Social-emotional learning (SEL) is a process of acquiring and applying knowledge, skills, and attitudes needed for managing emotions, establishing positive relationships, making responsible decisions, and achieving personal and academic goals. SEL has become increasingly important in recent years as educators have recognized the importance of teaching children more than just academic skills.
Research has shown that students who receive social-emotional education are more successful in school and later in life. A 2017 meta-analysis of 82 studies found that students who participated in SEL programs showed an average gain of 11 percentile points on achievement tests compared to those who did not participate. Additionally, these students had improved behaviors such as better attendance rates, less disruptive behavior, and lower rates of drug use.
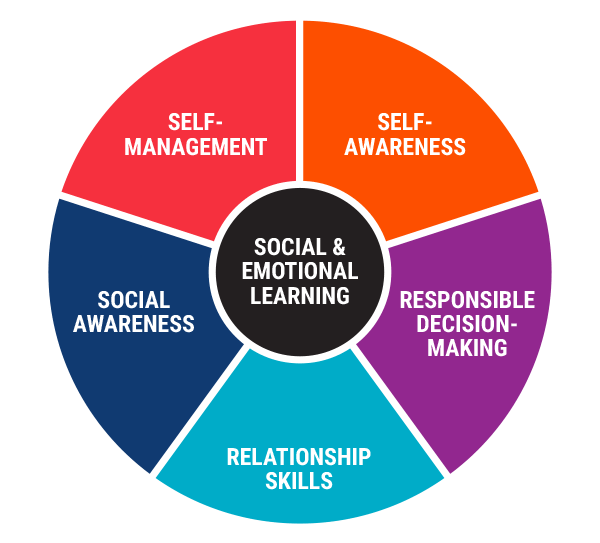
There are five core competencies that make up social-emotional learning: self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills, and responsible decision-making. Self-awareness involves understanding one’s own emotions and how they influence behavior. Self-management involves regulating these emotions effectively. Social awareness involves understanding others’ feelings and perspectives. Relationship skills involve building healthy relationships with peers and adults. Responsible decision-making involves making ethical choices based on consideration of others’ needs.
According to a report by the Collaborative for Academic, Social & Emotional Learning (CASEL), there are several key factors necessary for effective implementation of SEL programs in schools including supportive school leadership; teacher training; integration into the curriculum; family engagement; ongoing monitoring; partnering with community organizations; funding support; data collection to track progress over time.
One example of an effective SEL program is called “Second Step” which provides teachers with scripted lessons focused on empathy development through interactive classroom activities like role-playing scenarios where kids practice active listening or perspective-taking exercises which help them understand other people’s thoughts or feelings better.
Another program known as “MindUP” teaches mindfulness practices such as breathing exercises that help children calm themselves down when they’re feeling anxious or stressed. It also includes lessons on gratitude and empathy development, helping students understand the importance of treating others with kindness.
Social-emotional learning is not just important for academic success but it also correlates to improvements in mental health and overall well-being. Students who receive SEL education are less likely to suffer from depression, anxiety, or other mental health issues. Therefore, schools should prioritize social-emotional learning as an essential part of their curriculum.
In conclusion, social-emotional learning (SEL) has been shown to be a vital component of student success both academically and personally. The five core competencies – self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, relationship skills and responsible decision-making – provide students with the tools needed for managing emotions effectively while fostering healthy relationships with peers and adults alike. Effective implementation requires supportive leadership from school administrators; teacher training; integration into curricula; family involvement; ongoing monitoring; partnerships with community organizations; funding support; data collection to track progress over time. By prioritizing SEL education in our schools today we can help build better futures for tomorrow’s leaders!
Leave a comment