Multiple Intelligences Theory and Assessment: A Comprehensive Review
The concept of Multiple Intelligences (MI) theory was first proposed by Professor Howard Gardner in 1983. It suggests that intelligence is not a single, unified entity but rather a combination of several distinct abilities that are independent of one another. According to the theory, individuals possess different proportions of each intelligence type which can be assessed using various methods.
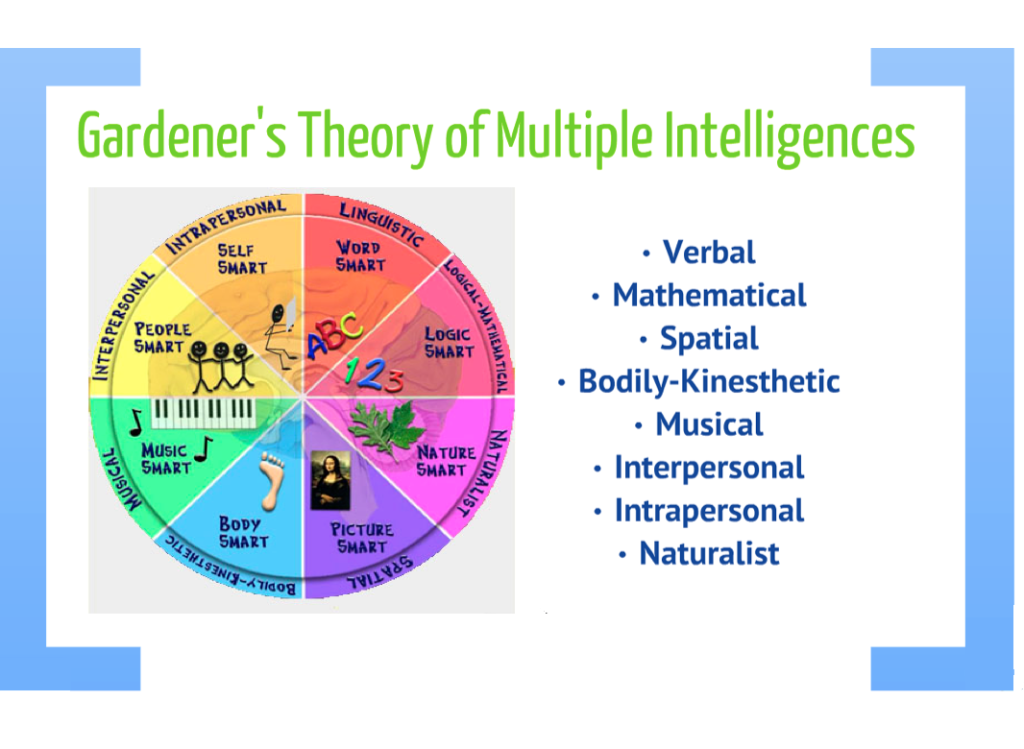
There are nine types of intelligences based on MI theory: linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, musical-rhythmic, interpersonal, intrapersonal, naturalistic and existential. Each type describes a different set of skills or talents that people use to solve problems or create products.
To assess an individual’s intelligences profile based on MI theory, there are various tools available such as questionnaires and tests. These assessments help identify the dominant intelligence types for an individual which can then be used to design education programs tailored to their strengths.
For instance, if someone has strong visual-spatial skills they might excel in art or architecture while those with high linguistic abilities may do well in journalism or writing. Similarly, those with strong interpersonal intelligence might find success in social work or counseling whereas individuals with naturalistic intelligence could thrive in fields such as botany or zoology.
Critics argue that MI has little empirical evidence supporting its claims but proponents argue it provides a more comprehensive understanding about human cognition than traditional IQ tests do. It acknowledges the importance of other forms of intellect beyond academic achievements and promotes diversity in teaching strategies.
Alternative schools often incorporate MI-based curriculums into their programs because they offer experiential learning opportunities that cater to students’ varied strengths instead of just focusing on traditional academic subjects like math and science.
In conclusion, Multiple Intelligence Theory proposes a broader definition for intelligence than traditional measures like IQ tests provide by recognizing different areas where people may excel at varying levels due to factors such as environment, genetics and life experiences. Assessments based on MI theory can help teachers create learning environments that cater to individual strengths, providing a more inclusive and diverse approach to education.
Leave a comment