Microlearning: A Comprehensive Guide
As the world of education continues to evolve, more and more people are seeking alternative forms of learning that meet their needs and fit into their busy schedules. Microlearning has emerged as a popular option for those who want to learn on-the-go, in short bursts of time. In this article, we’ll explore what microlearning is, how it works, its benefits and drawbacks, and some tips for implementing it.
What is Microlearning?
Microlearning is an approach to education that involves breaking down complex topics into small, easily digestible chunks. It’s designed to deliver bite-sized pieces of information that can be consumed quickly and efficiently. Generally speaking, microlessons should take no longer than five minutes to complete.
The goal of microlearning is not to replace traditional forms of education but rather to supplement them. It can be used as a standalone method or combined with other approaches like blended learning or online courses.
How Does Microlearning Work?
Microlearning relies on digital technology such as videos, podcasts, infographics, interactive quizzes/games etc., which enable learners to access information anywhere anytime they have internet access from any device.
This approach typically involves creating targeted learning objects that focus on specific skills or knowledge areas. These objects may include videos explaining a concept or demonstrating a skill; interactive quizzes or games designed to reinforce knowledge; infographics presenting data in an easy-to-digest format; audio clips providing context for key concepts; simulations offering scenarios where learners can apply what they’ve learned in real-time situations etc.
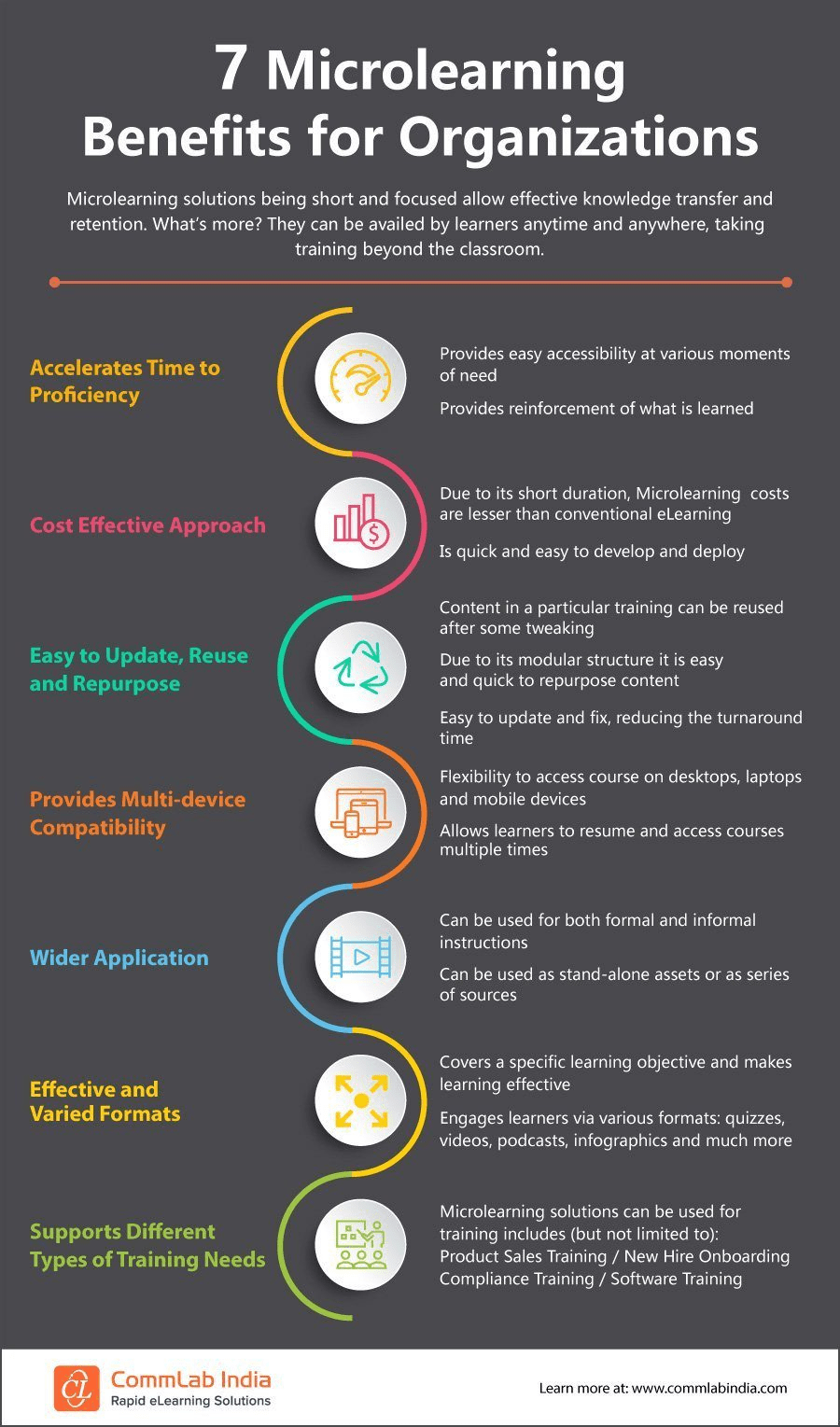
Benefits of Microlearning
1) Flexibility: One significant benefit of microlearning is its flexibility. It allows learners to consume information when they want and where they want at their own pace without being limited by location constraints since all the materials are available online 24/7 around the world through web-based Learning Management Systems (LMS).
2) Better Retention: By delivering content in smaller doses, microlearning can help learners retain more information. This is because the brain is better able to process and store short-term memories than long-term ones.
3) Improved Engagement: Microlearning often uses interactive elements such as quizzes and games that make learning fun and engaging for learners.
4) Cost-Effective: Compared to traditional forms of education, microlearning can be a cost-effective option since it requires less time, effort, and resources to develop.
5) Personalized Learning Experience: Microlearning allows learners to choose what they want to learn based on their specific needs or interests. It gives them greater control over their learning experience by enabling them to customize content according to their preferences.
Drawbacks of Microlearning
1) Limited Depth: One downside of microlearning is that it’s not designed for in-depth exploration of topics. While it’s an effective way to deliver targeted information quickly, it may not provide enough context or depth for more complex subjects.
2) Lack of Interaction with Instructors or Peers: Since microlessons are self-contained units delivered online without real-time interaction with instructors or peers, there might not be opportunities for discussions or feedback on assignments.
3) Reduced Attention Span: With so much content available online today in various formats from social media sites like Twitter where people are used 140 characters tweets maximum up until Instagram Reels which have a limit on how long videos could last; our attention spans have become shorter than ever before. As a result, some students may struggle with staying focused during longer lessons requiring deeper thinking skills despite the bite-sized nature of each lesson in micro-learning materials.
Tips for Implementing Microlearning
1) Identify Specific Learning Objectives: Before creating any learning objects, you must define your objectives first. The goals should be clear so that you can align your course material accordingly while ensuring that every topic fits into its designated objective area within the curriculum structure you are working with at the moment.
2) Use a Variety of Formats: It’s essential to deliver content in various formats, including video, audio, text-based materials, and interactive elements like quizzes or games. This approach will keep learners engaged and interested.
3) Keep Content Relevant: Microlearning works best when it’s relevant to the learner’s needs. Ensure that your content is up-to-date and reflects current trends and developments.
4) Encourage Active Learning: Since microlessons are short and focused on specific concepts or skills, it’s important to encourage active learning where students can apply what they’ve learned in practical scenarios.
5) Track Progress: Tracking progress helps both instructors and learners identify areas of strength as well as those which require further attention.
Conclusion
Microlearning is an innovative form of education that has gained popularity due to its flexibility, cost-effectiveness, personalized experience for learners while still delivering bite-sized pieces of information that can be consumed quickly. However, it may not be suitable for every learning situation since there are limitations concerning depth exploration of topics or interactions with instructors/peers during lessons’ delivery timeframes online. Still yet – by following some tips such as identifying specific learning objectives upfront; using different formats (videos/audio/texts/interactions); keeping content relevant; encouraging active participation; tracking progress – you’ll create effective micro-learning experiences for your audience!
Leave a comment