Experiential Learning: A Guide to Hands-On Education
For many years, traditional classroom learning has been the norm for students. However, as education evolves, there is a growing interest in experiential learning. Experiential learning is a teaching method that involves hands-on experiences and immersing oneself in real-world situations to gain knowledge and skills.
What is Experiential Learning?
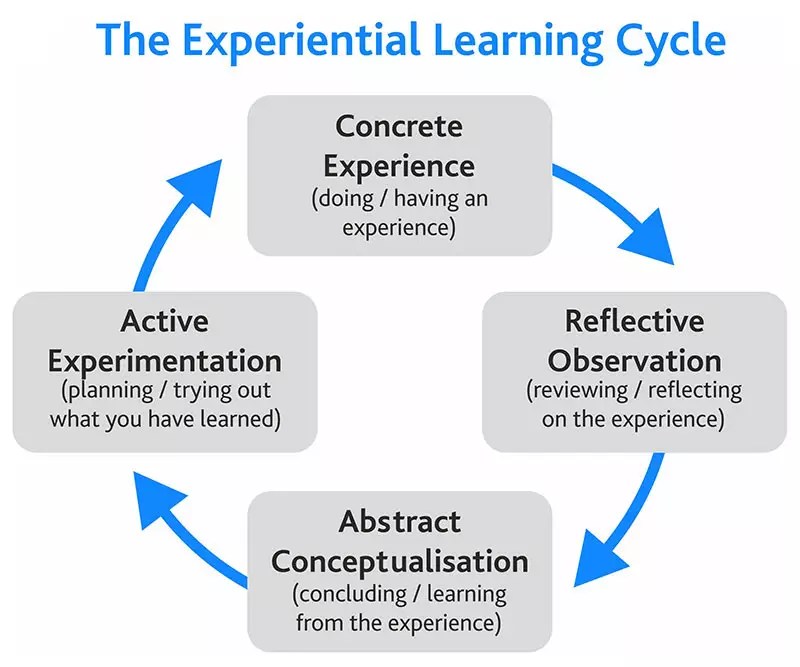
According to David Kolb’s theory of experiential learning, it is defined as “the process whereby knowledge is created through the transformation of experience.” This means that instead of solely relying on lectures or textbooks to learn new concepts, students are given opportunities to engage with the material through activities such as field trips or simulations.
Experiential learning can occur in various formats. For example, apprenticeships allow individuals to work alongside professionals in their desired field while receiving training. Service-learning projects involve volunteering for community service activities that align with academic curriculum requirements. Outdoor education provides opportunities for students to explore nature while developing problem-solving and teamwork skills.
Why Choose Experiential Learning?
The benefits of experiential learning are numerous. Firstly, it allows learners to connect theory with practice by applying what they have learned in a real-world context. This helps them retain information better than if they were just reading about it from a book.
Secondly, experiential learning fosters critical thinking skills by encouraging individuals to analyze problems and come up with solutions based on their own observations and experiences. This type of active engagement promotes creativity and innovation.
Thirdly, experiential learning enhances interpersonal communication skills by requiring collaboration among peers or mentors during group projects or internships. Students must interact effectively with others who may have differing opinions or backgrounds which helps them develop empathy and an appreciation for diversity.
Lastly, experiential learning can lead directly into career paths because it offers practical training that prepares graduates for the workforce immediately after graduation.
Examples of Experiential Learning
There are various ways to incorporate experiential learning into the classroom or outside of it. Here are some examples:
1. Service-Learning: This is a type of experiential learning that combines community service with academic coursework. Students volunteer for local organizations and apply what they learn in their classes to real-world issues.
2. Project-Based Learning: Project-based learning involves students working on long-term projects that require research, planning, and execution to solve real-world problems.
3. Apprenticeships/Internships: These programs allow students to work alongside professionals in their desired field while receiving training and mentorship.
4. Outdoor Education: Outdoor education provides opportunities for students to learn about nature through activities such as hiking, camping, or kayaking.
5. Simulations: Simulations provide an opportunity for learners to experience different scenarios in a controlled environment which helps them develop problem-solving skills.
6. Field Trips/Museum Visits: Field trips offer an opportunity for learners to observe firsthand how concepts they have learned in class apply in real-world settings such as museums or historical sites.
Summary
Experiential learning offers numerous benefits over traditional classroom instruction by providing hands-on experiences that promote critical thinking, collaboration, creativity, empathy and prepares graduates directly for the workforce.
Incorporating experiential learning into educational institutions will offer our future generation’s valuable skills beyond textbooks and lectures alone can offer!
Leave a comment