognitive function and emotional well-being.
Research has demonstrated that regular meditation practice leads to increased gray matter density in brain regions associated with attention, memory, and learning. This structural change indicates improved neural connections within these areas – crucial for effective information processing and retention.
Furthermore, mindfulness practices help students cultivate metacognitive skills – the ability to monitor one’s own thinking processes. By developing an awareness of their thoughts and emotions during learning activities, students can better regulate their attention and stay engaged in the task at hand.
Additionally, mindfulness exercises promote emotional resilience by reducing stress levels. High-stress environments can impair cognitive functions such as memory retrieval or problem-solving abilities. By incorporating brief mindfulness breaks throughout the day or implementing dedicated mindfulness sessions into alternative schooling schedules, educators create opportunities for students’ mental well-being while optimizing their learning potential.
Alternative schools can also integrate mindful movement practices such as yoga or tai chi into their physical education programs. These activities not only improve physical fitness but also enhance body awareness and concentration – both essential elements of academic success.
By embracing meditation and mindfulness practices within alternative education settings, schools foster environments that prioritize holistic development by promoting focus,
emotional regulation,
and overall well-being among students.
Exploring the Use of Virtual Reality in Alternative Education Settings
Virtual reality (VR) technology offers exciting possibilities for enhancing learning experiences in alternative education settings. By immersing students in virtual environments that simulate real-world scenarios or abstract concepts difficult to visualize otherwise, VR provides unique opportunities for hands-on exploration and experiential learning.
For example,
In science classes,
students can explore outer space,
travel through human anatomy systems,
or observe chemical reactions from a molecular level perspective.
In history classes,
VR can transport students to historical events or ancient civilizations,
allowing them to witness firsthand the context and significance of specific time periods.
Language learners can practice conversations in realistic virtual scenarios with native speakers, improving their conversational fluency and cultural understanding.
Moreover, VR experiences offer accessibility advantages for students who may face physical or geographical limitations. By removing physical barriers, VR allows all students to engage equally in immersive learning experiences that would otherwise be challenging or impossible to access.
However, it is crucial to balance the use of VR technology with other instructional methods. Virtual reality should not replace real-world experiences but rather complement and enhance them. Alternative schools must ensure that VR activities are purposefully integrated into the curriculum and align with educational objectives while providing meaningful learning opportunities.
As virtual reality continues to evolve and become more accessible, alternative education settings have a unique opportunity to harness its potential for engaging, immersive,
and transformative learning experiences – expanding horizons beyond conventional classroom boundaries.
Nootropics and Cognitive Enhancers in Accelerated Learning
Nootropics, also known as “smart drugs” or cognitive enhancers, are substances claimed to improve cognitive functions such as memory retention, focus, creativity,
or problem-solving abilities. While their efficacy remains a topic of debate among researchers and educators alike – their potential role in accelerating learning cannot be ignored when considering alternative schooling approaches.
Some commonly used nootropics include caffeine-based stimulants like coffee or tea,
as well as supplements containing compounds such as omega-3 fatty acids,
vitamin B12,
or herbal extracts like ginkgo biloba.
Prescription medications like Modafinil have also been explored for their potential cognition-enhancing effects;
However,
it is essential
to approach the use of nootropics cautiously and responsibly within an educational context,
especially considering legal restrictions,
ethical considerations,
and potential side effects associated with these substances.
Alternative schools should prioritize a holistic approach to education that promotes overall well-being and healthy lifestyle choices.
While nootropics may offer short-term cognitive benefits,
their long-term effects and potential risks need further research.
Instead of relying solely on external substances,
alternative education settings can encourage students to adopt natural methods for optimizing brain function such as regular exercise,
adequate sleep,
a balanced diet rich in nutrients necessary for brain health,
and stress management techniques like mindfulness or meditation.
By focusing on holistic approaches to cognitive enhancement,
alternative schools create sustainable learning environments that empower students to develop effective self-regulation skills
and make informed decisions about their own well-being – key elements of lifelong learning.
The Role of Nutrition and Diet in Optimizing Brain Function for Alternative Schooling
Proper nutrition is essential for optimal brain function, making it a crucial aspect of alternative schooling strategies focused on accelerated learning. By providing students with nutrient-rich meals and emphasizing the importance of a balanced diet, alternative schools can support cognitive development and enhance academic performance.
Certain nutrients have been shown to positively impact various aspects of brain function. For example:
– Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are critical for brain health and have been linked to improved memory retention and focus.
– B vitamins (B6, B12, folate) found in whole grains, leafy greens, eggs, poultry, dairy products play a vital role in neurotransmitter synthesis – chemicals involved in communication between brain cells.
– Antioxidants found in fruits and vegetables protect the brain from oxidative stress caused by free radicals – unstable molecules that can damage cells over time.
– Complex carbohydrates from sources like whole grains provide steady glucose supply to the brain – its primary energy source.
Alternative schools should consider incorporating nutrition education into their curriculum,
teaching students about the importance of making healthy food choices
and equipping them with practical knowledge about preparing nutritious meals.
Additionally,
alternative schools can provide access to balanced meals and healthy snacks on campus,
making it easier for students to adhere to a nutrient-rich diet.
By prioritizing nutrition as a core component of their educational approach,
alternative schools can optimize brain function, positively impacting cognitive abilities, concentration levels, and overall academic performance.
Harnessing the Power of Creativity and Imagination for Accelerated Learning
Creativity and imagination play vital roles in alternative schooling environments aimed at fostering independent thinking, problem-solving skills, and innovation. By harnessing these innate human qualities effectively, educators can enhance accelerated learning outcomes among students.
Alternative schools should create an atmosphere that encourages divergent thinking – the ability to generate multiple ideas or solutions. This involves promoting open-ended assignments that allow for creative expression rather than rigidly defined tasks with only one correct answer.
Furthermore, incorporating project-based learning into the curriculum enables students to apply their creativity towards real-world problems or challenges. Such projects often require interdisciplinary collaboration, critical thinking skills, and imaginative approaches – all essential components of accelerated learning experiences.
Teachers in alternative education settings should also employ instructional strategies that stimulate imagination by connecting lessons to students’ personal experiences or interests. Storytelling techniques bring abstract concepts to life through narrative structures that engage emotions and ignite curiosity.
Visual arts like drawing or painting encourage self-expression while enhancing visual-spatial skills. Drama exercises develop communication abilities through role-playing activities that require improvisation and creative thinking on-the-spot.
Music classes foster creativity by allowing students to compose their own melodies or experiment with different instruments.
By integrating creativity-enhancing activities across various subjects,
alternative schools empower learners to think outside the box,
approach problems from unique angles,
and explore novel perspectives –
ultimately accelerating their intellectual growth
and cultivating a lifelong love for learning itself.
Utilizing Spaced Repetition Techniques to Enhance Long-Term Retention
Leave a comment