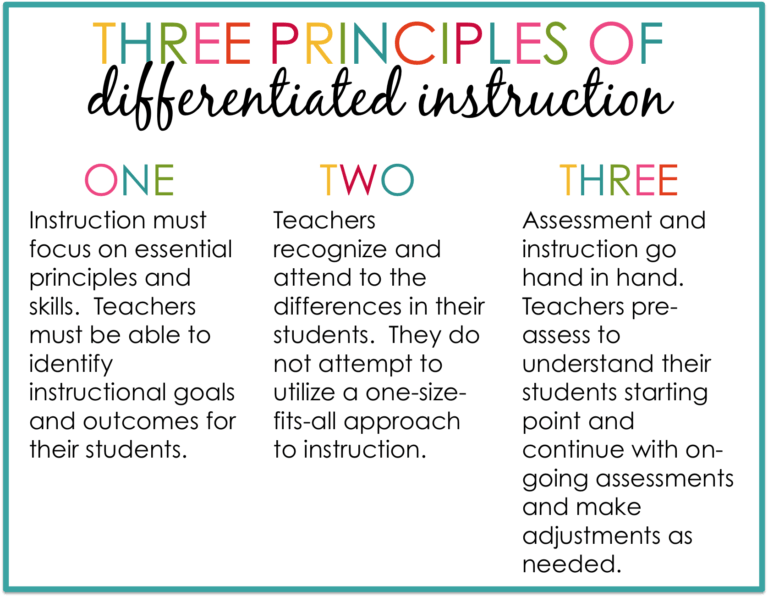
Differentiated instruction is a teaching approach that tailors the content, process, and product of learning to meet the needs of each individual student. It is a flexible method that can be applied in any classroom setting or subject area, with students of varying ages and abilities. The goal of differentiated instruction is to create an inclusive environment where every student feels valued and supported in their learning journey.
One key aspect of differentiated instruction is recognizing that students have different strengths, interests, and learning styles. Some students may learn best through visual aids or hands-on activities while others prefer reading and writing tasks. Teachers must be aware of these differences and adjust their teaching methods accordingly to ensure all students are engaged and able to learn effectively.
To implement differentiated instruction successfully, teachers need to use a variety of strategies such as flexible grouping, tiered assignments, choice boards or menus, interest-based projects, and alternative assessments. These techniques allow teachers to differentiate content by providing varied levels of difficulty or complexity based on each student’s needs.
Flexible grouping involves organizing students into small groups based on their ability level or specific needs for support. This allows teachers to provide targeted instruction for struggling learners while challenging advanced learners with more rigorous tasks.
Tiered assignments involve creating multiple versions of an assignment at different levels of difficulty so that all students can work towards the same learning objective but at their own pace and level.
Choice boards or menus give students options for completing assignments using various formats such as videos, podcasts, posters or presentations which cater specifically towards their preferred way of working.
Interest-based projects encourage students’ creativity by allowing them to pursue topics they are passionate about while also meeting academic standards set out by the teacher.
Alternative assessments include performance-based tasks like presentations or group projects rather than traditional exams which may not accurately reflect some student’s knowledge due to test anxiety issues among other factors.
Differentiated instruction benefits all types of learners including those who struggle academically as well as gifted learners. Struggling learners benefit from targeted support and individualized attention, while gifted learners are challenged through more complex tasks and projects.
Another advantage of differentiated instruction is that it promotes student engagement and motivation. When students feel they have a choice in their learning, they are more likely to be invested in the process, leading to deeper understanding and retention of information.
In addition to supporting student achievement and engagement, differentiated instruction also supports social-emotional learning by creating an inclusive classroom environment where students feel valued and supported. This helps build positive relationships between students and teachers which contribute towards their overall wellbeing.
A common misconception about differentiated instruction is that it requires excessive amounts of planning time for teachers. However, with proper training and resources such as online tools or lesson plans specifically designed for this approach educators can integrate differentiation into their teaching practices without adding undue stress or workload.
In conclusion, Differentiated Instruction is a powerful tool for meeting the diverse needs of all students in any classroom setting. It promotes inclusion, engagement, motivation while also enhancing academic achievement by allowing every learner to reach his/her full potential regardless of ability or background. Teachers who implement this approach effectively will see significant improvements in student performance along with higher levels of satisfaction from both parents/guardians as well as learners themselves!
Leave a comment