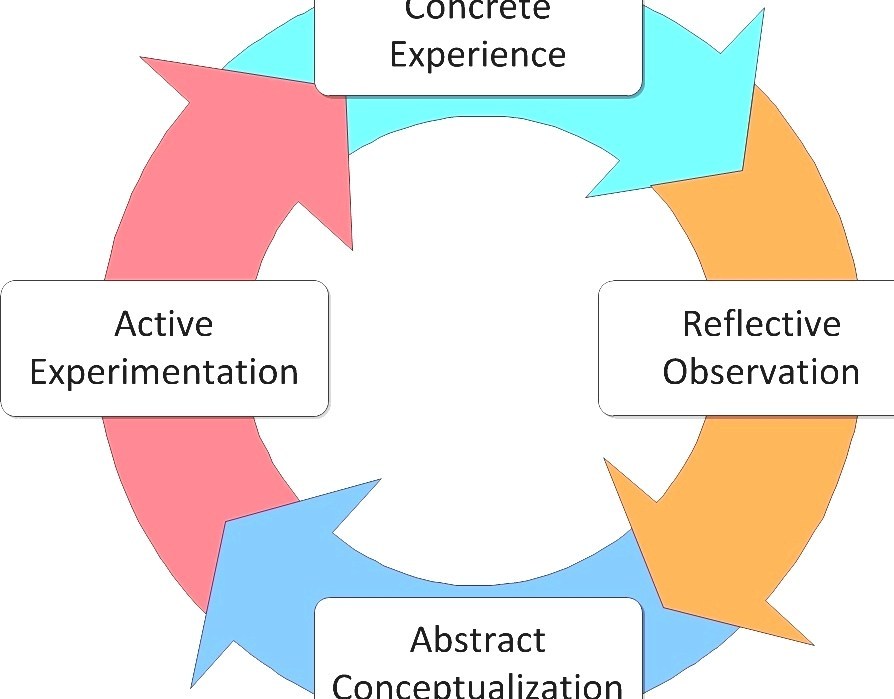
Experiential learning is a hands-on approach to education that involves actively engaging students in real-world experiences. As opposed to traditional classroom-based instruction, experiential learning encourages students to learn through direct experience, reflection, and analysis.
The concept of experiential learning has been around for centuries, with philosophers like John Dewey and Jean Piaget advocating for it as an effective way of teaching. However, it has gained renewed attention in recent years as educators look for ways to engage students and prepare them for the challenges of the 21st century.
One of the key features of experiential learning is its focus on practical skills and knowledge. Rather than simply memorizing facts or theories, students are encouraged to apply what they have learned in real-world settings. This can take many different forms depending on the subject matter – from conducting scientific experiments or building structures to participating in community service projects or internships.
Another important aspect of experiential learning is its emphasis on reflection. After completing a project or activity, students are given time to reflect on their experiences and analyze what they have learned. This process helps them develop critical thinking skills and gain a deeper understanding of how their actions impact the world around them.
There are many benefits associated with experiential learning. For one thing, it allows students to take ownership of their education by giving them control over their own learning experiences. By working collaboratively with others and taking risks outside their comfort zones, they also build confidence and resilience.
Experiential learning can also help bridge the gap between school and work by providing opportunities for students to explore potential career paths before entering the workforce. Through internships or job-shadowing programs, they can gain valuable insights into different industries while developing essential skills like communication, problem-solving, and teamwork.
In addition to these individual benefits, there are broader societal advantages associated with experiential learning as well. By engaging directly with issues facing their communities, students can become more socially aware and develop a sense of responsibility for creating positive change. This is especially important given the many complex challenges facing our world today, from climate change to social inequality.
Of course, there are also some challenges associated with implementing experiential learning in schools. For one thing, it can be difficult for teachers to find the time and resources necessary to design and implement engaging projects or activities. Additionally, assessment can be tricky since traditional methods like tests and quizzes may not accurately reflect what students have learned through hands-on experiences.
Despite these challenges, however, many educators believe that experiential learning has enormous potential to transform education for the better. By focusing on practical skills and knowledge while encouraging reflection and analysis, it provides a more holistic approach to learning that prepares students for success in all areas of life.
So how can schools begin incorporating experiential learning into their curricula? One option is to partner with community organizations or local businesses to provide opportunities for students to engage in real-world projects or internships. Another approach is to design project-based units that allow students to explore topics of interest using a variety of different tools and techniques.
Regardless of the specific strategy adopted by each school or teacher, there are several key principles that should guide any successful implementation of experiential learning. These include:
– Focusing on practical outcomes: Rather than simply imparting knowledge or theories, focus on helping students develop tangible skills they can apply outside the classroom.
– Encouraging reflection: Provide ample time for students to reflect on their experiences and analyze what they have learned.
– Providing opportunities for collaboration: Experiential learning often involves working collaboratively with others – whether peers or professionals – so make sure your curriculum includes plenty of chances for teamwork.
– Emphasizing diversity: Make sure your projects and activities are inclusive of diverse perspectives and backgrounds so all learners feel welcome.
– Incorporating technology thoughtfully: While technology can be a valuable tool for experiential learning, it should be used thoughtfully and intentionally to support learning outcomes rather than as an end in itself.
By following these principles and adapting them to meet the needs of your own students and community, you can help create a more engaging, meaningful educational experience that prepares learners for success both inside and outside the classroom.
Leave a comment